Navigating North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude
The vast and diverse continent of North America, spanning from the Arctic Circle to the tropics, requires a system for precise location and navigation. This is where the concept of latitude and longitude comes into play, forming the foundation of maps and global positioning systems (GPS). Understanding these coordinates is crucial for numerous applications, ranging from everyday navigation to scientific research and disaster response.
Latitude: Measuring North and South
Latitude lines are imaginary circles that run parallel to the equator, dividing the Earth into a grid. The equator, situated at 0 degrees latitude, acts as the reference point. Lines north of the equator are assigned positive values, while those south are assigned negative values. Each degree of latitude is approximately 69 miles (111 kilometers) apart, with smaller units called minutes and seconds further dividing each degree.
For example, a location at 40 degrees north latitude is situated 40 degrees north of the equator. The higher the latitude, the further a location is from the equator and the closer it is to the North Pole.
Longitude: Measuring East and West
Longitude lines, also known as meridians, are imaginary circles that run from the North Pole to the South Pole, perpendicular to the equator. The Prime Meridian, located at 0 degrees longitude, passes through Greenwich, England. Lines east of the Prime Meridian are assigned positive values, while those west are assigned negative values.
Each degree of longitude is not constant, unlike latitude. The distance between two meridians decreases as one moves away from the equator and converges at the poles.
The Power of Latitude and Longitude
The combination of latitude and longitude creates a unique coordinate system for every point on Earth, allowing for precise location identification. These coordinates are crucial for various purposes:
- Navigation: From personal travel to global shipping routes, latitude and longitude guide our movement across the globe. GPS devices rely on these coordinates to provide real-time location information.
- Mapping: Latitude and longitude form the foundation of maps, enabling accurate representation of geographical features and distances. From detailed city maps to global atlases, this coordinate system is essential for spatial understanding.
- Scientific Research: Latitude and longitude are critical in scientific research, particularly in disciplines like meteorology, geology, and oceanography. They allow researchers to track weather patterns, analyze geological formations, and study ocean currents.
- Disaster Response: In the event of natural disasters, precise location data is paramount for effective rescue and relief efforts. Latitude and longitude facilitate communication and coordination among emergency responders.
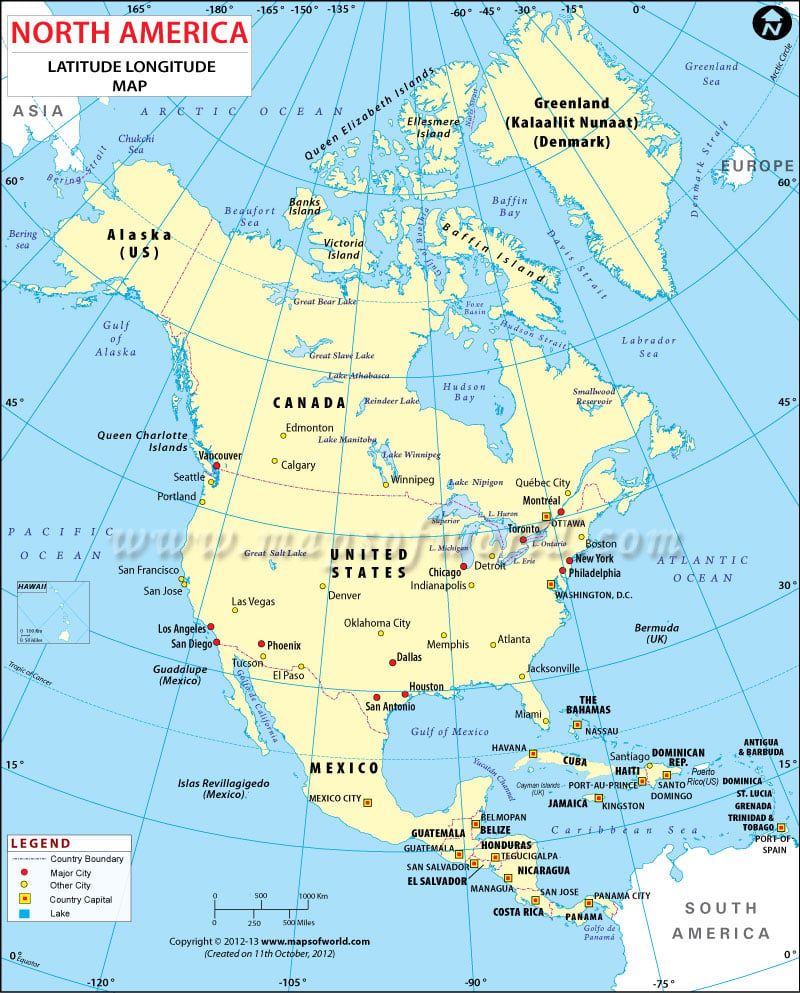
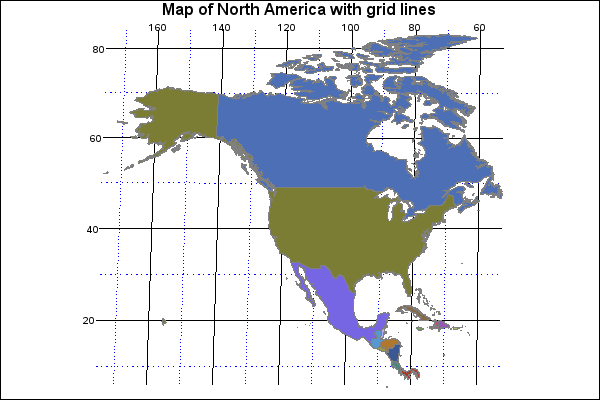
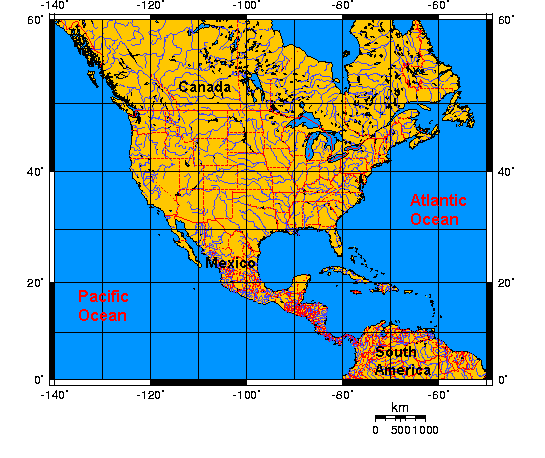
Understanding the North American Grid
North America, situated between the Arctic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, is encompassed by a wide range of latitudes and longitudes. The continent’s northernmost point, Cape Columbia, lies at approximately 83 degrees north latitude, while the southernmost point, Isla Mujeres, is at roughly 21 degrees north latitude. The westernmost point, Cape Prince of Wales, is located at about 168 degrees west longitude, while the easternmost point, Cape Spear, is at approximately 55 degrees west longitude.
Within this vast geographical expanse, diverse landscapes and climates prevail. The Arctic regions experience extreme cold and prolonged darkness, while the tropics boast warm temperatures and abundant rainfall. This variation in climate and geography is reflected in the distribution of latitude and longitude across North America.
FAQs about Latitude and Longitude in North America
1. What are the most extreme latitudes and longitudes found in North America?
The most extreme latitude in North America is found at Cape Columbia, Canada, at approximately 83 degrees north latitude. The southernmost point is Isla Mujeres, Mexico, located at approximately 21 degrees north latitude. The westernmost point is Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, at about 168 degrees west longitude. The easternmost point is Cape Spear, Newfoundland, at approximately 55 degrees west longitude.
2. How can I find the latitude and longitude of a specific location in North America?
You can use online mapping tools like Google Maps or Bing Maps to locate a specific location and obtain its latitude and longitude coordinates. Many GPS devices also display latitude and longitude readings.
3. What are some interesting geographical features located at specific latitudes in North America?
- The Arctic Circle (66.5 degrees north latitude): This imaginary line marks the southernmost point where the sun remains above the horizon for 24 hours during the summer solstice.
- The Tropic of Cancer (23.5 degrees north latitude): This line marks the northernmost point where the sun can be directly overhead.
- The Great Lakes (42-49 degrees north latitude): These five massive freshwater lakes are a defining feature of the North American landscape.
4. How does latitude influence climate in North America?
Latitude plays a significant role in determining climate patterns. Locations closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight and experience warmer temperatures throughout the year. As latitude increases, the angle of sunlight decreases, resulting in cooler temperatures and distinct seasons.
5. How does longitude influence climate in North America?
Longitude influences climate primarily by its impact on prevailing winds and ocean currents. For example, the western coast of North America experiences a milder climate due to the influence of the Pacific Ocean and its currents.
Tips for Using Latitude and Longitude in North America
- Use reliable mapping tools: Utilize online mapping services or GPS devices to obtain accurate latitude and longitude coordinates.
- Understand the relationship between latitude and longitude: Remember that latitude measures north and south, while longitude measures east and west.
- Consider the impact of latitude and longitude on climate: When planning travel or exploring different regions, be aware of the influence of latitude and longitude on temperature, precipitation, and other climate factors.
- Practice using latitude and longitude: Familiarize yourself with the coordinate system by practicing locating places on a map or using a GPS device.
Conclusion
Latitude and longitude provide a fundamental framework for understanding and navigating the vast and diverse landscape of North America. These coordinates are essential for accurate location identification, mapping, scientific research, and disaster response. By understanding and applying this system, individuals can enhance their spatial awareness and navigate the continent with greater precision and confidence.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Latitude and Longitude. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!