A Visual Guide to Nuclear Power in the United States: Understanding the Map
Related Articles: A Visual Guide to Nuclear Power in the United States: Understanding the Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Visual Guide to Nuclear Power in the United States: Understanding the Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Visual Guide to Nuclear Power in the United States: Understanding the Map
![U.S. Nuclear Power Plants and Production by State [1650x1275] : r/MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/IabWt3J8zmHtcCP04mPXZQaKuufPN2t7tvlvUtSatUU.png?auto=webpu0026s=1975186631472d884266d7203a43a2c315d85930)
The United States, a nation with a diverse energy landscape, relies on nuclear power as a significant source of electricity. Understanding the distribution and operation of nuclear reactors across the country requires a visual representation. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the nuclear reactors us map, exploring its significance, benefits, and the factors influencing its current state.
The Map: A Snapshot of Nuclear Power in the U.S.
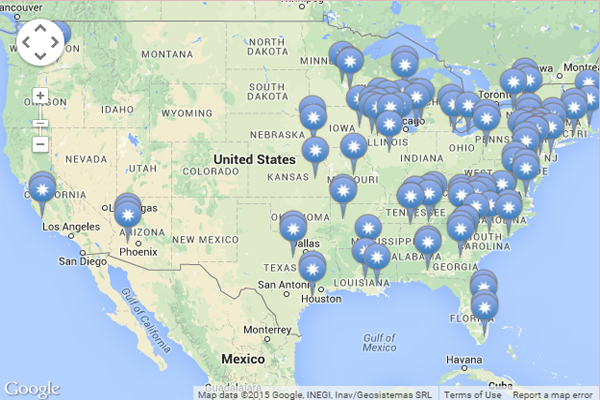
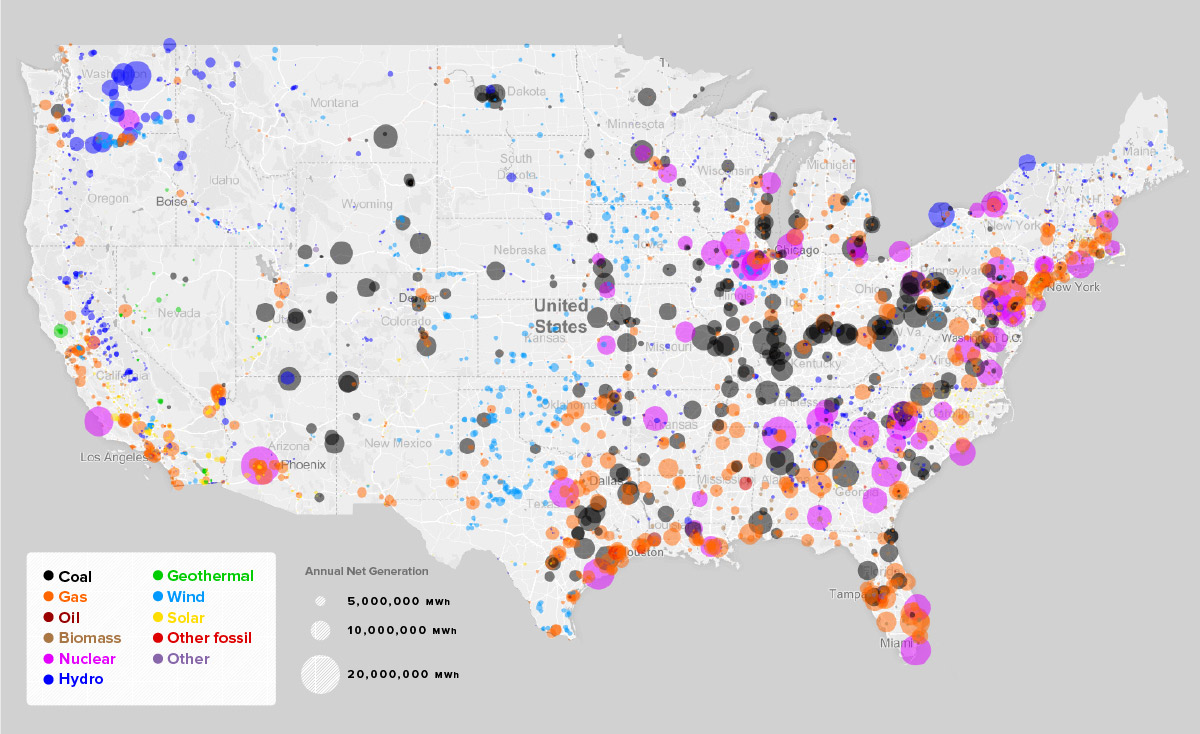
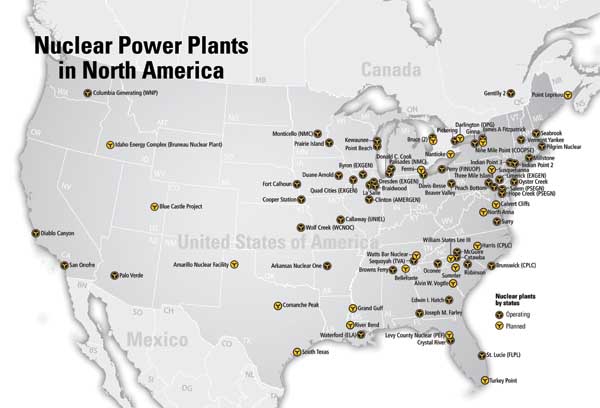
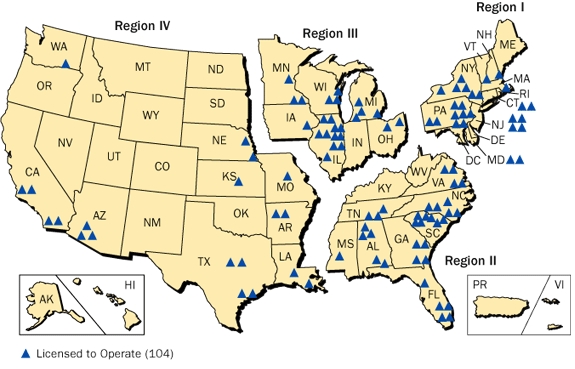
The nuclear reactors us map presents a geographical overview of the nation’s nuclear power infrastructure. It showcases the locations of operational and decommissioned nuclear power plants, highlighting the states with the most significant reliance on this energy source.
Key Features of the Map:
- Distribution: The map reveals a concentration of nuclear power plants in the Eastern and Midwestern regions of the U.S., with notable clusters in the Northeast, the Great Lakes region, and the Southeast. This distribution reflects historical factors such as population density, industrial development, and access to cooling water sources.
- Operational Reactors: The map differentiates between active and inactive reactors, providing insights into the current state of nuclear power generation in the U.S. The number of operational reactors has been steadily declining in recent years due to factors such as aging infrastructure, regulatory challenges, and economic considerations.
- Decommissioned Reactors: The map also displays the locations of decommissioned reactors, signifying the ongoing process of retiring nuclear power plants after their operational lifespan. Decommissioning involves dismantling and safely disposing of radioactive materials, ensuring environmental protection and public safety.
Benefits of Nuclear Power:
The nuclear reactors us map underscores the significant role of nuclear power in the U.S. energy mix. It highlights the following benefits:
- Low Carbon Emissions: Nuclear power plants generate electricity without releasing greenhouse gases, making them a crucial component of efforts to combat climate change.
- Reliable Baseload Power: Nuclear power plants provide consistent, reliable energy, contributing to grid stability and ensuring a continuous supply of electricity.
- Energy Security: Nuclear power reduces reliance on fossil fuels, enhancing energy independence and national security.
- Economic Benefits: Nuclear power plants generate jobs, stimulate local economies, and contribute to the overall economic well-being of the country.
Challenges Facing Nuclear Power:
While the nuclear reactors us map showcases the contributions of nuclear power, it also reflects the challenges facing this industry:
- High Capital Costs: Constructing new nuclear power plants requires significant upfront investments, making them less attractive compared to other energy sources.
- Nuclear Waste Management: The safe and long-term storage of nuclear waste remains a complex and controversial issue, requiring careful planning and implementation.
- Public Perception: Nuclear power continues to face public concerns regarding safety, security, and the potential for accidents.
The Future of Nuclear Power in the U.S.:
The future of nuclear power in the U.S. is a topic of ongoing debate. The map serves as a visual representation of the current state, highlighting the need for continued investment in existing infrastructure and the potential for new technologies.
- Modernization and Upgrading: Existing nuclear power plants require ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and modernization to ensure their safety and efficiency.
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): SMRs are a new generation of smaller, modular nuclear reactors offering potential advantages in terms of cost, safety, and flexibility.
- Advanced Reactor Designs: Research and development efforts are underway to explore advanced reactor designs that address concerns related to waste management, safety, and proliferation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: What is the current status of nuclear power in the U.S.?
A: Nuclear power currently accounts for approximately 20% of the U.S.’s electricity generation. The number of operational reactors has been declining in recent years, but there are ongoing efforts to modernize existing plants and explore new technologies.
Q: What are the main concerns regarding nuclear power?
A: Public concerns surrounding nuclear power include the potential for accidents, the management of nuclear waste, and the risk of proliferation of nuclear weapons.
Q: What is the role of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC)?
A: The NRC is the independent federal agency responsible for regulating the civilian use of nuclear materials in the U.S. It ensures the safe operation of nuclear power plants and the protection of public health and the environment.
Tips for Understanding the Nuclear Reactors Us Map:
- Focus on the Key Features: Pay attention to the distribution of reactors, the distinction between operational and decommissioned plants, and the states with the highest concentration of nuclear power.
- Consider Historical Context: The map reflects historical decisions regarding the siting of nuclear power plants, influenced by factors such as population density, industrial development, and access to cooling water sources.
- Analyze Trends: Observe the changes in the number of operational and decommissioned reactors over time, understanding the factors driving these trends.
- Explore the Future of Nuclear Power: Consider the potential for modernization, new technologies like SMRs, and the role of advanced reactor designs in shaping the future of nuclear power in the U.S.
Conclusion:
The nuclear reactors us map provides a valuable visual tool for understanding the landscape of nuclear power in the United States. It highlights the significant contributions of nuclear power to the nation’s energy mix while acknowledging the challenges and opportunities facing the industry. As the U.S. navigates its energy future, the map serves as a reminder of the vital role nuclear power plays in achieving energy independence, environmental sustainability, and economic growth.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Visual Guide to Nuclear Power in the United States: Understanding the Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!