Mastering Data Transformation with JavaScript’s Map and Reduce: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Mastering Data Transformation with JavaScript’s Map and Reduce: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mastering Data Transformation with JavaScript’s Map and Reduce: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Mastering Data Transformation with JavaScript’s Map and Reduce: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Mastering Data Transformation with JavaScript’s Map and Reduce: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Map Function
- 3.2 Understanding the Reduce Function
- 3.3 Combining Map and Reduce for Powerful Data Operations
- 3.4 FAQs on JavaScript Map and Reduce
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Use of Map and Reduce
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Mastering Data Transformation with JavaScript’s Map and Reduce: A Comprehensive Guide
JavaScript’s map and reduce methods are powerful tools for data manipulation, offering elegant solutions for a wide range of tasks. While often used together, they are distinct functions with unique roles in transforming and summarizing data. This guide explores the functionalities of map and reduce, their individual strengths, and how their combined power simplifies complex data operations.
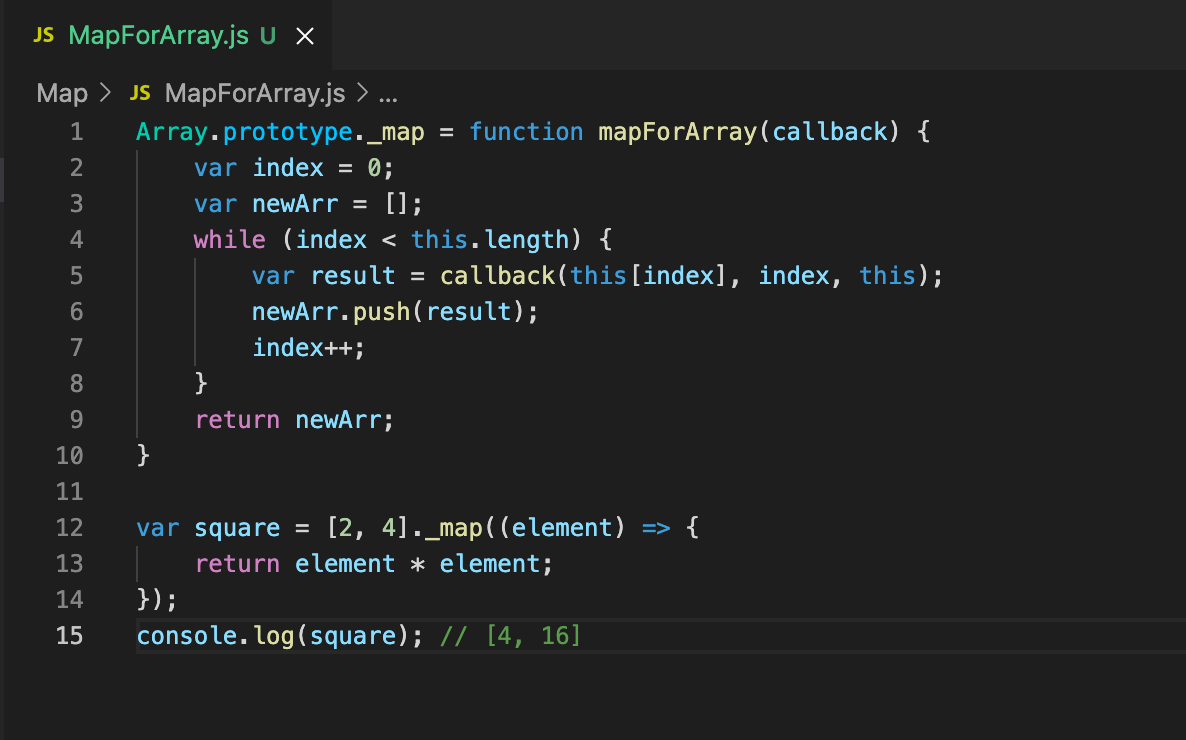
Understanding the Map Function
The map method is a versatile tool for creating new arrays by applying a specified function to each element of an existing array. It iterates through the original array, transforming each element and producing a new array with the transformed values.
Syntax:
const newArray = originalArray.map(callbackFunction);Parameters:
-
callbackFunction: A function that takes a single argument (the current element) and returns the transformed value.
Example:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// Square each number in the array
const squaredNumbers = numbers.map(number => number * number);
console.log(squaredNumbers); // Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, the map method iterates through each element in the numbers array. The callback function number => number * number squares each element, producing a new array squaredNumbers containing the transformed values.
Key Benefits of map:
-
Data Transformation:
mapallows for efficient and concise data transformation without the need for explicit loops. -
Preserving Array Structure:
mapcreates a new array with the same length as the original array, maintaining the original structure. -
Readability and Conciseness:
mapenhances code readability by separating the transformation logic from the iteration process.
Understanding the Reduce Function
The reduce method is a powerful tool for aggregating data into a single value. It iterates through an array, accumulating the results of a callback function applied to each element.
Syntax:
const accumulator = originalArray.reduce(callbackFunction, initialValue);Parameters:
-
callbackFunction: A function that takes two arguments: the accumulator and the current element. It returns the updated accumulator value. -
initialValue(optional): The initial value of the accumulator. If not provided, the first element of the array is used as the initial value.
Example:
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// Calculate the sum of all numbers in the array
const sum = numbers.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue, 0);
console.log(sum); // Output: 15In this example, the reduce method iterates through the numbers array. The callback function (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue adds each element to the accumulator, starting with the initial value of 0. The final accumulator value, which is the sum of all numbers, is stored in the sum variable.
Key Benefits of reduce:
-
Data Aggregation:
reduceenables efficient data aggregation, summarizing data into a single value. -
Flexibility:
reducecan be used for various aggregation tasks, such as finding the maximum value, calculating the average, or concatenating strings. -
Code Reusability:
reducecan be applied to different data types and aggregation operations, promoting code reusability.
Combining Map and Reduce for Powerful Data Operations
The combined power of map and reduce allows for complex data manipulations in a concise and efficient manner. By first transforming data using map and then aggregating the transformed data using reduce, you can perform intricate operations with minimal code.
Example:
const products = [
name: 'Apple', price: 1.5 ,
name: 'Banana', price: 0.75 ,
name: 'Orange', price: 1.25
];
// Calculate the total cost of all products
const totalCost = products.map(product => product.price).reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue, 0);
console.log(totalCost); // Output: 3.5In this example, map is used to extract the price from each product object, creating a new array of prices. Then, reduce is used to sum the prices in the new array, calculating the total cost of all products.
Real-world Applications:
-
Calculating the average of an array: Use
mapto transform values to their absolute values and then usereduceto calculate the sum and divide by the array length. -
Filtering data based on a condition: Use
filterto remove unwanted elements, then usemapto transform the remaining elements, and finally usereduceto aggregate the results. -
Finding the most frequent element in an array: Use
reduceto count occurrences of each element and then find the element with the highest count.
FAQs on JavaScript Map and Reduce
1. What is the difference between map and reduce?
map transforms each element of an array into a new element, creating a new array with the same length. reduce aggregates the elements of an array into a single value.
2. Can I use map and reduce with objects?
Yes, both map and reduce can be used with arrays of objects. The callback functions for both methods should handle object properties as needed.
3. What is the difference between reduce and forEach?
forEach iterates through an array, executing a callback function for each element. reduce aggregates the elements of an array into a single value.
4. What are some common use cases for map and reduce?
map is commonly used for data transformation, such as converting units, applying formatting, or extracting specific properties. reduce is commonly used for data aggregation, such as calculating sums, averages, or finding the maximum value.
5. Can I use reduce without an initial value?
Yes, if no initial value is provided, reduce will use the first element of the array as the initial value.
6. How can I chain map and reduce?
You can chain map and reduce by applying reduce to the result of map. This allows for multi-step data processing.
Tips for Effective Use of Map and Reduce
-
Choose the right tool for the job: Use
mapfor element transformation andreducefor data aggregation. - Keep callback functions concise: Avoid complex logic within callback functions to maintain readability.
- Use destructuring for clarity: Destructure object properties within callback functions for improved readability.
-
Consider using
filterfor selective transformation: Usefilterto select specific elements before applyingmaporreduce. - Test thoroughly: Thorough testing ensures the accuracy of data transformations and aggregations.
Conclusion
JavaScript’s map and reduce methods provide powerful tools for data manipulation. By understanding their individual functionalities and combining them effectively, developers can streamline data processing tasks, enhance code readability, and improve overall code efficiency. Mastering these methods empowers developers to work with data more effectively, unlocking new possibilities for data analysis and transformation.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mastering Data Transformation with JavaScript’s Map and Reduce: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!