Mapping Poverty: Understanding and Addressing Low-Income Communities
Related Articles: Mapping Poverty: Understanding and Addressing Low-Income Communities
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping Poverty: Understanding and Addressing Low-Income Communities. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping Poverty: Understanding and Addressing Low-Income Communities
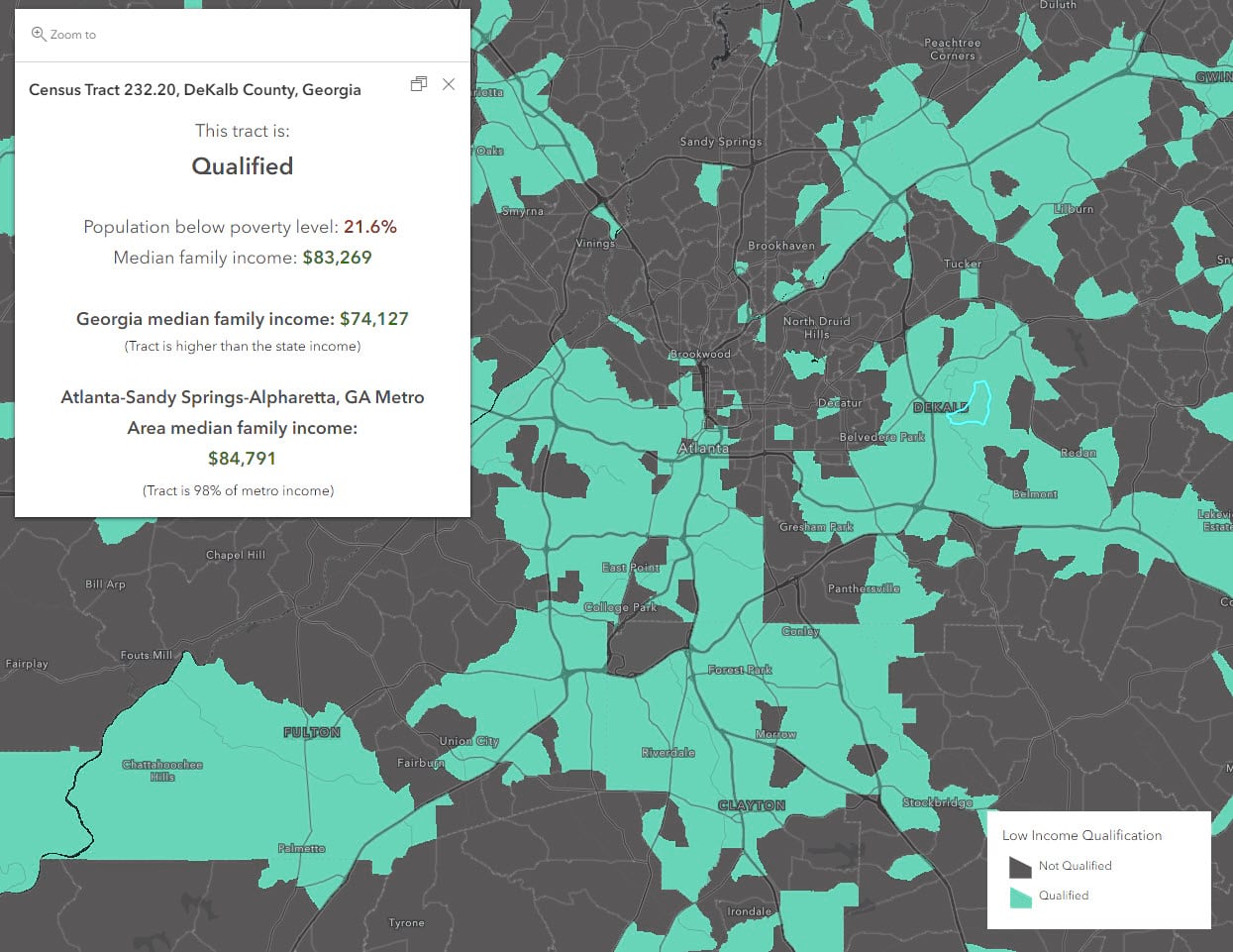
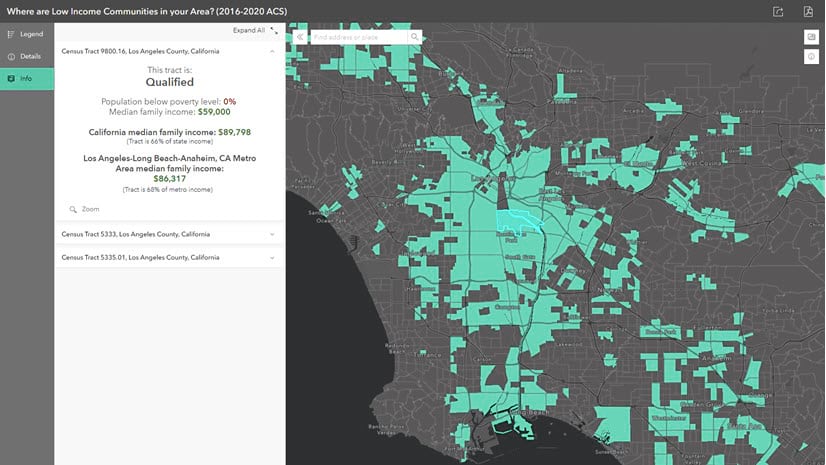
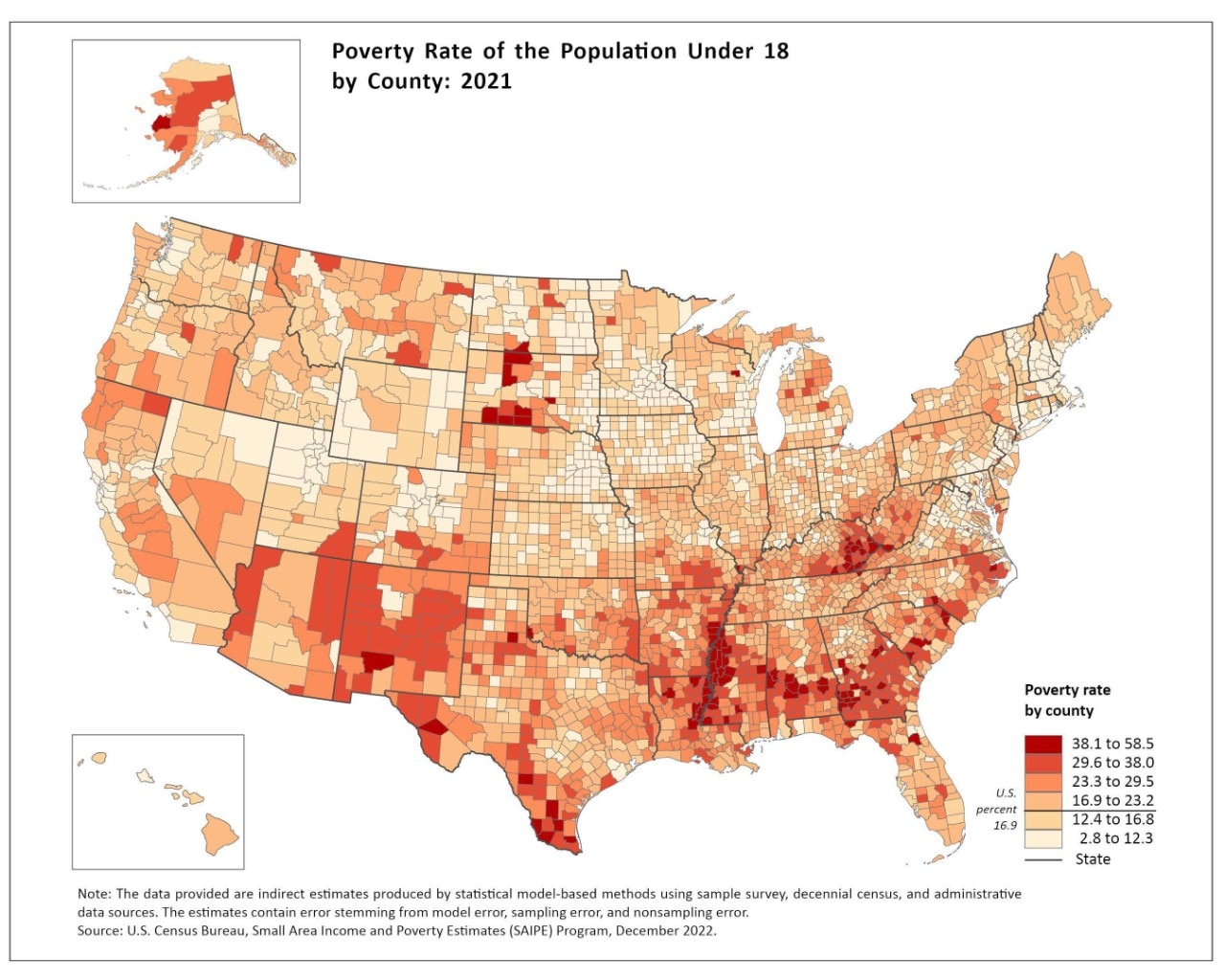
The concept of a "low-income community map" transcends a mere visual representation of poverty. It serves as a powerful tool for understanding, analyzing, and ultimately addressing the complex challenges faced by communities grappling with economic hardship. This map, often generated through a combination of demographic data, economic indicators, and spatial analysis, provides a detailed and nuanced picture of where poverty exists, its intensity, and the factors contributing to its persistence.
Understanding the Data Landscape:
A low-income community map relies on a diverse range of data sources, including:
- Census Data: The U.S. Census Bureau provides a wealth of information on population demographics, income distribution, housing characteristics, and other socioeconomic factors. This data is crucial for identifying areas with high concentrations of low-income households.
- Economic Indicators: Data on unemployment rates, poverty rates, median household income, and per capita income provide insights into the economic health of communities. These indicators can be used to identify areas with high levels of economic distress.
- Housing Data: Information on housing costs, rental rates, and housing affordability is essential for understanding the housing challenges faced by low-income communities. This data can be used to identify areas with high rates of overcrowding, homelessness, and substandard housing.
- Health Data: Access to healthcare, health outcomes, and health disparities are often directly linked to socioeconomic factors. Data on these indicators can highlight areas with high rates of chronic illness, premature mortality, and limited access to healthcare services.
- Education Data: Educational attainment, school performance, and access to quality education are crucial for breaking the cycle of poverty. Data on these indicators can identify areas with high rates of school dropout, low test scores, and limited access to educational resources.
Beyond Data Points: A Holistic Perspective:
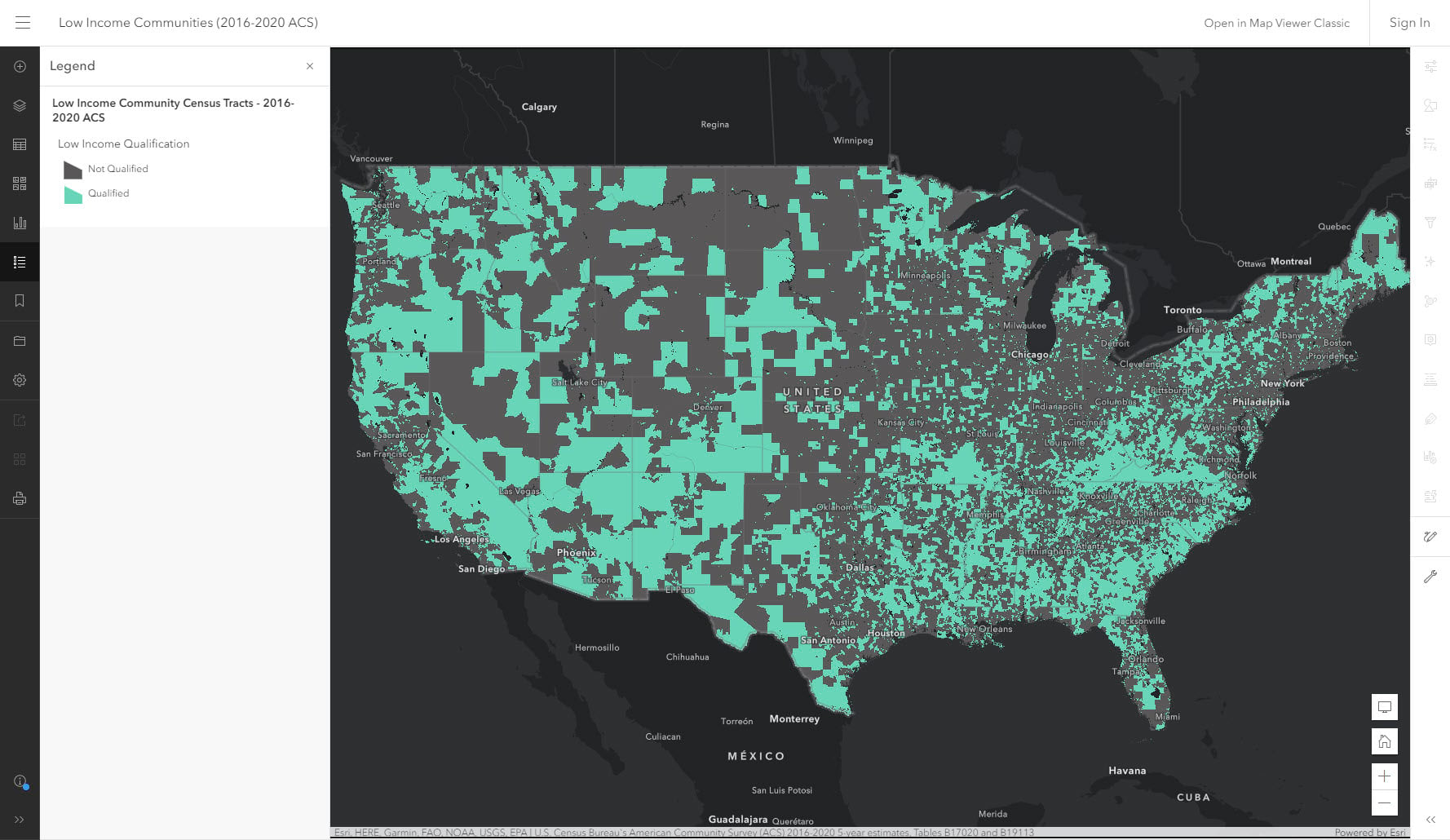
While data is essential, a low-income community map goes beyond simple data points. It incorporates a spatial perspective, allowing for the visualization of poverty’s geographic distribution. This spatial analysis enables the identification of:
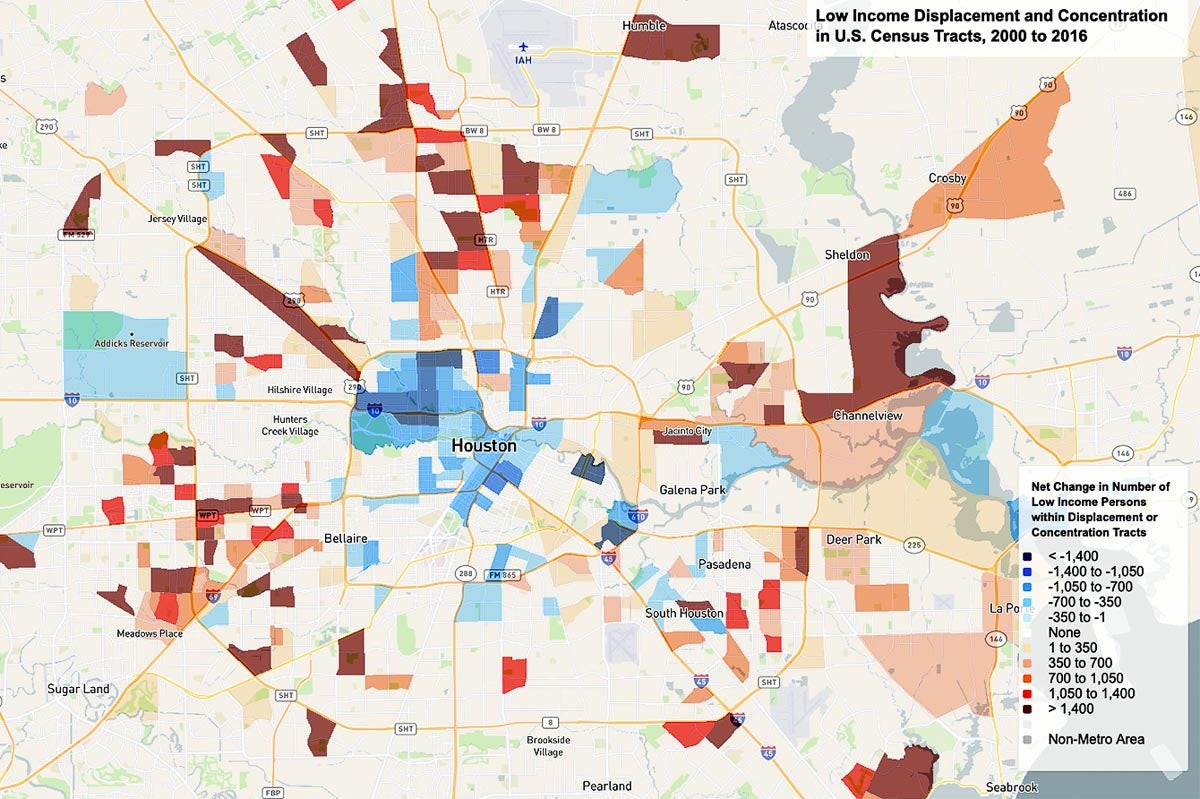
- Geographic Clusters: Areas with high concentrations of low-income households often form distinct geographic clusters. These clusters may reflect historical patterns of segregation, economic decline, or lack of investment in infrastructure and services.
- Spatial Inequalities: The map can highlight spatial disparities in access to resources, amenities, and opportunities. This includes disparities in access to healthcare, education, transportation, and employment opportunities.
- Environmental Factors: The map can incorporate environmental factors such as air quality, water quality, and access to green spaces. These factors can have a significant impact on health, well-being, and quality of life, particularly in low-income communities.
The Power of Visualization:
The visual representation of poverty through a low-income community map offers several advantages:
- Increased Awareness: The map serves as a powerful visual tool for raising awareness of the extent and severity of poverty within a region or community.
- Targeted Interventions: By identifying specific areas of need, the map facilitates the development of targeted interventions and programs. This ensures that resources are allocated effectively and efficiently.
- Community Engagement: The map can be used to engage community members, stakeholders, and policymakers in a dialogue about poverty and its impact. This dialogue can lead to collaborative efforts to address the underlying causes of poverty.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: The map provides a data-driven foundation for decision-making, ensuring that interventions and policies are based on evidence rather than assumptions.
Beyond Mapping: The Path to Action:
A low-income community map is not simply a static representation of poverty; it is a starting point for action. The map serves as a catalyst for:
- Policy Development: The map can inform the development of policies aimed at addressing the root causes of poverty, such as investing in affordable housing, expanding access to healthcare, promoting job creation, and improving educational opportunities.
- Program Implementation: The map can guide the implementation of programs and services that target specific needs within low-income communities. This includes programs that provide housing assistance, job training, financial literacy, and community development initiatives.
- Community Empowerment: The map can empower community members to advocate for their own needs and participate in the development of solutions to poverty. This includes supporting community-based organizations, fostering community leadership, and promoting civic engagement.
FAQs about Low-Income Community Maps:
1. What is the purpose of creating a low-income community map?
The primary purpose of creating a low-income community map is to provide a visual and data-driven understanding of the distribution and intensity of poverty within a specific region or community. This understanding is crucial for developing targeted interventions and policies to address the challenges faced by low-income communities.
2. How are low-income community maps created?
Low-income community maps are created using a combination of data sources, including census data, economic indicators, housing data, health data, and education data. This data is then analyzed spatially to identify areas with high concentrations of low-income households and to understand the spatial distribution of poverty.
3. What are the limitations of low-income community maps?
While low-income community maps provide valuable insights, they have limitations. For instance, they may not capture the full complexity of poverty, as they rely on quantitative data and may not adequately reflect qualitative experiences. Additionally, the data used to create the maps may not be readily available or may be outdated.
4. Who benefits from low-income community maps?
Low-income community maps benefit a wide range of stakeholders, including:
- Policymakers: The maps provide data-driven evidence to support policy decisions aimed at reducing poverty.
- Community organizations: The maps help organizations identify areas of need and target their services effectively.
- Researchers: The maps provide valuable data for academic research on poverty and its impacts.
- Community members: The maps raise awareness of poverty and empower community members to advocate for change.
Tips for Using Low-Income Community Maps Effectively:
- Ensure data quality: Verify the accuracy and reliability of the data used to create the map.
- Consider the context: Understand the historical, social, and economic context of the area being mapped.
- Engage with the community: Involve community members in the development and interpretation of the map.
- Focus on solutions: Use the map to identify opportunities for intervention and to develop strategies for reducing poverty.
- Monitor and evaluate: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of interventions and adjust strategies as needed.
Conclusion:
A low-income community map serves as a crucial tool for understanding and addressing the complex challenges of poverty. By providing a visual and data-driven representation of poverty’s distribution and intensity, the map facilitates targeted interventions, empowers community members, and informs policy decisions. It is a powerful tool for fostering a more equitable and just society, where all communities have the opportunity to thrive.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping Poverty: Understanding and Addressing Low-Income Communities. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!