Illuminating the Night: A Deep Dive into Light Pollution in the United States
Related Articles: Illuminating the Night: A Deep Dive into Light Pollution in the United States
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Illuminating the Night: A Deep Dive into Light Pollution in the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Illuminating the Night: A Deep Dive into Light Pollution in the United States
The United States, a nation renowned for its sprawling urban landscapes and vibrant nocturnal life, faces a growing challenge: light pollution. This phenomenon, the excessive and misdirected use of artificial light, has far-reaching consequences for human health, wildlife, and the natural environment. Understanding the extent and impact of light pollution is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate its negative effects.
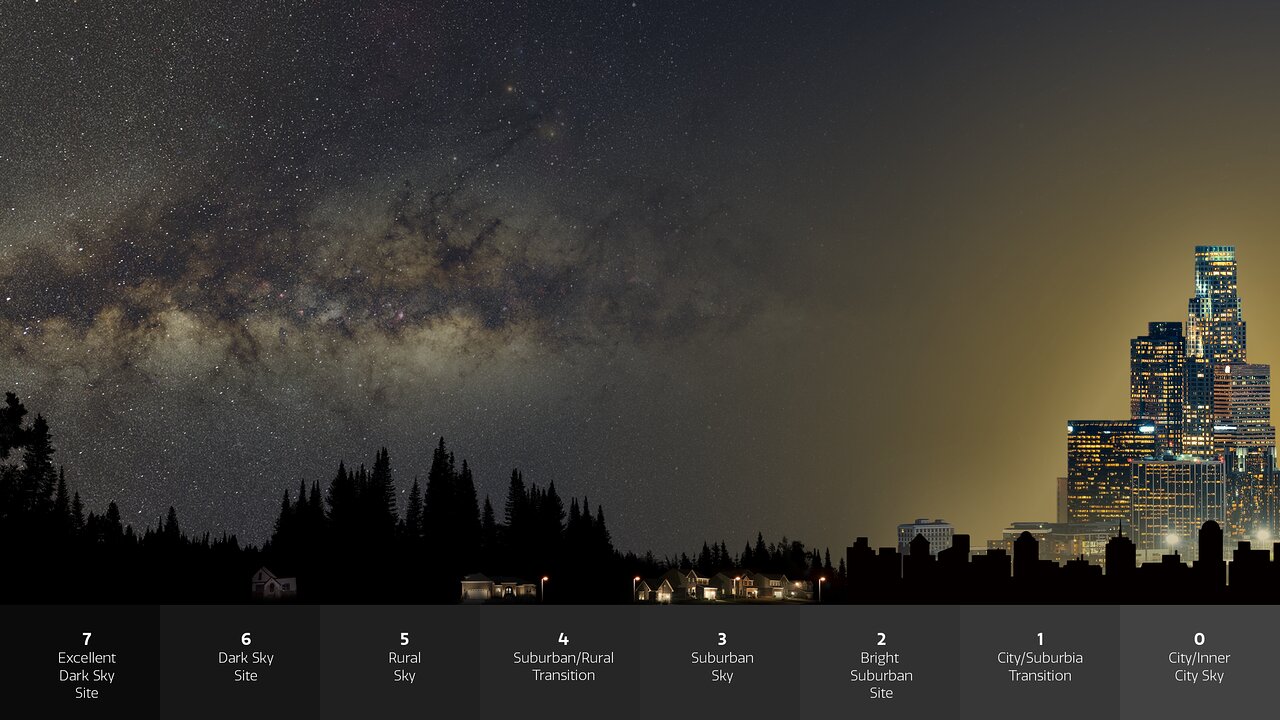
Mapping the Glow: A Visual Representation of Light Pollution
Light pollution maps serve as a visual tool for understanding the spatial distribution of artificial light at night. These maps utilize data collected from satellites, ground-based sensors, and citizen science initiatives to depict the intensity and geographical spread of light pollution. The most prominent light pollution map for the United States is the National Geographic’s “World Atlas of Artificial Night Sky Brightness,” a comprehensive resource that visualizes the severity of light pollution across the globe.
The Impact of Light Pollution: A Multifaceted Challenge
Light pollution extends beyond aesthetic concerns, impacting various aspects of life:
1. Human Health:
- Disrupted Sleep Cycles: Artificial light at night disrupts the natural production of melatonin, a hormone crucial for regulating sleep patterns. This disruption can lead to sleep disorders, increased risk of chronic diseases, and reduced cognitive function.
- Eye Strain and Vision Problems: Excessive exposure to artificial light, particularly blue light emitted from electronic devices, can strain the eyes and contribute to conditions like macular degeneration.
- Mental Health Impacts: Studies suggest a correlation between light pollution and increased rates of depression and anxiety.
2. Wildlife Disruption:
- Nocturnal Animal Behavior: Light pollution disrupts the natural rhythms of nocturnal animals, impacting their foraging, mating, and navigation behaviors. This can lead to habitat loss, population decline, and ecological imbalances.
- Migratory Bird Disorientation: Artificial light disorients migrating birds, leading them to collide with buildings and other structures, resulting in significant mortality rates.
- Sea Turtle Hatchling Disorientation: Beach lighting disorients hatchling sea turtles, leading them away from the ocean and towards inland areas, increasing their vulnerability to predators and dehydration.
3. Environmental Impacts:
- Increased Energy Consumption: Light pollution signifies inefficient use of energy, contributing to increased carbon emissions and environmental degradation.
- Skyglow and Astronomical Observation: Excessive artificial light obscures the night sky, hindering astronomical observation and research.
- Reduced Biodiversity: Light pollution’s impact on nocturnal wildlife contributes to a decline in biodiversity, impacting ecosystem stability and function.
Solutions for Mitigating Light Pollution:
Addressing light pollution requires a multi-pronged approach involving individual actions, community initiatives, and policy changes:
1. Individual Actions:
- Use Light Efficiently: Choose energy-efficient light bulbs and fixtures, and utilize light only when necessary.
- Shielding and Directing Light: Use shields and shades to direct light downwards and minimize upward spill.
- Minimize Blue Light Exposure: Reduce screen time before bed and use blue light filters on electronic devices.
2. Community Initiatives:
- Dark Sky Initiatives: Encourage the adoption of dark sky ordinances, which promote responsible lighting practices in communities.
- Citizen Science Programs: Participate in citizen science projects that gather data on light pollution and its impact.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Raise awareness about the consequences of light pollution and promote sustainable lighting practices.
3. Policy Changes:
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Implement stricter energy efficiency standards for outdoor lighting fixtures.
- Tax Incentives: Provide tax incentives for businesses and homeowners to adopt energy-efficient lighting technologies.
- Regulation of Outdoor Lighting: Establish regulations that limit the intensity, duration, and direction of outdoor lighting.
FAQs about Light Pollution in the United States:
1. What are the most light-polluted areas in the United States?
The most light-polluted areas in the United States are typically concentrated around major metropolitan areas like Los Angeles, New York City, and Chicago. These regions exhibit high levels of artificial light due to dense urban development and extensive nighttime activity.
2. How does light pollution impact my health?
Light pollution can disrupt your sleep cycle by suppressing melatonin production, leading to sleep disorders, fatigue, and increased risk of chronic diseases. It can also strain your eyes and contribute to vision problems.
3. Can I do anything to reduce light pollution in my neighborhood?
Yes, you can make a difference by adopting responsible lighting practices at home, advocating for dark sky ordinances in your community, and participating in citizen science projects to gather data on light pollution.
4. How can I protect wildlife from light pollution?
You can protect wildlife by using shielded and directed lighting, minimizing unnecessary outdoor lighting, and supporting organizations that advocate for dark sky initiatives.
5. What are the future prospects for mitigating light pollution?
The future of mitigating light pollution is promising, with growing awareness of its impact and advancements in technology. The development of energy-efficient lighting solutions, smart lighting systems, and stricter regulations are expected to contribute to a reduction in light pollution in the coming years.
Tips for Reducing Light Pollution:
- Choose LED lights: LED lights are energy-efficient and produce less light pollution than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- Use motion sensors: Motion sensors can help reduce unnecessary lighting by only illuminating areas when needed.
- Shield and direct light: Use shields and shades to direct light downwards and minimize upward spill.
- Dim or turn off lights: Dim or turn off unnecessary outdoor lights, especially during the night.
- Support dark sky initiatives: Advocate for dark sky ordinances and participate in citizen science projects.
Conclusion:
Light pollution is a multifaceted challenge with far-reaching consequences for human health, wildlife, and the environment. By understanding its impact and adopting responsible lighting practices, individuals, communities, and policymakers can work together to mitigate light pollution and restore the beauty and ecological integrity of our night skies. The future of light pollution mitigation lies in collaborative efforts, technological advancements, and a commitment to preserving the darkness for generations to come.








Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Illuminating the Night: A Deep Dive into Light Pollution in the United States. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!