A Comprehensive Exploration of the Five Great Lakes: A Geographical and Cultural Tapestry
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Exploration of the Five Great Lakes: A Geographical and Cultural Tapestry
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Exploration of the Five Great Lakes: A Geographical and Cultural Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Exploration of the Five Great Lakes: A Geographical and Cultural Tapestry
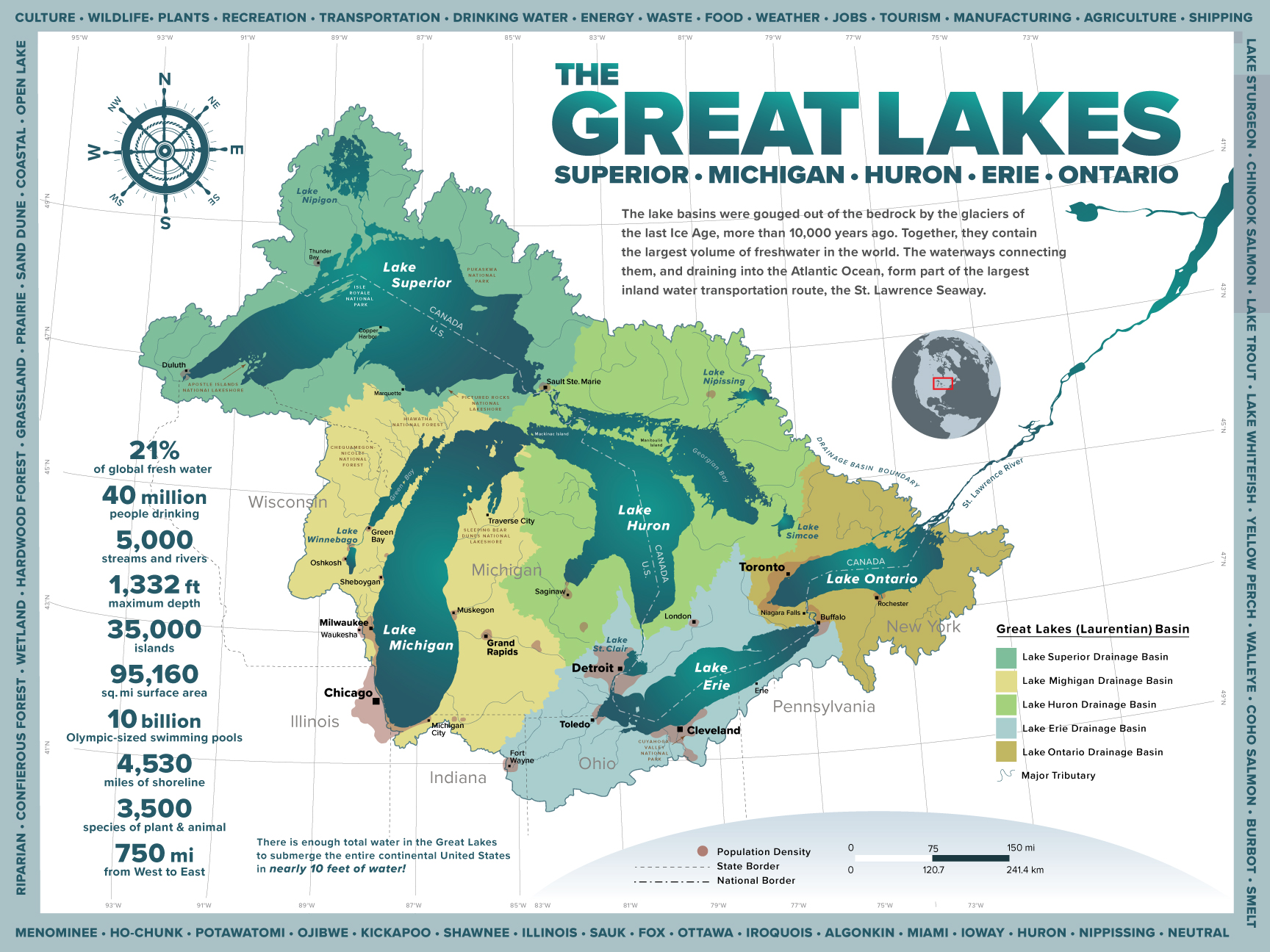
The Great Lakes, a collection of five freshwater behemoths nestled in the heart of North America, form a geographical and cultural tapestry of immense significance. This article delves into the intricacies of the Great Lakes region, examining its physical characteristics, ecological importance, historical influence, and economic contributions.
A Glimpse into the Great Lakes’ Geography
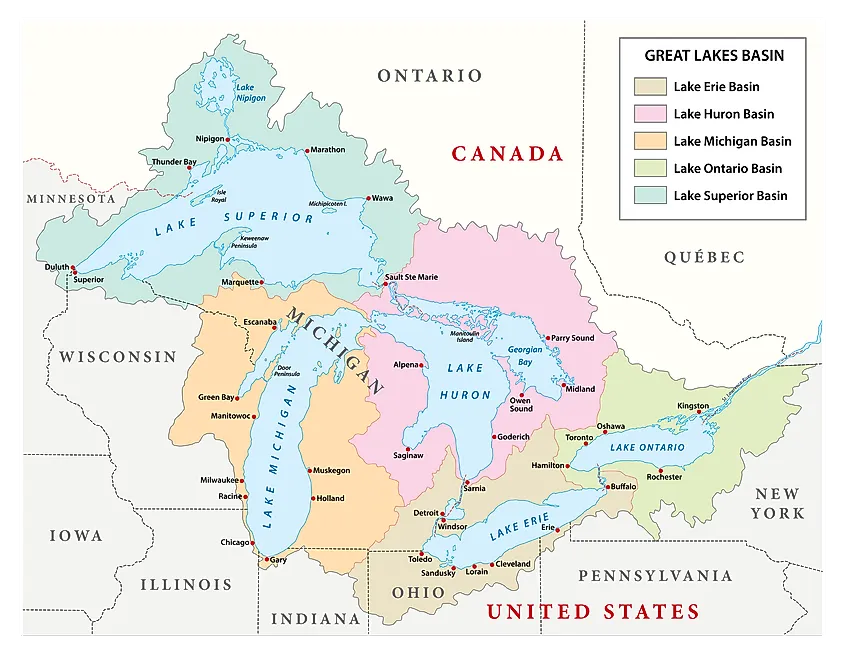
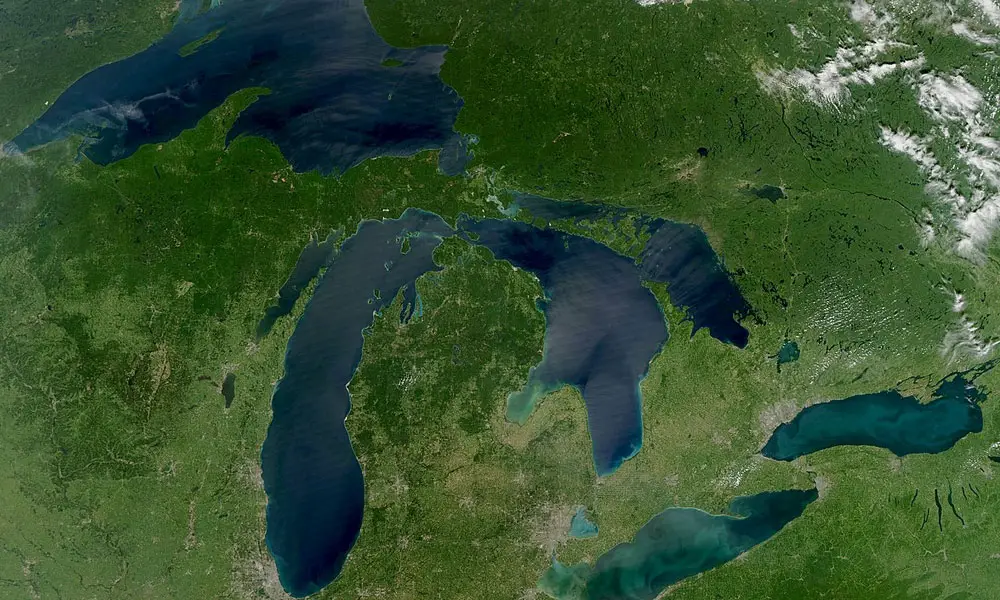
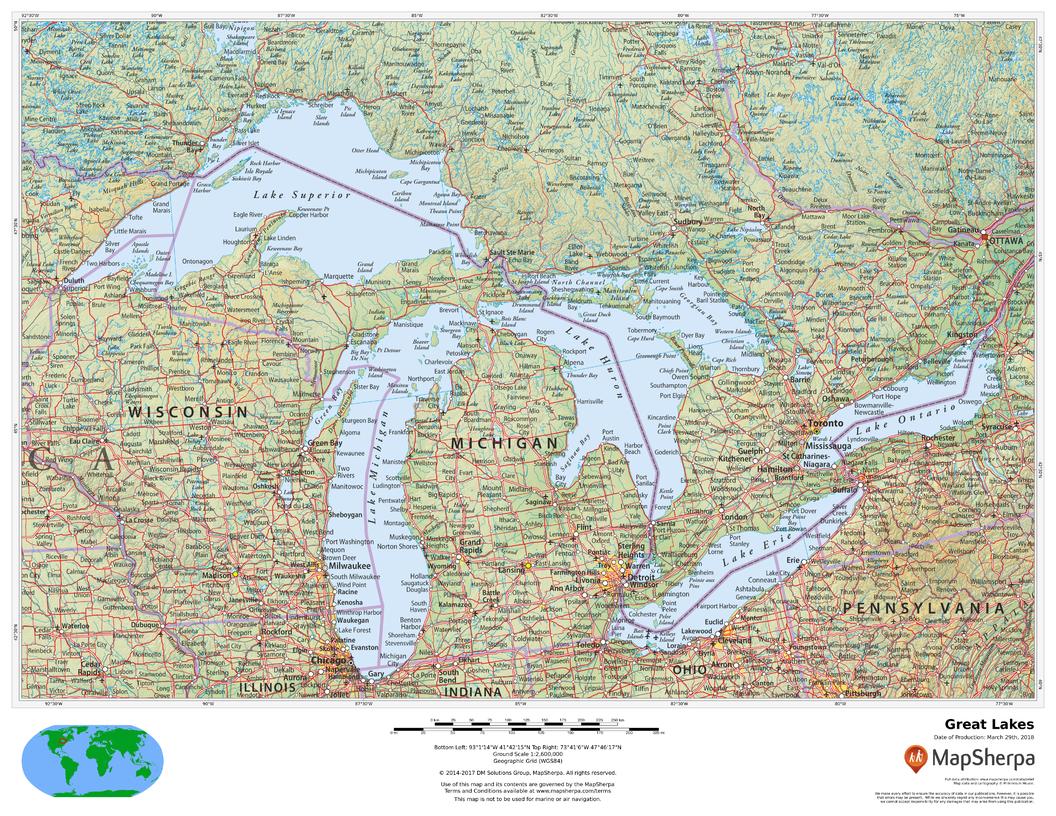
The five Great Lakes – Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario – are interconnected by a series of rivers and channels, forming a vast network of waterways. Their sheer size is staggering, encompassing over 94,000 square miles of surface area and holding nearly 20% of the world’s freshwater supply.
Superior: The King of the Great Lakes
Lake Superior, the largest and deepest of the five, boasts a surface area exceeding 31,700 square miles. Its vastness, coupled with its relatively cold and clear waters, contributes to its reputation as a "freshwater sea."
Michigan: The Second Largest
Lake Michigan, the second largest, is unique in that it is entirely within the United States. It is a popular destination for recreational activities like boating, fishing, and swimming. Its shallow waters warm quickly during the summer months, making it a haven for beachgoers.
Huron: The Third Largest
Lake Huron, the third largest, is connected to Lake Michigan by the Straits of Mackinac. Its numerous islands, including the iconic Mackinac Island, provide picturesque scenery and unique cultural experiences.
Erie: The Shallowest and Warmest
Lake Erie, the shallowest and warmest of the five, is known for its vibrant ecosystem and fertile surrounding lands. It is also a significant source of drinking water for several major cities.
Ontario: The Easternmost
Lake Ontario, the easternmost of the five, is the smallest but plays a crucial role in the St. Lawrence Seaway system, connecting the Great Lakes to the Atlantic Ocean. Its location near major urban centers like Toronto and Rochester has significantly influenced its economic development.
Ecological Significance and Challenges
The Great Lakes are not just a geographical marvel; they are also a vital ecological resource. They support a diverse array of wildlife, including fish, birds, mammals, and amphibians. The region’s wetlands and forests serve as important habitats for migratory species.
However, the Great Lakes face numerous environmental challenges, including invasive species, pollution, and climate change. Invasive species like zebra mussels and quagga mussels have had a devastating impact on native ecosystems. Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and urban development continues to threaten water quality. Climate change is impacting water levels, ice cover, and the overall health of the Great Lakes ecosystem.
Historical and Cultural Significance
The Great Lakes have played a pivotal role in shaping the history and culture of North America. For centuries, they served as vital transportation routes for indigenous peoples, who relied on the lakes for fishing, hunting, and trade. European explorers and settlers arrived in the region, drawn by the promise of abundant resources and fertile lands. The Great Lakes became a hub for the fur trade, timber industry, and later, the development of major cities like Chicago, Detroit, and Cleveland.
Economic Contributions
The Great Lakes region continues to be a major economic engine, contributing billions of dollars to the North American economy. The region is home to major industries such as manufacturing, shipping, tourism, and agriculture. The Great Lakes provide transportation corridors for goods and services, support vibrant fishing and tourism industries, and contribute to the economic well-being of surrounding communities.
FAQs about the Great Lakes
Q: What are the Great Lakes?
A: The Great Lakes are a group of five freshwater lakes located in North America: Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario.
Q: Why are the Great Lakes important?
A: The Great Lakes are significant for their ecological, historical, cultural, and economic contributions. They are a vital freshwater resource, support diverse ecosystems, and play a critical role in the region’s history and economy.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the Great Lakes?
A: The Great Lakes face challenges related to invasive species, pollution, and climate change. These issues threaten the health of the ecosystem and the well-being of the region.
Q: What are some ways to protect the Great Lakes?
A: Protecting the Great Lakes requires a multifaceted approach, including reducing pollution, managing invasive species, mitigating the effects of climate change, and promoting sustainable practices.
Tips for Visiting the Great Lakes
1. Explore the Diverse Landscapes: The Great Lakes region offers a variety of landscapes to explore, from sandy beaches and towering cliffs to lush forests and rolling hills.
2. Experience the Local Culture: Each Great Lakes city and town has its unique character and charm. Engage with local communities, sample regional cuisine, and immerse yourself in the region’s cultural heritage.
3. Enjoy Water-Based Activities: The Great Lakes offer endless opportunities for water-based activities, including boating, fishing, swimming, and kayaking.
4. Embrace the Outdoors: The Great Lakes region is a paradise for outdoor enthusiasts. Hike through scenic trails, camp under the stars, and enjoy the beauty of nature.
5. Learn about the Region’s History: Visit historical sites and museums to learn about the rich history and cultural heritage of the Great Lakes.
Conclusion
The Great Lakes are a testament to the power and beauty of nature. Their vastness, ecological significance, historical importance, and economic contributions make them a vital part of the North American landscape. Understanding the intricacies of the Great Lakes region, its challenges, and its potential for sustainable development is crucial for ensuring its continued well-being for generations to come.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Exploration of the Five Great Lakes: A Geographical and Cultural Tapestry. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!