Navigating the Grid: Understanding the Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Grid: Understanding the Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Grid: Understanding the Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Grid: Understanding the Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) Map

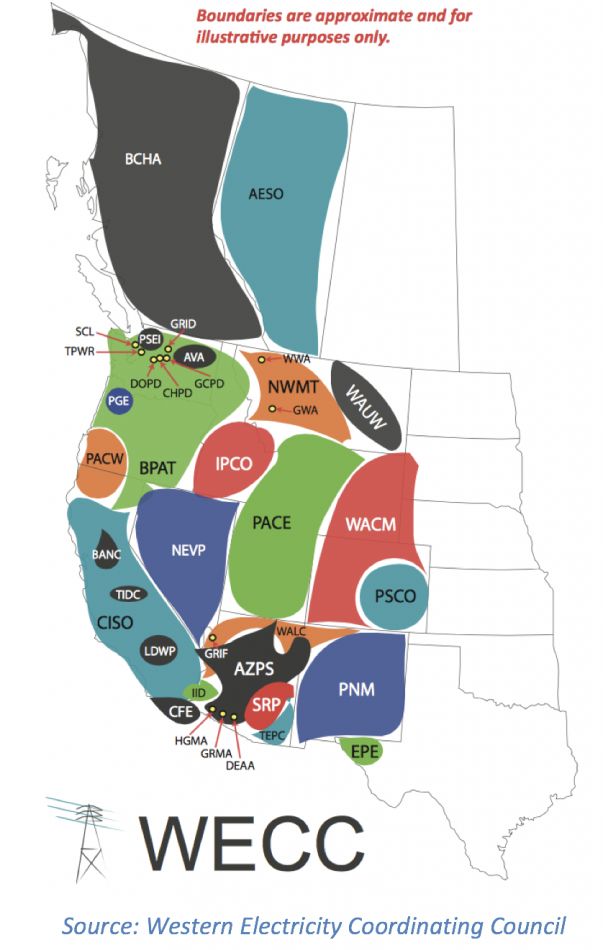
The Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) map, a visual representation of the interconnected electric grid spanning the western United States and portions of Canada, is a crucial tool for ensuring reliable and efficient electricity delivery to millions of consumers. It depicts a complex network of power plants, transmission lines, and control centers, showcasing the intricate ballet of power generation and distribution that underpins modern life.
The WECC: A Vital Hub for Western Power
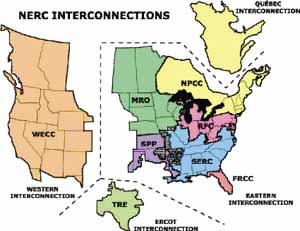
The WECC, established in 1971, is a non-profit, non-governmental organization responsible for coordinating the operation, planning, and reliability of the bulk electric system in its vast geographic area. This region, encompassing 14 states and two Canadian provinces, boasts a diverse energy landscape, including hydropower, wind, solar, geothermal, and fossil fuel-based generation.
The WECC map serves as a visual representation of this intricate network, highlighting the interconnectedness of various entities, including:
- Balancing Authorities (BAs): Responsible for ensuring the balance between electricity supply and demand within their designated areas.
- Control Areas (CAs): Operating independently within a BA, responsible for real-time control of power flows.
- Interconnections: Connecting BAs and CAs, facilitating the transfer of electricity across jurisdictional boundaries.
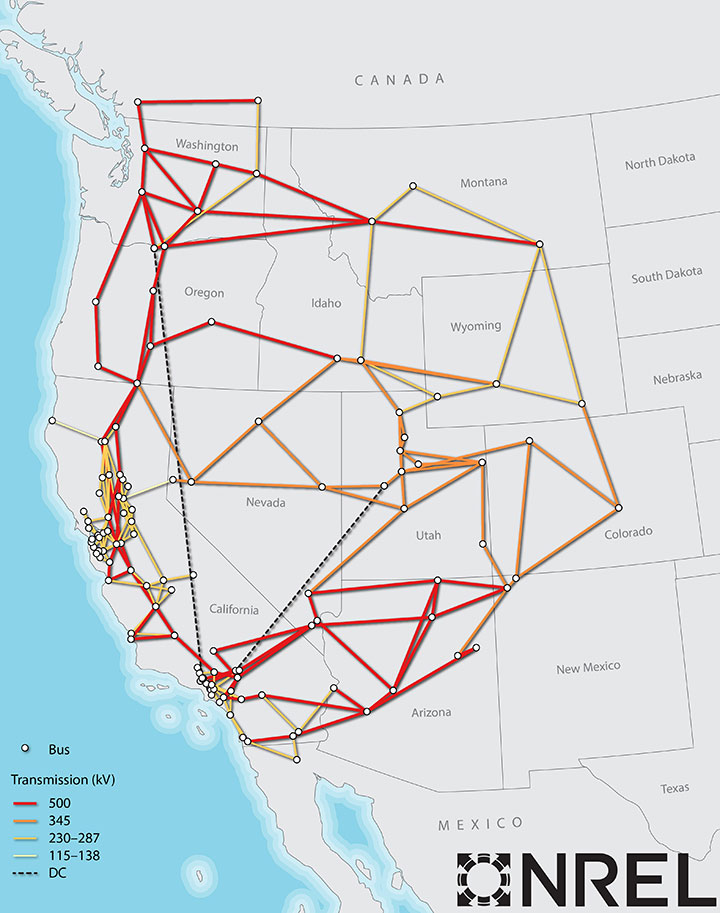
- Transmission Lines: The arteries of the grid, carrying electricity from generating stations to load centers.
- Substations: Key nodes in the grid, transforming voltage levels and facilitating the distribution of electricity.
- Generating Stations: The sources of power, ranging from large hydroelectric dams to smaller wind farms.
Understanding the Dynamics of the WECC Map
The WECC map is not merely a static representation but a dynamic tool reflecting the ever-changing flow of electricity across the grid. Several factors influence the power flow patterns, including:
- Demand: The amount of electricity required by consumers fluctuates throughout the day and year, influenced by factors like weather, industrial activity, and seasonal variations.
- Generation: The availability of electricity from various power plants is subject to factors like weather, maintenance schedules, and fuel availability.
- Transmission Constraints: Physical limitations of transmission lines, including capacity and voltage limits, restrict the flow of electricity.
- System Reliability: The WECC prioritizes maintaining system reliability, implementing measures to prevent blackouts and ensure continuous power supply.
The Importance of the WECC Map
The WECC map is crucial for several reasons:
- System Reliability: By visualizing the grid, operators can identify potential vulnerabilities and take proactive measures to prevent system disruptions.
- Resource Optimization: The map facilitates the efficient allocation of resources, enabling the coordinated use of diverse generation sources to meet fluctuating demand.
- Interregional Collaboration: The map promotes communication and cooperation between different entities within the WECC, ensuring seamless power flow across jurisdictional boundaries.
- Planning and Development: The map provides a framework for long-term planning, guiding investments in new generation and transmission infrastructure to meet future energy needs.
FAQs about the WECC Map
1. What is the role of the WECC in ensuring grid reliability?
The WECC sets standards, develops operating procedures, and coordinates with member entities to ensure the reliable operation of the Western Interconnection. The WECC map plays a vital role in identifying potential vulnerabilities and facilitating timely interventions to prevent system disruptions.
2. How does the WECC map contribute to resource optimization?
By visualizing the grid, the WECC map allows operators to track the flow of electricity from various generation sources. This data helps them optimize resource allocation, ensuring efficient use of available generation capacity to meet fluctuating demand.
3. What are some challenges faced by the WECC in maintaining grid stability?
Challenges include:
- Integration of Renewable Energy: Incorporating large-scale renewable energy sources, like solar and wind, requires careful planning and coordination to ensure grid stability.
- Extreme Weather Events: Climate change is increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, posing significant challenges to grid reliability.
- Cybersecurity Threats: The interconnected nature of the grid makes it vulnerable to cyberattacks, requiring robust security measures to protect critical infrastructure.
4. How does the WECC map promote interregional collaboration?
The map provides a common visual language for entities within the WECC, facilitating communication and coordination. This collaborative approach is crucial for ensuring seamless power flow across jurisdictional boundaries, optimizing resource utilization, and maintaining grid reliability.
5. What are the future challenges and opportunities for the WECC?
The WECC faces challenges related to integrating renewable energy, adapting to climate change, and addressing cybersecurity threats. However, it also presents opportunities for innovation, including the development of smart grid technologies, advanced energy storage solutions, and improved communication systems.
Tips for Understanding the WECC Map
- Start with the Basics: Familiarize yourself with the key components of the grid, including generation sources, transmission lines, substations, and control areas.
- Explore the Interconnections: Pay attention to how different regions are interconnected, understanding the flow of electricity across jurisdictional boundaries.
- Consider the Dynamics: Remember that the WECC map is a dynamic representation, reflecting changes in demand, generation, and transmission constraints.
- Focus on Key Features: Pay attention to areas with high concentrations of generation, load centers, and critical transmission infrastructure.
- Engage with Resources: Utilize the WECC website and other resources to gain a deeper understanding of the map’s significance and the complexities of the Western Interconnection.
Conclusion
The WECC map is a critical tool for understanding the complex interconnectedness of the Western Interconnection. By visualizing the flow of electricity across the grid, it enables operators to maintain system reliability, optimize resource allocation, and promote interregional collaboration. As the energy landscape continues to evolve, the WECC map will remain a vital resource for ensuring a reliable and efficient power supply for millions of consumers in the Western United States and Canada.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Grid: Understanding the Western Electricity Coordinating Council (WECC) Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!