Charting the Western World: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Charting the Western World: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Charting the Western World: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Western World: A Geographical Exploration

The Western world, a term encompassing a vast expanse of lands and cultures, is often defined by its shared history, values, and cultural influences. While its boundaries are fluid and contested, the concept of a "Western world" remains a powerful tool for understanding global dynamics, historical trends, and contemporary issues. A map, as a visual representation of this region, serves as an invaluable tool for navigating its complexities.
Defining the Western World: A Geographic Perspective
The Western world is typically understood as encompassing Europe, North America, and Australia. This definition, however, is not without its limitations. It excludes regions like Latin America, which share significant cultural and historical ties with Europe, while including countries like Australia, which have a distinct indigenous heritage.
The Importance of Mapping the Western World:
A map of the Western world offers a unique perspective on the region’s geography, history, and cultural connections. It highlights:
- Spatial Relationships: A map visually demonstrates the proximity and interconnectedness of different countries and regions within the Western world. This understanding is crucial for analyzing trade routes, migration patterns, and the spread of ideas.
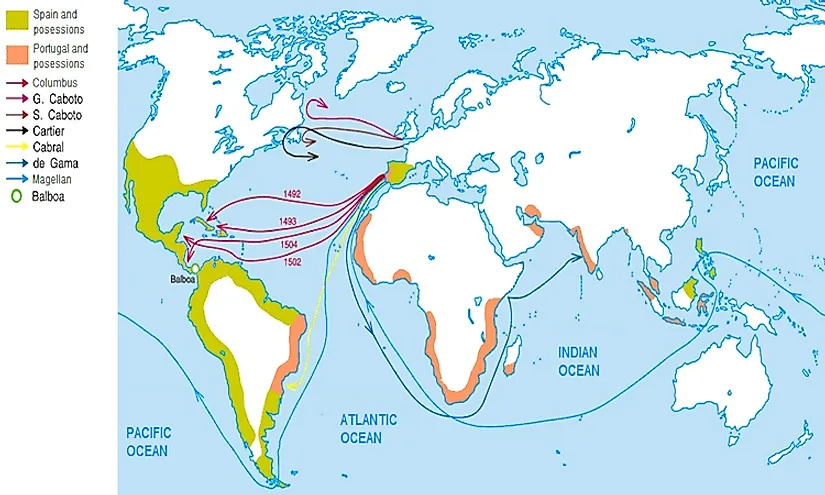
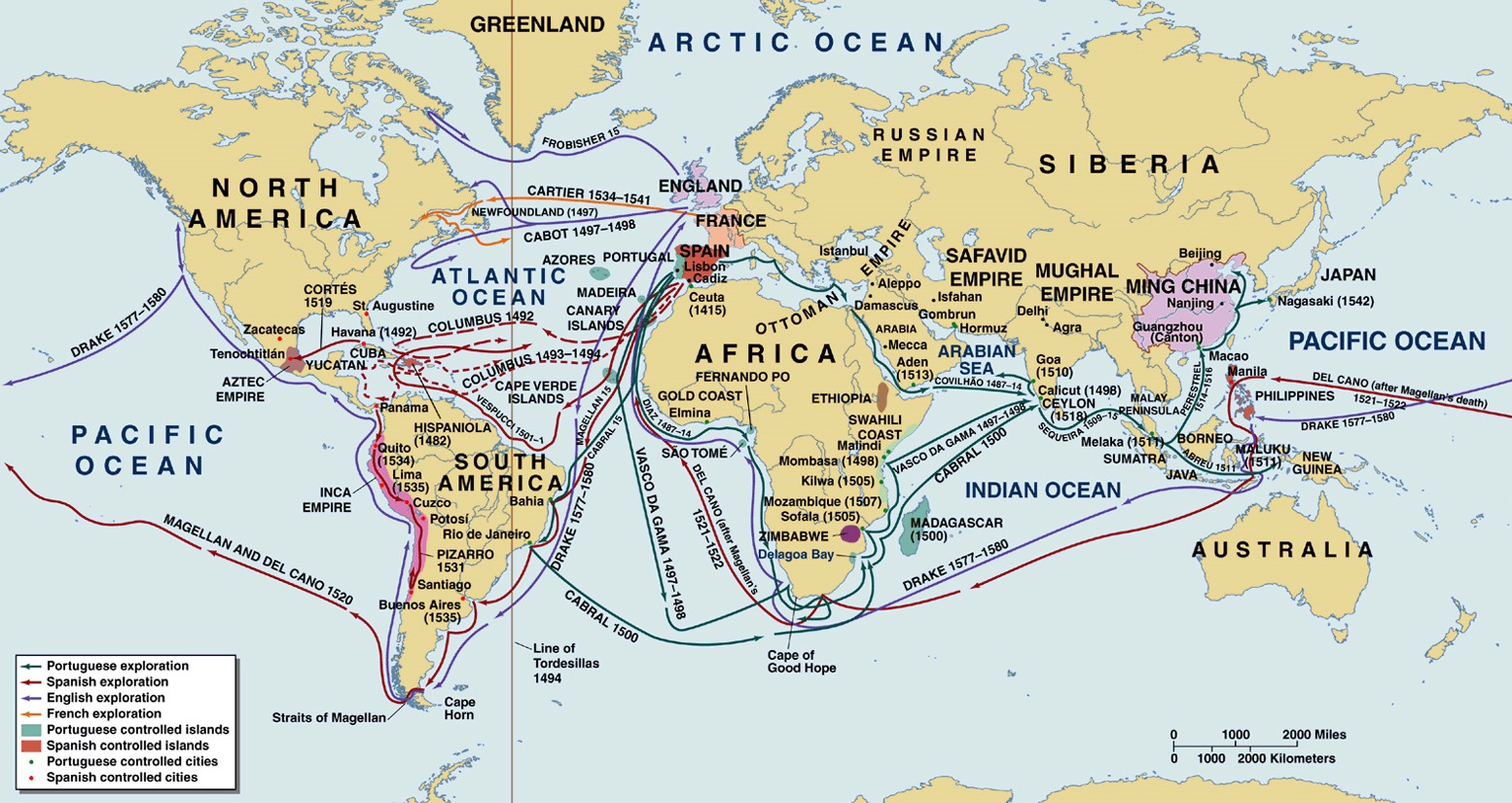
- Historical Context: Maps can trace the evolution of borders, the rise and fall of empires, and the impact of significant historical events like colonization, migration, and wars. They provide a visual framework for understanding the region’s complex past.
- Cultural Influences: Maps can showcase the distribution of languages, religions, and cultural practices. This information is crucial for understanding the diverse tapestry of cultures within the Western world and the dynamics of cultural exchange.
- Economic Connections: Maps can highlight key trade routes, economic hubs, and resource distribution, revealing the intricate network of economic relationships that define the Western world.
- Contemporary Challenges: Maps can visualize the impact of climate change, environmental degradation, and resource scarcity, highlighting the interconnectedness of these issues and the need for international cooperation.
Types of Maps and their Uses:
- Political Maps: These maps depict national borders, capital cities, and major administrative divisions, providing a clear overview of the political landscape.
- Physical Maps: These maps focus on landforms, elevation, rivers, and other physical features, offering insights into the region’s natural environment and its impact on human settlement.
- Thematic Maps: These maps highlight specific data, such as population density, language distribution, or economic activity, providing a visual representation of specific trends and patterns.
- Historical Maps: These maps depict the evolution of borders, the movement of populations, and the spread of empires over time, offering a visual narrative of the region’s past.
Navigating the Map: Key Features and Regions
Europe: The continent of Europe is the historical heart of the Western world, with a diverse array of cultures, languages, and political systems.
- Western Europe: This region includes countries like France, Germany, Italy, and Spain, known for their strong economies, rich cultural heritage, and historical influence.
- Eastern Europe: This region includes countries like Poland, Russia, and Ukraine, with a history marked by political instability and economic challenges.
- Nordic Countries: This region, encompassing countries like Sweden, Norway, and Denmark, is known for its social welfare systems, high standard of living, and strong emphasis on environmental sustainability.
North America: The continent of North America is characterized by its vast size, diverse landscapes, and vibrant cultural mix.
- United States: The largest country in North America, the United States is a global superpower with a diverse population and a powerful economy.
- Canada: A country with a strong social safety net, Canada is known for its natural beauty, multicultural society, and close relationship with the United States.
- Mexico: A country with a rich cultural heritage and a strong economy, Mexico is a key player in the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA).
Australia: A continent with a unique history and diverse landscape, Australia is known for its vibrant multicultural society, strong economy, and unique wildlife.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Western World’s Dynamics
While maps provide a valuable visual framework for understanding the Western world, they cannot fully capture its dynamic nature. The region is constantly evolving, shaped by factors such as:
- Globalization: The increasing interconnectedness of economies, cultures, and societies across the globe is transforming the Western world, leading to new opportunities and challenges.
- Technological Advancements: Technological innovations, from the internet to artificial intelligence, are rapidly changing the way we live, work, and interact with each other.
- Demographic Shifts: Population growth, aging populations, and migration patterns are altering the demographic landscape of the Western world, with significant implications for social, economic, and political systems.
- Environmental Challenges: Climate change, resource scarcity, and environmental degradation are pressing issues facing the Western world, requiring international cooperation and innovative solutions.
FAQs about the Western World:
Q: What are the key values associated with the Western world?
A: The Western world is often associated with values such as democracy, individual liberty, human rights, and the rule of law. These values have been shaped by historical events, philosophical movements, and cultural influences.
Q: What is the impact of colonialism on the Western world?
A: Colonialism had a profound impact on the Western world, shaping its economic, political, and cultural landscapes. It led to the exploitation of resources, the displacement of indigenous populations, and the imposition of Western values on other cultures.
Q: What are the challenges facing the Western world in the 21st century?
A: The Western world faces a range of challenges, including economic inequality, political polarization, climate change, and the rise of populism.
Q: How is the Western world changing?
A: The Western world is undergoing significant transformations, driven by globalization, technological advancements, demographic shifts, and environmental challenges. These changes are leading to new opportunities and challenges for the region.
Tips for Understanding the Western World:
- Explore different maps: Use a variety of maps to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region’s geography, history, and cultural dynamics.
- Read historical accounts: Learn about the region’s past to understand the forces that have shaped its present.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out different perspectives on the Western world, including those from within and outside the region.
- Stay informed about current events: Follow news and developments in the Western world to stay abreast of the region’s evolving challenges and opportunities.
Conclusion:
A map of the Western world offers a powerful tool for understanding the region’s geography, history, and cultural connections. It highlights the interconnectedness of its various components, providing a visual framework for analyzing its complex dynamics. However, it is important to remember that maps are static representations of a dynamic reality. The Western world is constantly evolving, shaped by globalization, technological advancements, demographic shifts, and environmental challenges. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the region’s complex present and future.

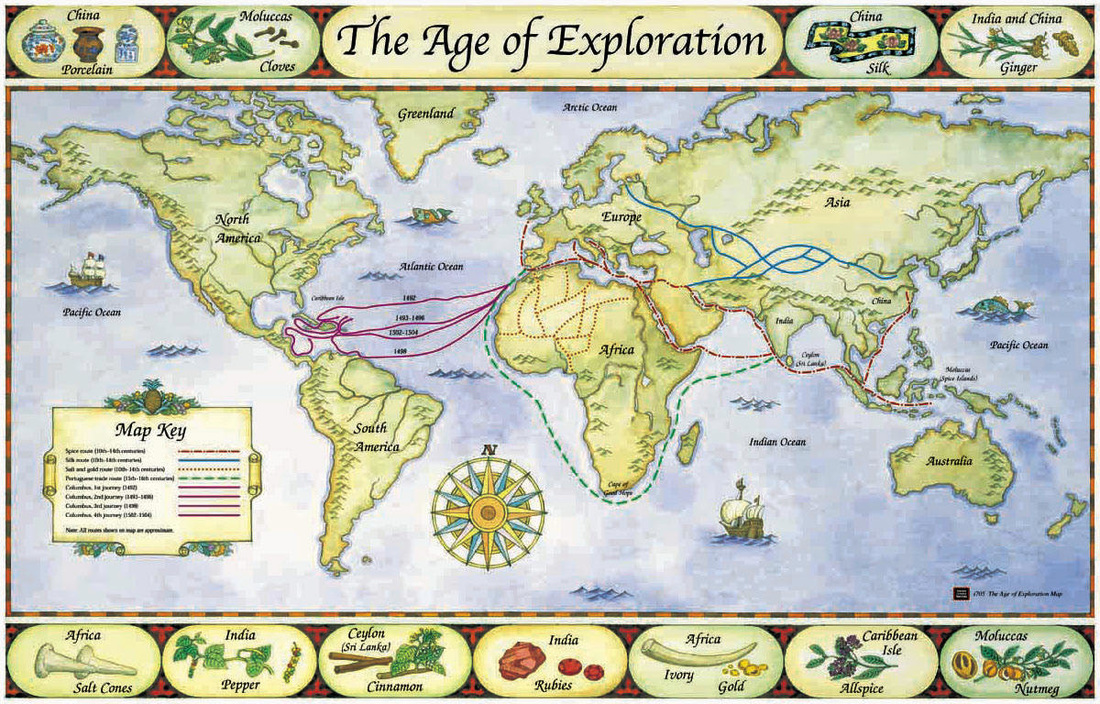

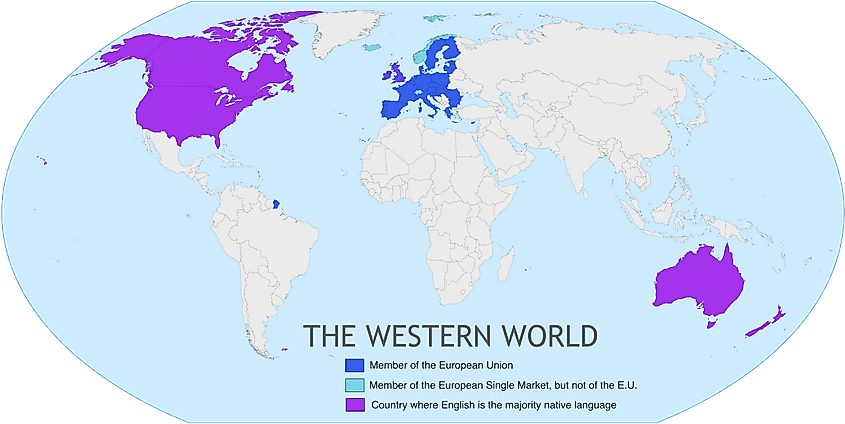
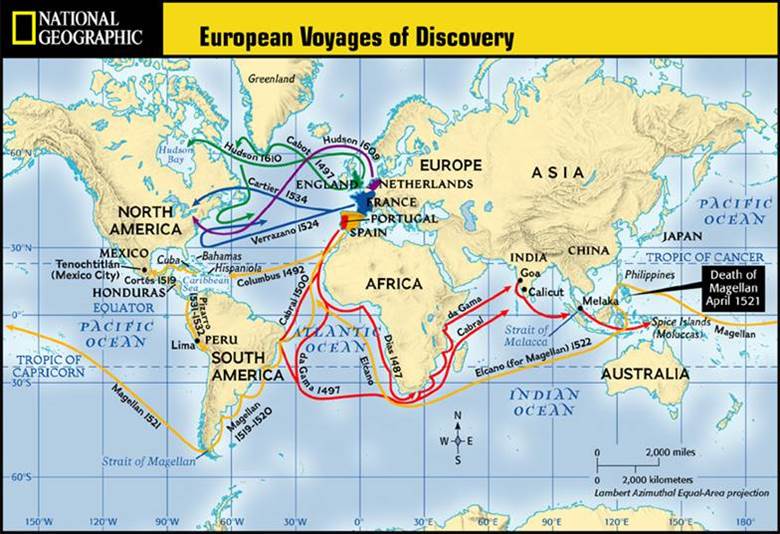
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Western World: A Geographical Exploration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!