Foundation Maps: Charting the Path to a Robust Digital Foundation
Related Articles: Foundation Maps: Charting the Path to a Robust Digital Foundation
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Foundation Maps: Charting the Path to a Robust Digital Foundation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Foundation Maps: Charting the Path to a Robust Digital Foundation
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Foundation Maps: Charting the Path to a Robust Digital Foundation
- 3.1 Understanding Foundation Maps: A Visual Representation of Digital Infrastructure
- 3.2 The Benefits of Foundation Mapping: A Foundation for Success
- 3.3 Key Elements of a Foundation Map: A Comprehensive Blueprint
- 3.4 Creating a Foundation Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.5 FAQs about Foundation Maps: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Foundation Mapping: A Guide to Success
- 3.7 Conclusion: Foundation Maps – A Foundation for Digital Success
- 4 Closure
Foundation Maps: Charting the Path to a Robust Digital Foundation
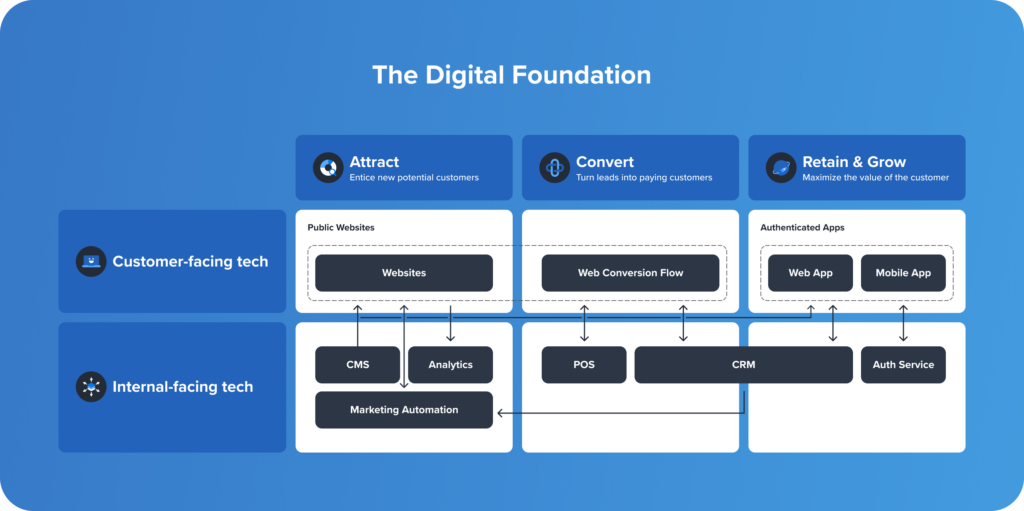
In the realm of digital transformation, the foundation upon which an organization builds its technology infrastructure plays a pivotal role in its success. A robust digital foundation is not merely a collection of disparate technologies but a carefully orchestrated ecosystem of interconnected components designed to support seamless operations, foster innovation, and drive growth. Foundation mapping, a critical process in this endeavor, provides a comprehensive blueprint for constructing this robust foundation, outlining the key elements, their interdependencies, and their alignment with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Understanding Foundation Maps: A Visual Representation of Digital Infrastructure
Foundation maps are visual representations of an organization’s digital infrastructure, depicting the critical components that underpin its technological operations. They serve as a comprehensive roadmap, offering a holistic view of the technology landscape, encompassing hardware, software, data, network infrastructure, applications, and security systems. By visualizing these interconnected elements, foundation maps provide a clear understanding of how each component contributes to the overall functionality and performance of the digital infrastructure.
The Benefits of Foundation Mapping: A Foundation for Success
The benefits of foundation mapping extend beyond mere visualization. It serves as a strategic tool, empowering organizations to:
1. Gain a Holistic Perspective: Foundation maps provide a comprehensive overview of the existing technology landscape, revealing hidden dependencies, potential vulnerabilities, and areas for optimization. This holistic perspective enables organizations to identify inefficiencies, optimize resource allocation, and make informed decisions regarding technology investments.
2. Achieve Alignment with Business Objectives: By linking technology components with specific business goals, foundation maps ensure that the digital infrastructure is strategically aligned with the organization’s overall vision. This alignment fosters a culture of collaboration between IT and business departments, ensuring that technology investments directly support business objectives.
3. Enhance Risk Management: Foundation maps facilitate a comprehensive risk assessment by highlighting potential vulnerabilities within the digital infrastructure. By identifying these risks, organizations can proactively implement mitigation strategies, minimizing the likelihood of disruptions and ensuring business continuity.
4. Foster Innovation and Agility: A well-defined foundation map fosters a culture of innovation and agility by providing a clear understanding of the existing technology landscape. This clarity enables organizations to quickly identify opportunities for adopting new technologies, adapting to changing market demands, and responding to emerging threats.
5. Facilitate Collaboration and Communication: Foundation maps serve as a common language for all stakeholders, facilitating effective communication and collaboration between IT departments, business units, and external partners. This shared understanding fosters transparency, improves decision-making, and streamlines project execution.
Key Elements of a Foundation Map: A Comprehensive Blueprint
A comprehensive foundation map encompasses a wide range of elements, including:
1. Infrastructure: This component captures the physical and virtual hardware resources, such as servers, network devices, storage systems, and cloud infrastructure. It outlines their interconnectivity, capacity, and performance characteristics.
2. Software: The software component includes operating systems, middleware, applications, and databases. It details their functionality, dependencies, versions, and licensing agreements.
3. Data: This element focuses on the organization’s data assets, including their types, sources, storage locations, and access controls. It highlights the data governance policies and data security measures in place.
4. Network: The network component depicts the communication infrastructure, including internal and external networks, firewalls, routers, and switches. It illustrates the flow of data, network security measures, and bandwidth capacity.
5. Security: This element focuses on the security posture of the digital infrastructure, encompassing access controls, authentication mechanisms, encryption protocols, and threat detection systems. It highlights the security policies and compliance requirements in place.
6. Applications: This component lists the applications used by the organization, including their functionality, user interfaces, integrations, and dependencies on other systems.
7. Business Processes: The foundation map should also connect technology components with specific business processes, demonstrating how technology enables and supports key business functions.
Creating a Foundation Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Developing a foundation map is a collaborative process that requires input from various stakeholders within the organization. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating a comprehensive and effective foundation map:
1. Define Scope and Objectives: Begin by clearly defining the scope of the foundation map, specifying the technologies and business processes to be included. Determine the specific objectives to be achieved through the mapping process, such as identifying potential vulnerabilities, optimizing resource allocation, or facilitating technology adoption.
2. Gather Data: Collect comprehensive data about the organization’s technology infrastructure, including hardware specifications, software licenses, network configurations, security policies, and application details. This data can be gathered through interviews, surveys, documentation reviews, and system audits.
3. Choose a Visualization Method: Select a suitable visualization method to represent the interconnected elements of the digital infrastructure. Common methods include flowcharts, diagrams, and network maps. The choice of method should be guided by the complexity of the infrastructure and the target audience for the map.
4. Map the Components: Using the chosen visualization method, map the key components of the digital infrastructure, including hardware, software, data, network, security, applications, and business processes. Clearly label each component and its relationships with other elements.
5. Analyze and Interpret: Once the foundation map is complete, analyze the data to identify potential vulnerabilities, inefficiencies, or areas for improvement. Highlight key dependencies, bottlenecks, and security risks.
6. Communicate and Share: Communicate the findings of the foundation mapping process to relevant stakeholders, including IT professionals, business leaders, and external partners. The foundation map should be readily accessible and regularly updated to reflect changes in the technology landscape.
FAQs about Foundation Maps: Addressing Common Questions
1. Who is responsible for creating and maintaining the foundation map?
The responsibility for creating and maintaining the foundation map typically falls on the IT department, in collaboration with other relevant stakeholders, such as business units and security teams.
2. How often should the foundation map be updated?
The frequency of updates depends on the rate of change within the organization’s technology landscape. Regular updates, at least annually, are recommended to ensure the map remains accurate and relevant.
3. What are the key challenges in developing a foundation map?
Challenges include collecting accurate and comprehensive data, choosing the right visualization method, ensuring stakeholder buy-in, and maintaining the map over time.
4. How can organizations ensure the foundation map is effective?
Effectiveness is achieved by involving relevant stakeholders in the mapping process, using a clear and concise visualization method, regularly updating the map, and integrating it with other technology management tools.
5. What are the potential benefits of using a foundation map for cloud migration?
Foundation maps provide a clear understanding of the existing infrastructure, enabling organizations to identify dependencies, assess compatibility with cloud services, and plan for a smooth migration.
Tips for Effective Foundation Mapping: A Guide to Success
1. Start Small: Begin by mapping a specific area of the digital infrastructure, such as a particular application or business process. This allows for a more manageable scope and provides valuable experience for future mapping efforts.
2. Use a Standardized Format: Adopt a standardized format for the foundation map, ensuring consistency across different departments and projects. This facilitates communication and collaboration, ensuring everyone understands the same information.
3. Incorporate Data Visualization Tools: Leverage data visualization tools to create interactive and engaging foundation maps. These tools can provide insights into data relationships, trends, and potential areas for improvement.
4. Regularly Review and Update: Schedule regular reviews of the foundation map to ensure it remains accurate and relevant. Updates should reflect changes in the technology landscape, business processes, and security requirements.
5. Promote Collaboration: Foster collaboration between IT and business units to ensure the foundation map reflects the needs of both departments. This collaboration ensures that technology investments align with business objectives and drive value.
Conclusion: Foundation Maps – A Foundation for Digital Success
Foundation maps are an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to build a robust digital foundation. By providing a comprehensive overview of the technology landscape, highlighting key dependencies, and facilitating collaboration, foundation maps enable organizations to optimize resource allocation, mitigate risks, foster innovation, and drive business growth. As organizations navigate the ever-evolving digital landscape, foundation mapping emerges as a critical strategy for achieving digital success.
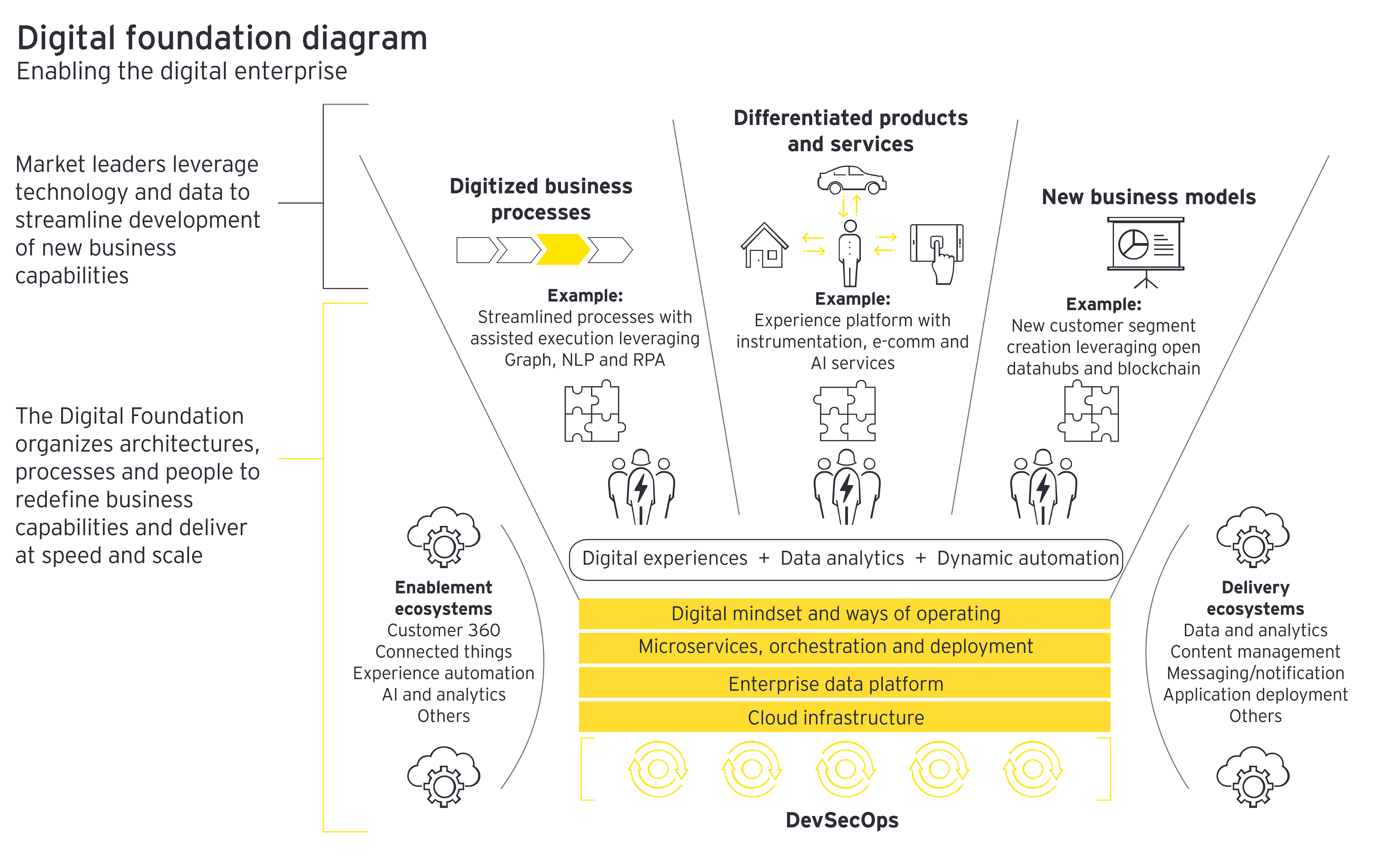
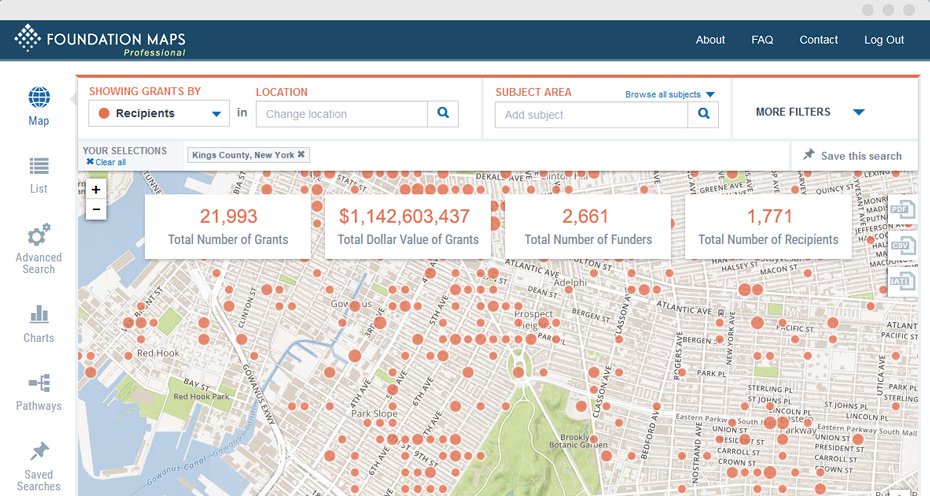

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Foundation Maps: Charting the Path to a Robust Digital Foundation. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!