Mapping the Ancient World: A Journey Through Asia’s Past
Related Articles: Mapping the Ancient World: A Journey Through Asia’s Past
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Ancient World: A Journey Through Asia’s Past. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Ancient World: A Journey Through Asia’s Past

Ancient Asia, a vast and diverse tapestry of civilizations, stretches across a continent that has witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the flourishing of great religions, and the development of groundbreaking technologies. To truly understand the intricate history of this region, a comprehensive map becomes an invaluable tool, providing a visual framework for navigating the complexities of its past.
This article delves into the significance of mapping ancient Asia, exploring the diverse landscapes, influential cultures, and historical events that shaped the continent’s past. We will examine the key geographical features, the major civilizations that emerged, and the interconnectedness that defined this region for millennia.
The Geographical Canvas:
Ancient Asia was a land of dramatic contrasts, encompassing sprawling plains, towering mountain ranges, fertile river valleys, and vast deserts. These geographical features played a pivotal role in shaping the development of civilizations and influencing their interactions.
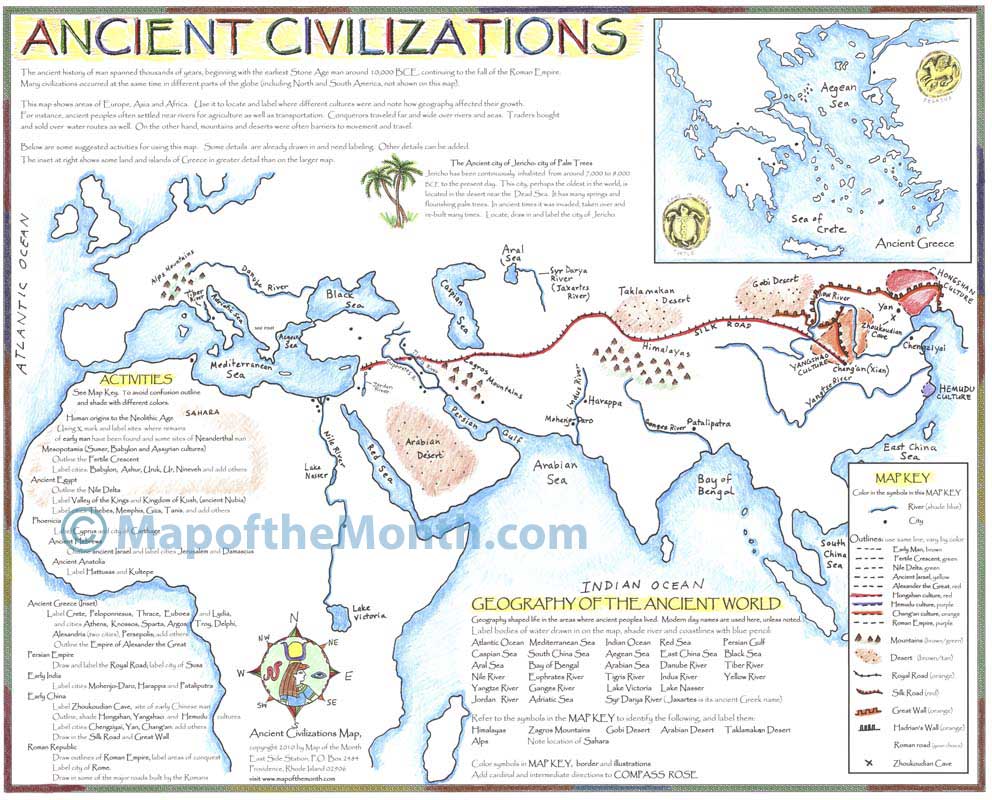
- The Fertile Crescent: This cradle of civilization, stretching from the eastern Mediterranean to the Persian Gulf, witnessed the rise of early agricultural societies. The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers provided fertile ground for agriculture, supporting the growth of powerful city-states like Sumer, Akkad, Babylon, and Assyria.
- The Indus Valley Civilization: Flourishing in the Indus River Valley, this civilization developed a sophisticated urban system with advanced technology, including planned cities, drainage systems, and standardized weights and measures. The Indus Valley civilization, spanning from modern-day Pakistan to northwestern India, remains shrouded in mystery, with its script yet to be deciphered.
- The Yellow River Valley: This region, known as the "Cradle of Chinese Civilization," witnessed the emergence of the Shang Dynasty, renowned for its bronze casting and sophisticated writing system. The Yellow River, with its fertile soil and predictable floods, provided a stable base for agriculture and the growth of early Chinese society.
- The Himalayan Mountains: This formidable mountain range, forming a natural barrier between India and China, played a crucial role in shaping the cultural and linguistic diversity of the region. Its high altitude and rugged terrain limited travel and communication, creating distinct cultural pockets within the Himalayas.
The Rise of Civilizations:
Ancient Asia was home to a multitude of civilizations, each with its own unique cultural identity, religious beliefs, and political systems.
- Mesopotamia: This region, located in the Fertile Crescent, witnessed the rise of the world’s first civilizations, including the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians. These civilizations developed sophisticated systems of writing, mathematics, astronomy, and law. The Code of Hammurabi, a Babylonian legal code, stands as a testament to the advanced legal system of this period.
- Ancient Egypt: While geographically located in Africa, ancient Egypt’s cultural and economic ties with Asia, particularly through trade routes, place it within the broader context of ancient Asian civilizations. The Egyptians developed advanced writing systems, intricate religious beliefs, and impressive architectural feats, such as the pyramids, that continue to fascinate the world.
- Ancient India: The Indian subcontinent witnessed the emergence of several major civilizations, including the Indus Valley Civilization, the Vedic Civilization, and the Mauryan Empire. These civilizations developed unique religious and philosophical systems, including Hinduism, Buddhism, and Jainism, which spread widely across Asia and beyond.
- Ancient China: The Yellow River Valley gave birth to the Xia, Shang, and Zhou dynasties, laying the foundation for Chinese civilization. These dynasties developed advanced technologies, including bronze casting, silk production, and sophisticated writing systems. The concept of the Mandate of Heaven, which justified the rule of emperors, played a crucial role in shaping Chinese political thought.
Interconnectedness and Exchange:
The civilizations of ancient Asia were not isolated entities. They were interconnected through trade routes, cultural exchanges, and religious movements.
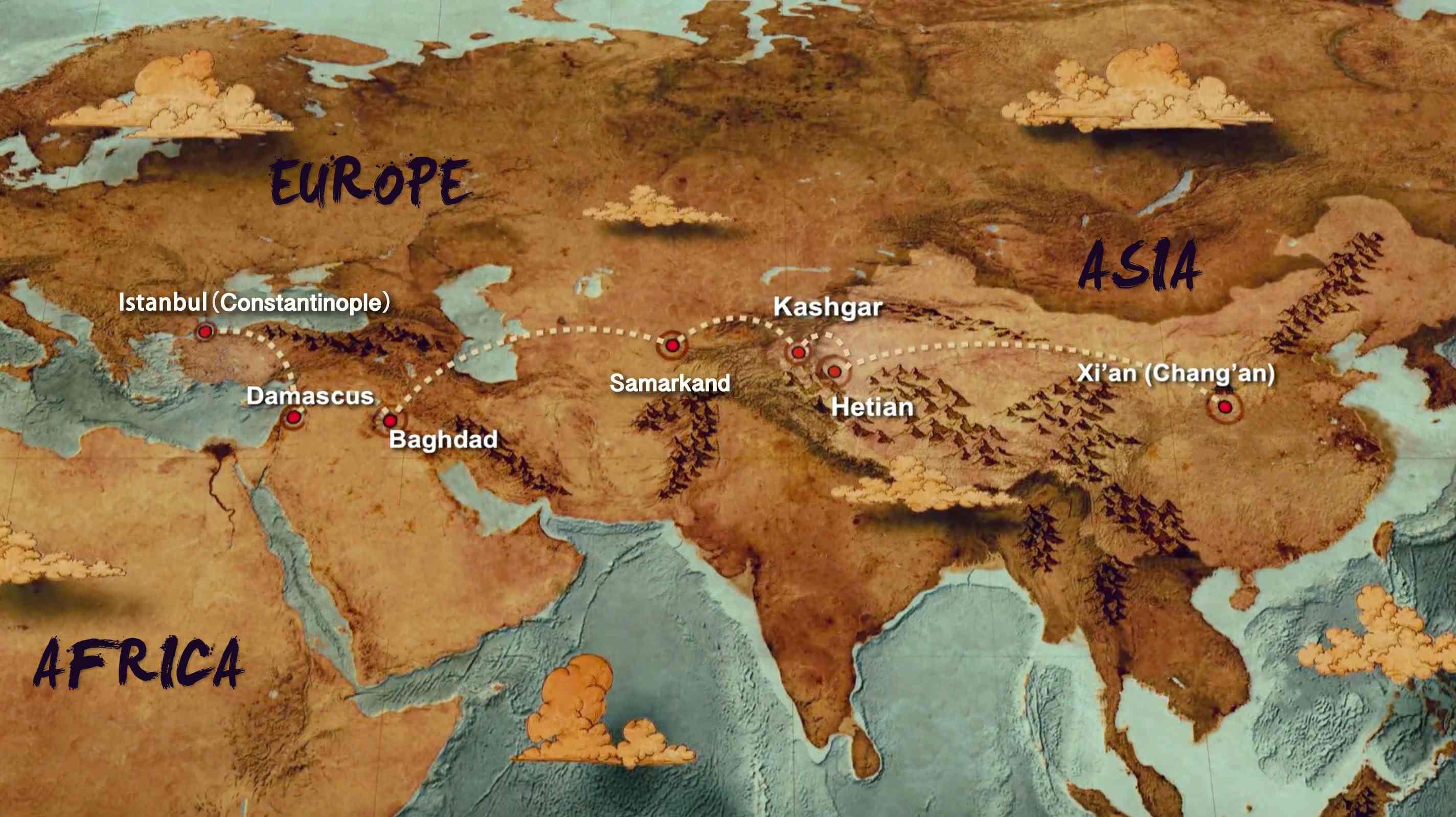
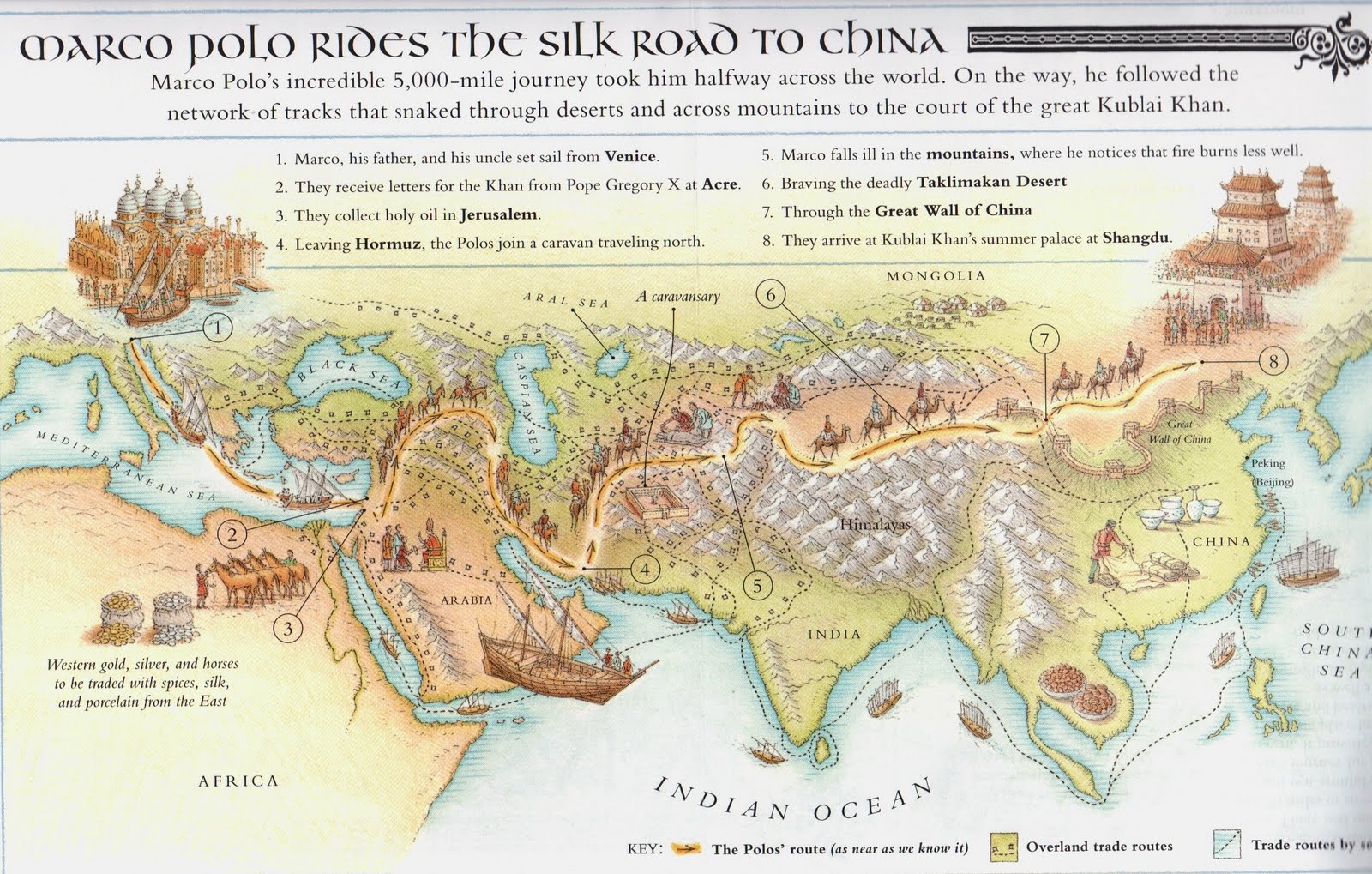
- The Silk Road: This ancient network of trade routes, stretching from East Asia to the Mediterranean, facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies. Silk, spices, porcelain, and other valuable commodities travelled along the Silk Road, connecting civilizations and fostering cultural exchange.
- Buddhism: Originating in ancient India, Buddhism spread widely across Asia, influencing the cultural and religious landscape of regions like China, Japan, Korea, and Southeast Asia. The teachings of Buddha, emphasizing compassion, non-violence, and enlightenment, resonated with people from diverse backgrounds.
- Cultural Diffusion: The exchange of ideas, technologies, and artistic styles across ancient Asia led to cultural diffusion. For example, the influence of Greek culture can be seen in the art and architecture of the Hellenistic period in Central Asia.
Mapping the Past:
Mapping ancient Asia serves as a powerful tool for understanding the complexities of this region’s past. It helps us visualize the geographical context, the locations of major civilizations, and the routes of trade and cultural exchange.
- Visualizing the Scale: A map allows us to comprehend the vastness of ancient Asia and the distances civilizations had to traverse to interact with each other. It highlights the challenges and opportunities presented by the continent’s diverse geography.
- Understanding Interconnections: By plotting the major trade routes, religious movements, and cultural influences, a map reveals the intricate network of connections that existed between ancient civilizations. It illustrates the interconnectedness of ancient Asia and the impact of cultural diffusion.
- Identifying Key Locations: Maps provide a visual guide to the locations of important cities, empires, and historical sites. They help us understand the geographical context of major events and the significance of specific locations.
FAQs about Mapping Ancient Asia:
1. What are the benefits of mapping ancient Asia?
Mapping ancient Asia provides a visual framework for understanding the region’s history, geography, and cultural dynamics. It helps us visualize the scale of the region, the location of major civilizations, and the routes of trade and cultural exchange.
2. How do maps help us understand the interconnectedness of ancient Asia?
Maps illustrate the networks of trade routes, religious movements, and cultural influences that connected civilizations across ancient Asia. They reveal the interconnectedness of the region and the impact of cultural diffusion.
3. What are some of the challenges in mapping ancient Asia?
Mapping ancient Asia presents challenges due to the vastness of the region, the lack of complete archaeological data, and the changing political boundaries over time.
4. How can maps be used in research on ancient Asia?
Maps can be used to identify potential archaeological sites, to study the spread of languages and cultures, and to analyze the impact of trade and migration patterns on the development of civilizations.
Tips for Mapping Ancient Asia:
- Use a variety of sources: Consult historical texts, archaeological evidence, and modern maps to create a comprehensive picture of ancient Asia.
- Consider the scale: Choose a map scale that allows you to visualize both the major features and the finer details of the region.
- Include key features: Highlight major geographical features, cities, trade routes, and cultural centers.
- Use color and symbols: Employ different colors and symbols to differentiate between civilizations, cultural influences, and historical periods.
Conclusion:
Mapping ancient Asia is an essential tool for understanding the rich and complex history of this region. By providing a visual framework for exploring the continent’s past, maps help us appreciate the diverse landscapes, influential cultures, and interconnectedness that shaped the course of history in Asia. As we continue to uncover the secrets of ancient Asia, maps will remain invaluable resources for navigating its intricate past and understanding the enduring legacy of its civilizations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Ancient World: A Journey Through Asia’s Past. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!