A Shifting Landscape: Tracing the History of Israel’s Map
Related Articles: A Shifting Landscape: Tracing the History of Israel’s Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Shifting Landscape: Tracing the History of Israel’s Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Shifting Landscape: Tracing the History of Israel’s Map
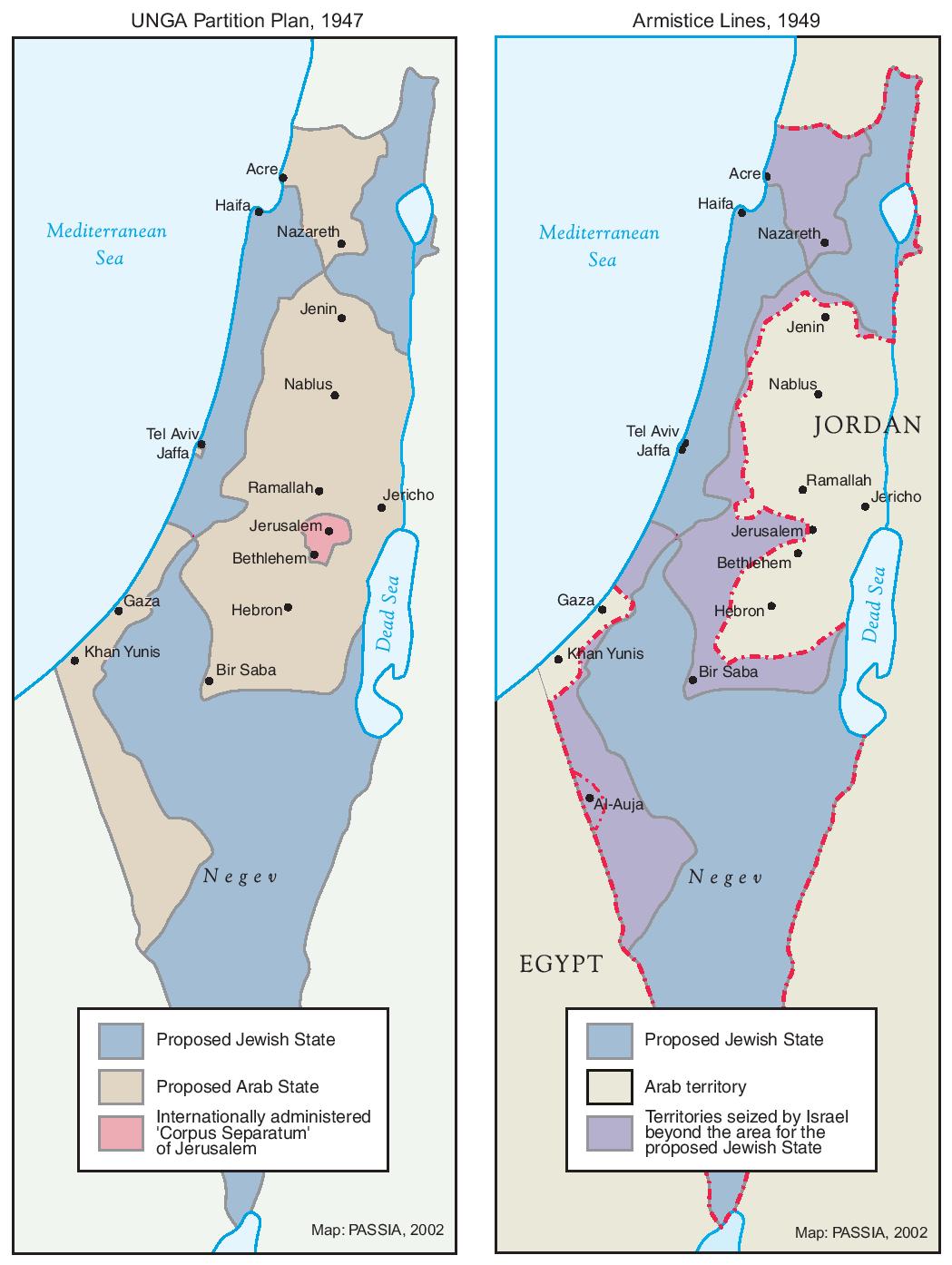
The map of Israel, a small nation nestled in the turbulent Middle East, reflects a complex and often contentious history. Its borders, a constant source of dispute and negotiation, have shifted dramatically over the centuries, mirroring the changing tides of power and the enduring struggle for control of this strategically vital region.
From Ancient Kingdoms to Roman Rule:
The story of Israel’s map begins with the ancient Israelites, who established their kingdom in the land of Canaan around 1000 BCE. This period, documented in the Hebrew Bible, saw the rise and fall of various Israelite kingdoms, ultimately leading to the Babylonian exile in the 6th century BCE. After the return from exile, the region was ruled by the Persian Empire, followed by the Hellenistic Seleucid dynasty.
During the Roman period, the land was incorporated into the Roman province of Judea, with Jerusalem becoming a significant city. The Jewish revolt against Roman rule in 66 CE led to the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE and the dispersal of Jews throughout the Roman Empire. The land was then divided into Roman provinces, with the name "Israel" fading into the historical record.
The Rise of Islam and the Ottoman Empire:
Following the decline of the Roman Empire, the region fell under the control of the Byzantine Empire, followed by the Arab conquest in the 7th century CE. The land became part of the Islamic caliphates, with Jerusalem gaining prominence as a holy city for both Muslims and Christians.
During the Crusades, European Christians attempted to wrest control of the Holy Land from the Muslims, but their efforts were ultimately unsuccessful. In the 16th century, the Ottoman Empire conquered the region, and it remained under Ottoman rule for centuries.
Zionism and the British Mandate:
The late 19th century witnessed the rise of Zionism, a movement advocating for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine. This movement, fueled by the growing antisemitism in Europe and the desire for a safe haven for Jews, gained momentum as the century progressed.
Following World War I, the Ottoman Empire collapsed, and the League of Nations granted Britain a mandate over Palestine. The British, tasked with creating a "national home for the Jewish people" while also safeguarding the rights of the existing Arab population, found themselves caught in a difficult position. The growing tension between the two communities resulted in numerous clashes and ultimately led to the creation of the State of Israel in 1948.
The 1948 War and the Birth of Israel:
The 1948 Arab-Israeli War, a conflict that erupted following the UN’s partition plan, marked a dramatic turning point in the history of Israel’s map. Israel emerged victorious, expanding its territory beyond the proposed partition boundaries. The war also resulted in the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinian Arabs, known as the "Nakba," and the creation of refugee camps in neighboring countries.
The 1967 War and the Occupied Territories:
The 1967 Six-Day War, a conflict sparked by a series of escalating tensions, saw Israel capture the Sinai Peninsula from Egypt, the West Bank from Jordan, and the Golan Heights from Syria. This expansion of territory significantly altered the map of Israel, adding a new dimension to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
The Oslo Accords and the Quest for Peace:
In the early 1990s, the Oslo Accords, a series of agreements between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), aimed to create a two-state solution, with an independent Palestinian state existing alongside Israel. However, the peace process stalled, and the Israeli-Palestinian conflict continues to be a source of tension and violence in the region.
The Current Landscape and Ongoing Challenges:
Today, the map of Israel remains a subject of ongoing debate and conflict. The Israeli government maintains control over the occupied territories, while Palestinian authorities govern parts of the West Bank. The status of Jerusalem, a holy city for Jews, Muslims, and Christians, remains a particularly sensitive issue.
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict, a complex and multifaceted issue, involves competing claims to land, religious sites, and national identity. The search for a lasting solution remains elusive, with both sides facing numerous challenges and obstacles.
FAQs about the History of Israel’s Map:
1. What is the significance of the 1948 Arab-Israeli War in the history of Israel’s map?
The 1948 war resulted in the establishment of the State of Israel and the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians. It also significantly altered the map of Israel, expanding its territory beyond the proposed UN partition plan.
2. What are the occupied territories, and why are they controversial?
The occupied territories refer to the West Bank, East Jerusalem, the Golan Heights, and the Sinai Peninsula, captured by Israel in the 1967 Six-Day War. They are controversial because they are claimed by Palestinians and are subject to international legal disputes.
3. What are the Oslo Accords, and what impact did they have on the map of Israel?
The Oslo Accords were a series of agreements aimed at creating a two-state solution, with an independent Palestinian state existing alongside Israel. They led to the establishment of the Palestinian Authority and the transfer of some administrative control over the West Bank to the Palestinians.
4. What is the status of Jerusalem in the history of Israel’s map?
Jerusalem is a holy city for Jews, Muslims, and Christians, and its status is a highly sensitive issue. Both Israelis and Palestinians claim Jerusalem as their capital, and the city’s future remains a major obstacle to peace.
5. What are the ongoing challenges to achieving a lasting peace in the region?
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict is a complex and multi-layered issue involving competing claims to land, religious sites, and national identity. Ongoing challenges include the settlement expansion in the West Bank, the status of Jerusalem, and the lack of trust between the two sides.
Tips for Understanding the History of Israel’s Map:
- Study the key events and dates that shaped the map of Israel. Understanding the historical context is crucial for comprehending the current situation.
- Explore different perspectives on the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Reading accounts from both Israelis and Palestinians can provide a more nuanced understanding of the complexities involved.
- Engage with primary sources, such as historical documents and maps. These sources can offer a direct glimpse into the past and provide valuable insights into the evolution of the map.
- Consider the impact of international actors and global events on the history of Israel’s map. The involvement of the League of Nations, the United Nations, and various countries has played a significant role in shaping the region’s political landscape.
- Recognize the human cost of conflict and the importance of seeking peaceful solutions. The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has caused immense suffering and displacement, highlighting the need for dialogue and reconciliation.
Conclusion:
The history of Israel’s map is a testament to the enduring struggle for control of a strategically vital region. The shifting borders, fueled by wars, political negotiations, and the clash of competing narratives, have left a lasting impact on the lives of Israelis and Palestinians alike. Understanding this complex history is essential for grasping the current challenges and opportunities for peace in the region. While the future of Israel’s map remains uncertain, the quest for a lasting solution requires a commitment to dialogue, compromise, and a shared vision for a peaceful and prosperous future for all.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Shifting Landscape: Tracing the History of Israel’s Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!