A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding Oklahoma’s Native American Tribes
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding Oklahoma’s Native American Tribes
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding Oklahoma’s Native American Tribes. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding Oklahoma’s Native American Tribes
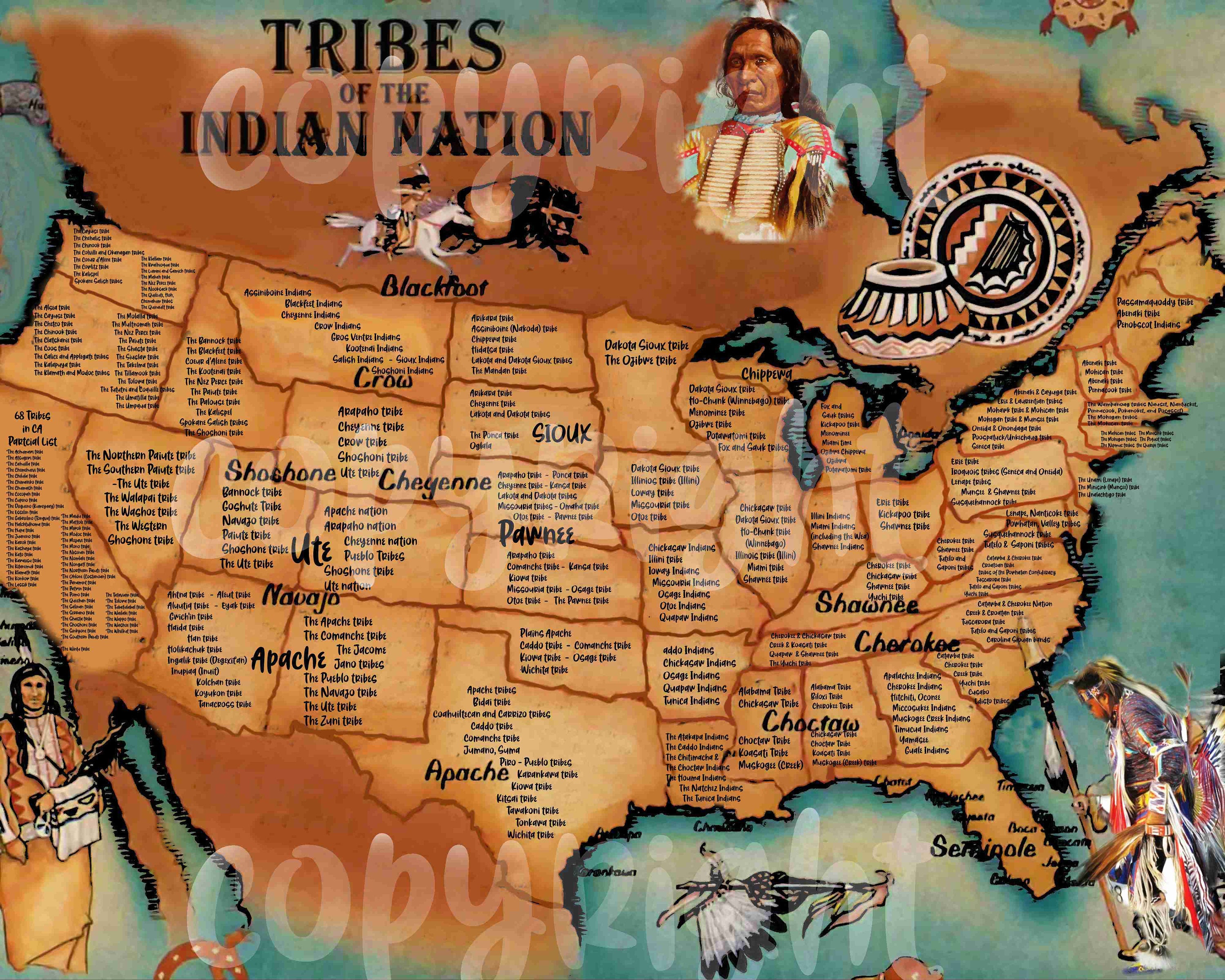
Oklahoma, often referred to as the "Sooner State," holds a rich history deeply intertwined with its indigenous populations. The state is home to 39 federally recognized tribes, each with a unique cultural heritage, language, and traditions. These tribes, representing diverse linguistic families and historical experiences, have left an indelible mark on Oklahoma’s landscape, economy, and cultural identity.
A Diverse Landscape of Tribes:
Oklahoma’s tribal map is a vibrant tapestry, showcasing the diversity of Native American cultures within the state. Some of the prominent tribes include:
-
Five Civilized Tribes: The Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek (Muscogee), and Seminole nations, known collectively as the "Five Civilized Tribes," were forcibly relocated to Oklahoma during the Trail of Tears. Their rich cultural heritage, including their languages, art forms, and governance structures, has endured despite the hardships they faced.
-
Other Major Tribes: The Osage Nation, renowned for its oil wealth, maintains a strong tribal government and cultural identity. The Kiowa, Comanche, and Apache tribes, historically known for their equestrian skills and nomadic lifestyle, have retained their traditions and languages. The Caddo Nation, with its deep roots in the region, continues to practice its traditional crafts and ceremonies.
-
Smaller Tribes: Numerous smaller tribes, such as the Pawnee, Ponca, and Otoe-Missouria, have also made Oklahoma their home. These tribes, despite their smaller population sizes, play a vital role in preserving their cultural legacies and contributing to the state’s cultural richness.
The Significance of the Tribal Map:
The Oklahoma tribal map serves as a visual representation of the state’s indigenous history and the ongoing presence of Native American communities. It highlights the following key points:
-
Historical Significance: The map serves as a reminder of the forced relocation of Native American tribes from their ancestral lands, known as the Trail of Tears. This event, a tragic chapter in American history, continues to shape the lives of Native Americans today.
-
Cultural Diversity: The map showcases the rich diversity of Native American cultures in Oklahoma. Each tribe possesses unique traditions, languages, and beliefs, contributing to the state’s cultural mosaic.
-
Political and Economic Power: The map underscores the political and economic power of Native American tribes in Oklahoma. Tribal governments have jurisdiction over their lands and resources, playing a significant role in the state’s economy.
-
Land Rights and Sovereignty: The map emphasizes the importance of tribal sovereignty and land rights. Native American tribes hold inherent rights to their lands and resources, which are recognized by the federal government.
Benefits of Understanding the Tribal Map:
Understanding the Oklahoma tribal map offers numerous benefits, including:
-
Appreciating Cultural Diversity: It fosters a deeper appreciation for the rich cultural heritage of Native American tribes in Oklahoma, promoting cross-cultural understanding and respect.
-
Promoting Historical Awareness: It sheds light on the history of Native Americans in Oklahoma, fostering awareness of the Trail of Tears and its lasting impact.
-
Strengthening Tribal-State Relations: It helps build stronger relationships between Native American tribes and the state government, promoting collaboration and mutual understanding.
-
Supporting Economic Development: It highlights the economic contributions of Native American tribes in Oklahoma, promoting investment and economic growth in tribal communities.
FAQs about Oklahoma’s Native American Tribes:
Q: How many federally recognized tribes are in Oklahoma?
A: There are 39 federally recognized tribes in Oklahoma.
Q: What is the largest tribe in Oklahoma?
A: The Cherokee Nation is the largest tribe in Oklahoma, with a population of over 300,000.
Q: What are the "Five Civilized Tribes"?
A: The "Five Civilized Tribes" are the Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek (Muscogee), and Seminole nations. They were forcibly relocated to Oklahoma during the Trail of Tears.
Q: What is the significance of tribal sovereignty?
A: Tribal sovereignty is the inherent right of Native American tribes to govern themselves and their lands. This right is recognized by the federal government.
Q: How do tribal governments operate in Oklahoma?
A: Tribal governments in Oklahoma have their own constitutions, laws, and courts. They govern their lands, resources, and citizens.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing Native American tribes in Oklahoma?
A: Some of the challenges facing Native American tribes in Oklahoma include poverty, lack of access to healthcare, and substance abuse.
Tips for Learning More about Oklahoma’s Native American Tribes:
-
Visit tribal museums and cultural centers: These institutions offer insights into the history, culture, and art of Oklahoma’s Native American tribes.
-
Attend tribal events and festivals: Participating in these events provides a firsthand experience of Native American traditions and culture.
-
Read books and articles about Native American history and culture: Engaging with these resources helps deepen understanding and appreciation of Native American heritage.
-
Support Native American-owned businesses: Patronizing these businesses contributes to the economic well-being of tribal communities.
Conclusion:
Oklahoma’s Native American tribes are an integral part of the state’s history, culture, and identity. Understanding the Oklahoma tribal map provides a valuable lens for appreciating the rich diversity of Native American cultures, recognizing the historical significance of the Trail of Tears, and acknowledging the importance of tribal sovereignty and land rights. By engaging with the map and learning more about these tribes, we can foster a deeper understanding and appreciation for the vibrant tapestry of cultures that makes Oklahoma truly unique.
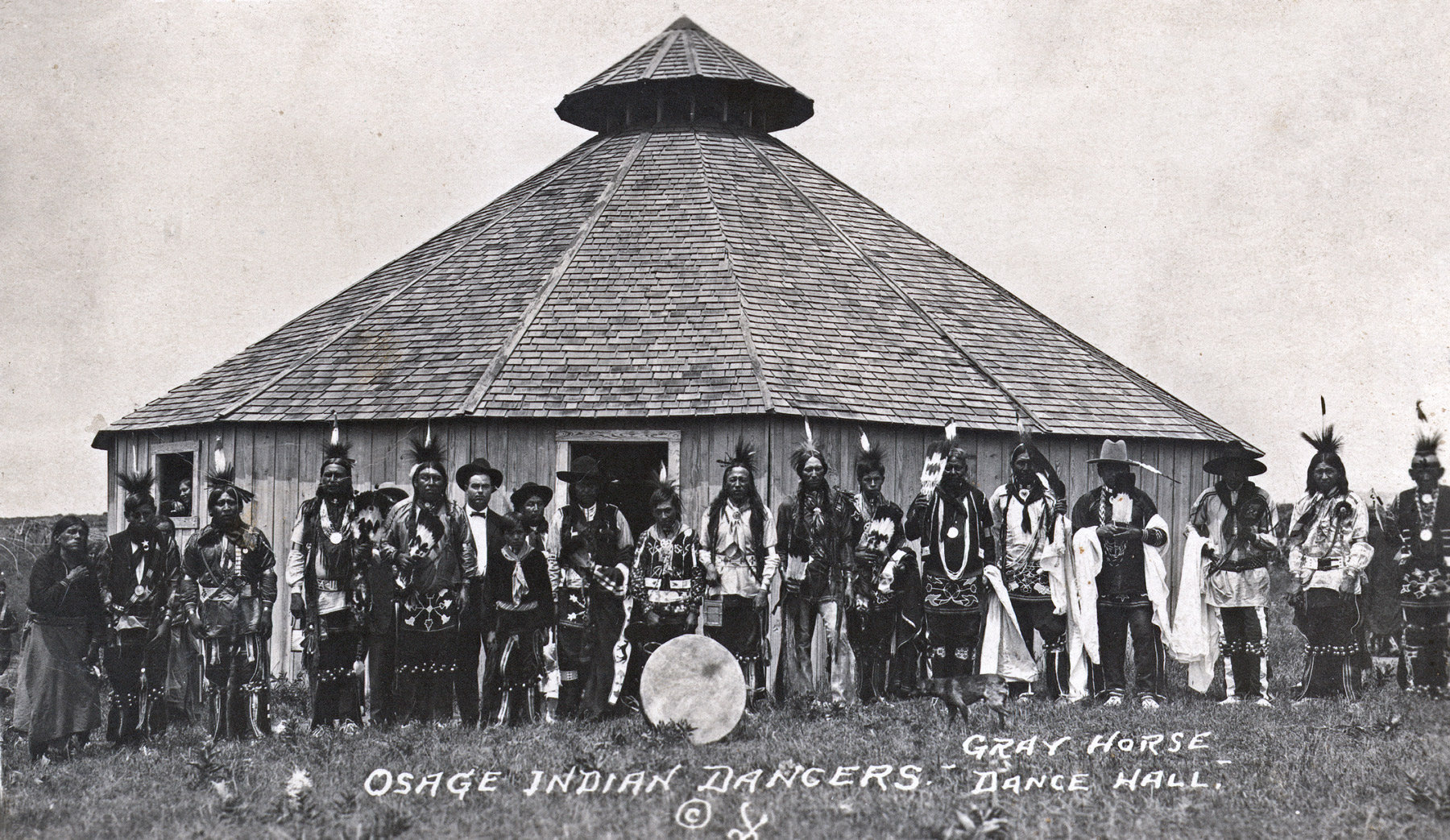






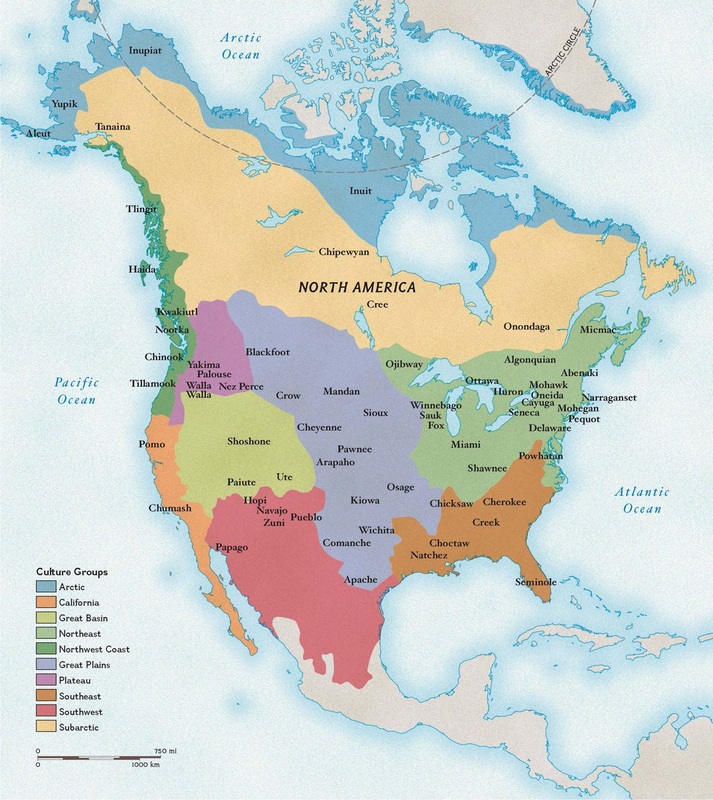
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Cultures: Understanding Oklahoma’s Native American Tribes. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!