Navigating the Heartland: Understanding North Dakota’s Geographic Position
Related Articles: Navigating the Heartland: Understanding North Dakota’s Geographic Position
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Heartland: Understanding North Dakota’s Geographic Position. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Heartland: Understanding North Dakota’s Geographic Position
North Dakota, a state often associated with vast plains, rolling hills, and a rich agricultural heritage, occupies a prominent position in the heart of the United States. Its geographical location, nestled within the northern Great Plains, is a key factor shaping its climate, culture, and economy.
A State in the Northern Plains:
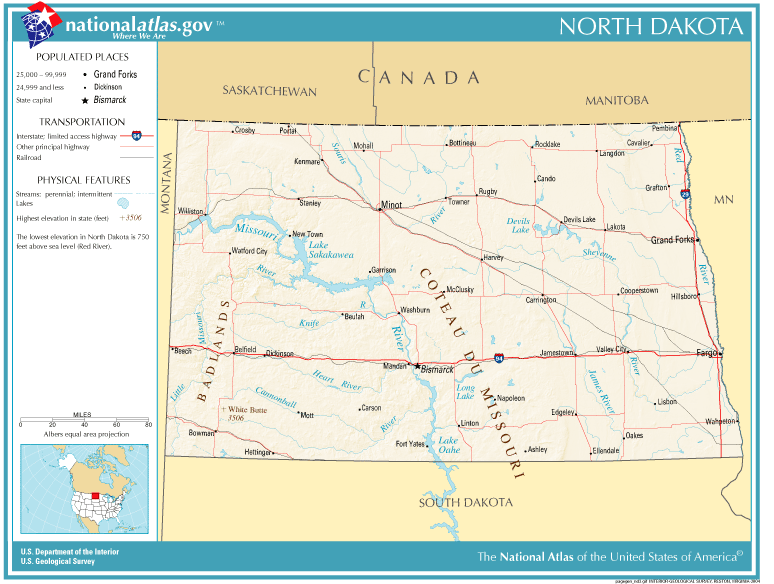
North Dakota’s geographic coordinates, 47.5282° N, 100.7765° W, place it firmly within the northern Great Plains region. This vast expanse of grasslands and prairies stretches from the Canadian border southward, encompassing parts of Montana, Wyoming, Nebraska, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas.
Bordering States and Proximity to Canada:
North Dakota shares borders with five other states: Montana to the west, South Dakota to the south, Minnesota to the east, and Manitoba and Saskatchewan in Canada to the north. This proximity to Canada has historically influenced the state’s cultural and economic ties.
The Missouri River and its Significance:
The Missouri River, a major waterway that flows through the heart of the United States, plays a significant role in North Dakota’s geography. The river bisects the state, creating a natural divide between the eastern and western regions. The Missouri River is a vital source of irrigation and transportation, contributing to the state’s agricultural and industrial development.
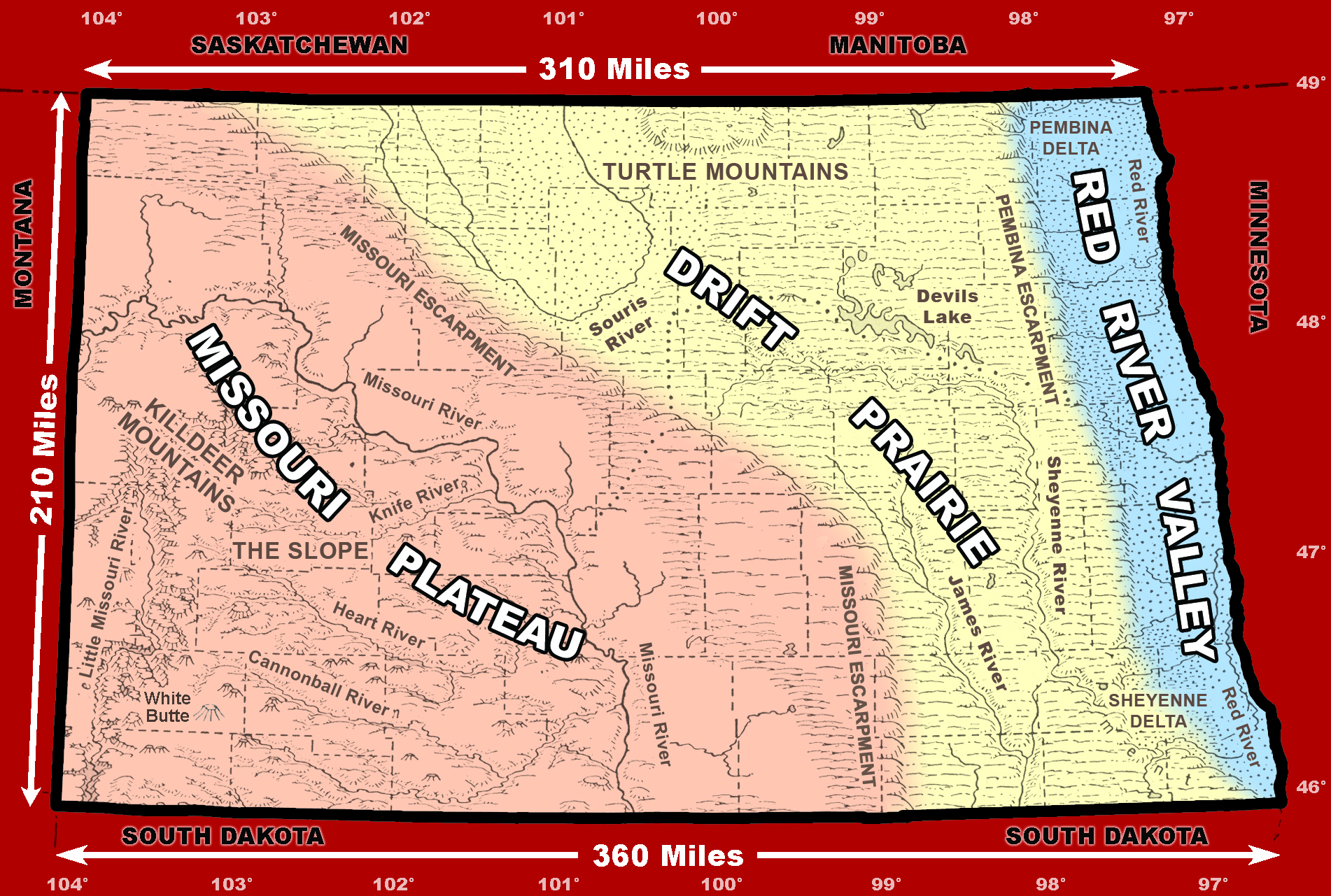
The Red River Valley: A Unique Geographic Feature:
A notable geographic feature in North Dakota is the Red River Valley, a fertile plain that stretches along the Red River of the North. This valley, known for its rich soil and agricultural productivity, is a major contributor to North Dakota’s agricultural economy.
Understanding the Importance of North Dakota’s Location:
North Dakota’s strategic location within the northern Great Plains has profound implications for its climate, economy, and culture:
- Climate and Agriculture: North Dakota’s location in the northern Great Plains contributes to its semi-arid climate, characterized by cold winters and warm summers. This climate, while challenging, is well-suited for the cultivation of hardy crops like wheat, barley, and sunflowers, making agriculture a cornerstone of the state’s economy.
- Energy Resources: North Dakota’s vast plains hold significant reserves of oil and natural gas, making it a major energy producer in the United States. This abundant resource has fueled economic growth and development in recent decades.
- Transportation and Infrastructure: North Dakota’s central location within the Great Plains region provides access to major transportation corridors, including highways, railroads, and pipelines. This facilitates the movement of goods and services, contributing to the state’s economic competitiveness.
- Cultural Influences: North Dakota’s proximity to Canada and its diverse population have shaped its cultural landscape, fostering a blend of traditions and perspectives.
FAQs about North Dakota’s Location:
Q: What is the capital of North Dakota?
A: The capital of North Dakota is Bismarck, situated in the center of the state.
Q: What is the largest city in North Dakota?
A: Fargo, located in the eastern part of the state, is the most populous city in North Dakota.
Q: What are the major industries in North Dakota?
A: North Dakota’s economy is primarily driven by agriculture, energy production (oil and gas), and manufacturing.
Q: What are some popular tourist destinations in North Dakota?
A: North Dakota offers a range of attractions, including Theodore Roosevelt National Park, the North Dakota Heritage Center, and the International Peace Garden.
Tips for Visiting North Dakota:
- Explore the state’s national parks: Theodore Roosevelt National Park and the Knife River Indian Villages National Historic Site offer opportunities to experience the state’s natural beauty and rich history.
- Visit the state capital: Bismarck boasts a vibrant downtown area, museums, and historical sites.
- Experience the state’s agricultural heritage: Visit a farm or attend a local agricultural festival to gain insights into the state’s agricultural economy.
- Enjoy the state’s unique culture: Explore the state’s vibrant arts scene, visit local museums, and engage with the diverse communities that make up North Dakota.
Conclusion:
North Dakota, with its strategic location in the northern Great Plains, is a state of vast landscapes, rich history, and diverse culture. Its geographic position has played a pivotal role in shaping its climate, economy, and way of life. From its fertile plains to its energy resources, North Dakota stands as a testament to the resilience and ingenuity of its people, contributing significantly to the nation’s agricultural and energy sectors. Understanding North Dakota’s geographic location provides a deeper appreciation for its unique character and its vital role in the broader context of the United States.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Heartland: Understanding North Dakota’s Geographic Position. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!