A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Biomes: Understanding the Continent’s Ecological Tapestry
Related Articles: A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Biomes: Understanding the Continent’s Ecological Tapestry
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Biomes: Understanding the Continent’s Ecological Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Biomes: Understanding the Continent’s Ecological Tapestry
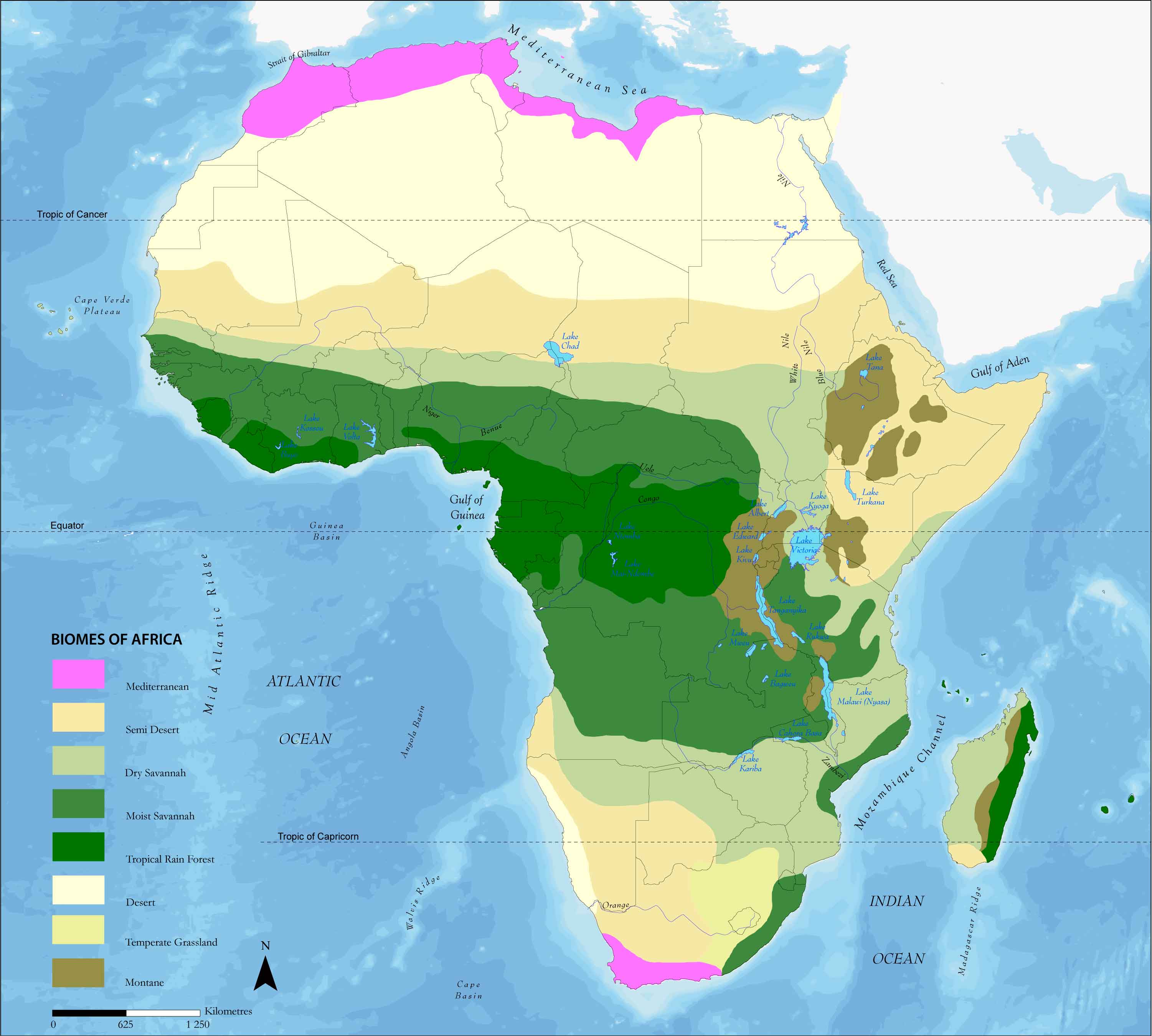
Africa, the second-largest continent, boasts a remarkable diversity of landscapes and ecosystems, collectively known as biomes. These distinct biological communities, shaped by climate, geography, and the interplay of living organisms, are crucial for understanding the continent’s rich biodiversity and the challenges it faces. A biomes map of Africa provides a visual representation of these intricate ecosystems, revealing their unique characteristics and distribution across the vast terrain.
Understanding Biomes in Africa: A Geographic and Ecological Perspective
Biomes in Africa are categorized based on factors such as temperature, precipitation, and vegetation. Each biome possesses a unique set of plant and animal species adapted to thrive under specific environmental conditions. This section delves into the major biomes found in Africa, exploring their defining features, characteristic species, and ecological significance.
1. Tropical Rainforests: Lush Green Canopies and Abundant Life
- Location: Equatorial regions, primarily in Central and West Africa.
- Characteristics: High rainfall, consistently warm temperatures, dense vegetation with multiple layers, high biodiversity.
- Key Species: Gorillas, chimpanzees, leopards, elephants, numerous bird species, diverse insects, and a vast array of plants.
- Ecological Significance: Crucial carbon sinks, vital for regulating global climate, contribute significantly to biodiversity, provide numerous ecosystem services.
2. Savannas: A Mosaic of Grasslands and Scattered Trees
- Location: Large parts of East, Central, and Southern Africa.
- Characteristics: Warm temperatures, seasonal rainfall, grasslands interspersed with trees, frequent wildfires.
- Key Species: Lions, elephants, giraffes, zebras, wildebeest, numerous bird species, insects, and reptiles.
- Ecological Significance: Support large herbivore populations, play a vital role in nutrient cycling, provide grazing lands for livestock, contribute to carbon sequestration.
3. Deserts: Harsh Environments with Remarkable Adaptations
- Location: Northern and Southern Africa, including the Sahara, Namib, and Kalahari Deserts.
- Characteristics: Extremely low rainfall, high temperatures, sparse vegetation, arid conditions.
- Key Species: Camels, desert foxes, scorpions, reptiles, specialized plants adapted to water conservation.
- Ecological Significance: Unique ecosystems with specific adaptations, contribute to global sand and dust cycles, provide habitat for specialized species.
4. Mediterranean Woodlands and Shrublands: A Blend of Temperate and Arid Influences
- Location: Coastal regions of North Africa, specifically the Maghreb region.
- Characteristics: Mild, wet winters, hot, dry summers, diverse vegetation including evergreen trees and shrubs.
- Key Species: Barbary macaques, fennec foxes, gazelles, diverse bird species, and a variety of plants.
- Ecological Significance: Important for biodiversity, provide valuable ecosystem services such as soil conservation, water regulation, and carbon sequestration.
5. Montane Forests: High-Altitude Ecosystems with Unique Adaptations
- Location: Mountain ranges in East and Central Africa, including the Ethiopian Highlands and the Rwenzori Mountains.
- Characteristics: Cool temperatures, high rainfall, diverse vegetation with distinct altitudinal zones.
- Key Species: Mountain gorillas, colobus monkeys, birds of prey, unique plant species adapted to cold climates.
- Ecological Significance: Important for biodiversity conservation, provide vital water resources, contribute to carbon sequestration.
6. Wetlands: Diverse Ecosystems at the Interface of Land and Water
- Location: Throughout Africa, including rivers, lakes, swamps, and coastal areas.
- Characteristics: High water availability, fluctuating water levels, diverse vegetation including reeds, grasses, and trees.
- Key Species: Hippopotamuses, crocodiles, waterbirds, fish, and various invertebrates.
- Ecological Significance: Important for biodiversity, water purification, flood control, and carbon sequestration.
7. Coastal Zones: Dynamic Ecosystems Shaped by Ocean Influences
- Location: Along Africa’s vast coastline, including the Atlantic, Indian, and Mediterranean coasts.
- Characteristics: Diverse habitats including beaches, dunes, estuaries, and mangroves.
- Key Species: Sea turtles, dolphins, whales, various fish species, seabirds, and mangrove-associated organisms.
- Ecological Significance: Provide important breeding grounds for marine species, protect coastlines from erosion, contribute to carbon sequestration.
The Importance of Understanding Africa’s Biomes
Beyond their inherent ecological value, understanding Africa’s biomes is crucial for addressing various challenges facing the continent:
- Conservation and Biodiversity: Biomes provide habitat for a vast array of species, many of which are threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and climate change. Understanding these ecosystems is essential for developing effective conservation strategies.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Biomes play a vital role in regulating the global climate. Understanding their role in carbon sequestration and climate regulation is crucial for developing sustainable solutions to climate change.
- Sustainable Development: Biomes provide essential ecosystem services such as water purification, soil fertility, and pollination. Understanding these services is crucial for developing sustainable development strategies that do not compromise ecological integrity.
- Human Well-being: Biomes provide numerous benefits for human populations, including food, medicine, and cultural resources. Understanding these benefits is essential for ensuring sustainable use and equitable access to these resources.
FAQs on Biomes in Africa Map
1. What are the main factors that influence biome distribution in Africa?
The distribution of biomes in Africa is primarily influenced by climate, including temperature, precipitation, and seasonality. Topography, soil type, and human activities also play significant roles.
2. What are the threats to Africa’s biomes?
Africa’s biomes face numerous threats, including habitat loss due to deforestation, agriculture, and urbanization, climate change, poaching, pollution, and invasive species.
3. How can we protect Africa’s biomes?
Protecting Africa’s biomes requires a multi-faceted approach including establishing protected areas, promoting sustainable land use practices, addressing climate change, combating poaching, and raising public awareness about the importance of biodiversity.
4. What is the role of biomes in carbon sequestration?
Biomes, particularly forests, play a crucial role in carbon sequestration, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in plant biomass and soil.
5. How does the biomes map of Africa help us understand the continent’s biodiversity?
The biomes map provides a visual representation of the distribution of different ecosystems, revealing the richness and diversity of plant and animal life across Africa.
Tips for Understanding Biomes in Africa
- Explore online resources: Websites such as the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) provide detailed information on Africa’s biomes.
- Use interactive maps: Online mapping tools like Google Earth and ArcGIS allow you to explore the biomes map of Africa in detail.
- Visit protected areas: Visiting national parks and other protected areas provides a firsthand experience of Africa’s diverse biomes.
- Support conservation efforts: Contribute to organizations working to protect Africa’s biomes by donating, volunteering, or advocating for conservation policies.
Conclusion
The biomes map of Africa offers a fascinating glimpse into the continent’s ecological tapestry, showcasing the remarkable diversity of life that thrives across its vast landscapes. Understanding these ecosystems is crucial for promoting conservation, mitigating climate change, and ensuring sustainable development in Africa. By appreciating the interconnectedness of life within these biomes, we can contribute to their preservation and ensure a vibrant future for Africa’s biodiversity.

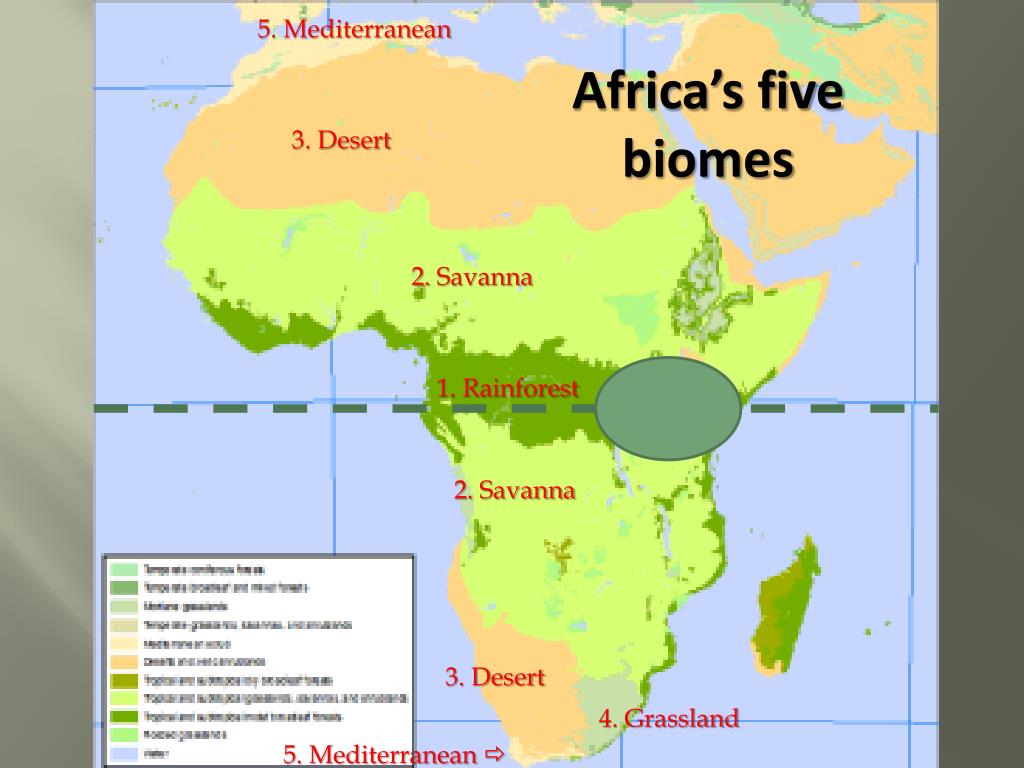


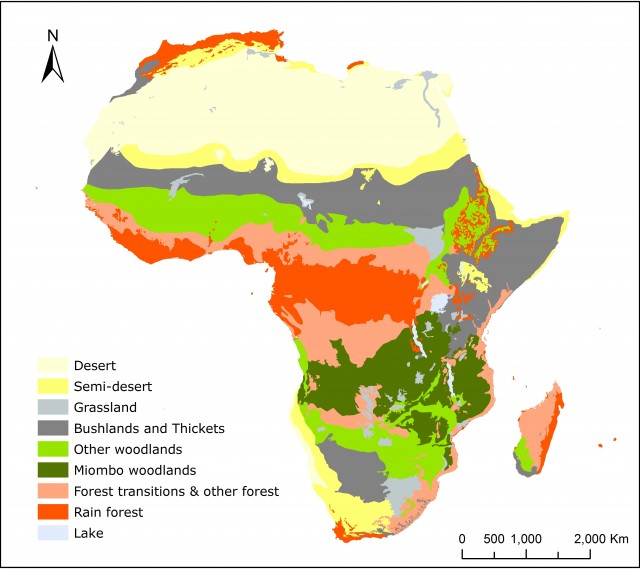

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Africa’s Diverse Biomes: Understanding the Continent’s Ecological Tapestry. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!