Navigating the Labyrinth of Pneumonia: A Visual Guide with Concept Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Labyrinth of Pneumonia: A Visual Guide with Concept Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Labyrinth of Pneumonia: A Visual Guide with Concept Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Labyrinth of Pneumonia: A Visual Guide with Concept Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Labyrinth of Pneumonia: A Visual Guide with Concept Maps
- 3.1 The Power of Visual Representation
- 3.2 A Conceptual Framework for Pneumonia
- 3.3 Unraveling the Mysteries: Frequently Asked Questions
- 3.4 Tips for Understanding and Managing Pneumonia
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Labyrinth of Pneumonia: A Visual Guide with Concept Maps
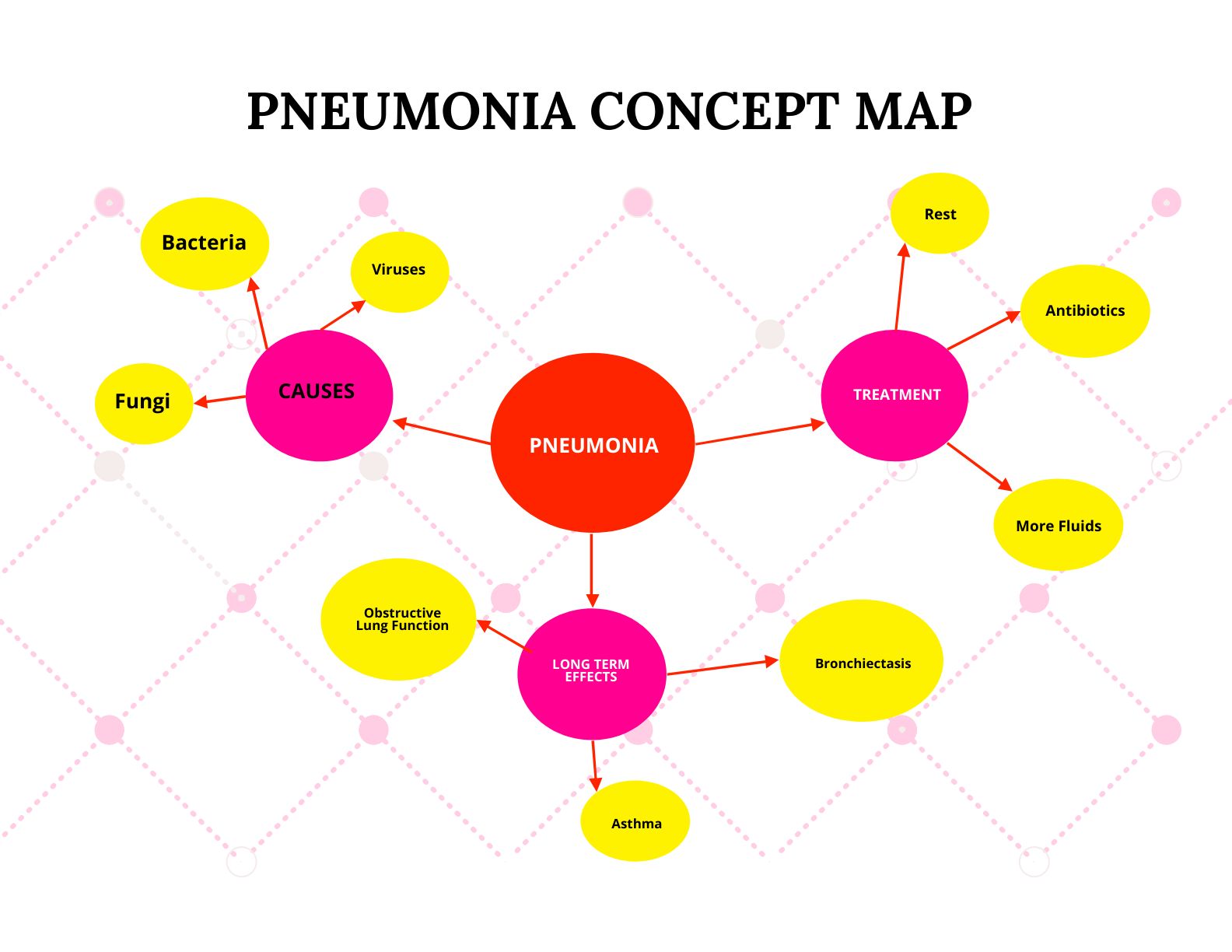
Pneumonia, an inflammation of the air sacs in the lungs, is a common and potentially serious illness that affects individuals of all ages. The complexity of this condition, encompassing various causes, symptoms, and treatment options, necessitates a clear and concise method of understanding and communicating its multifaceted nature. Enter the concept map, a visual representation of knowledge that aids in understanding complex topics by connecting related ideas and concepts.
The Power of Visual Representation
Concept maps, often described as "mind maps" or "knowledge maps," provide a structured and intuitive way to organize information. By arranging concepts within a hierarchical framework, they visually demonstrate the relationships between different elements, fostering deeper understanding and retention. In the context of pneumonia, concept maps serve as powerful tools for:
- Clarifying Complex Information: The intricate web of causes, symptoms, complications, and treatment options associated with pneumonia can be overwhelming. Concept maps break down this complexity by visually organizing key concepts and their connections, facilitating easier comprehension.
- Identifying Key Relationships: By depicting the interconnectedness of various aspects of pneumonia, concept maps highlight crucial relationships between different factors. For example, they illustrate how specific pathogens trigger inflammation, leading to characteristic symptoms and potentially serious complications.
- Enhancing Learning and Retention: The visual nature of concept maps aids in long-term retention of information. By actively engaging with the map, learners are encouraged to make connections and build a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
- Facilitating Communication: Concept maps serve as effective communication tools, enabling healthcare professionals to convey complex medical information to patients in a clear and understandable manner.
A Conceptual Framework for Pneumonia
A comprehensive concept map on pneumonia would typically include the following key categories:
1. Causes:
-
Infectious Agents:
- Bacteria: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Mycoplasma pneumoniae
- Viruses: Influenza virus, Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), Coronavirus
- Fungi: Pneumocystis jirovecii, Aspergillus fumigatus
-
Non-infectious Factors:
- Aspiration: Inhalation of foreign materials (e.g., food, vomit)
- Chemical Irritants: Smoke, fumes, dust
- Autoimmune Diseases: Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus
- Drug-induced: Certain medications, chemotherapy
2. Risk Factors:
- Age: Infants, young children, and older adults are more susceptible.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions like HIV/AIDS, organ transplantation, and certain medications compromise immune function.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Chronic lung diseases (e.g., asthma, COPD), heart disease, diabetes.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, alcohol abuse, poor nutrition.
3. Symptoms:
- Common Symptoms: Cough, fever, chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue
- Specific Symptoms: Wheezing, chills, rapid heart rate, disorientation, cyanosis (bluish skin)
4. Diagnosis:
- Physical Examination: Auscultation of the lungs, assessment of vital signs
- Imaging Studies: Chest X-ray, CT scan
- Laboratory Tests: Blood cultures, sputum cultures, blood gas analysis
5. Treatment:
- Antibiotics: For bacterial pneumonia
- Antivirals: For viral pneumonia
- Oxygen Therapy: To improve oxygen levels
- Supportive Care: Hydration, rest, pain relief
- Mechanical Ventilation: In severe cases
6. Complications:
- Pleural Effusion: Fluid accumulation in the space between the lungs and chest wall
- Empyema: Pus accumulation in the pleural space
- Respiratory Failure: Inability of the lungs to adequately oxygenate the blood
- Sepsis: Bloodstream infection
- Pneumonia-related Death: Mortality rates vary depending on severity and underlying health conditions.
7. Prevention:
- Vaccination: Pneumococcal vaccine, influenza vaccine
- Healthy Lifestyle: Quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, regular hand washing
- Environmental Measures: Avoiding exposure to smoke, dust, and other irritants
Unraveling the Mysteries: Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the difference between bacterial and viral pneumonia?
A: Bacterial pneumonia is typically caused by specific bacteria that infect the lungs, leading to inflammation and fluid buildup. Viral pneumonia, on the other hand, is caused by viruses that infect the respiratory system, resulting in inflammation and congestion.
Q: How is pneumonia diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies (chest X-ray or CT scan), and laboratory tests (blood cultures, sputum cultures).
Q: What are the treatment options for pneumonia?
A: Treatment depends on the underlying cause. Bacterial pneumonia is treated with antibiotics, while viral pneumonia may require antiviral medications. Supportive care, including oxygen therapy, hydration, and rest, is essential.
Q: Can pneumonia be prevented?
A: Vaccination against pneumococcal and influenza viruses is crucial for preventing these common causes of pneumonia. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including quitting smoking and washing hands frequently, also helps reduce the risk.
Tips for Understanding and Managing Pneumonia
- Stay Informed: Familiarize yourself with the causes, symptoms, and prevention strategies of pneumonia.
- Seek Medical Attention: If you experience symptoms suggestive of pneumonia, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
- Follow Treatment Recommendations: Adhere to prescribed medications and follow your doctor’s instructions for recovery.
- Practice Preventive Measures: Get vaccinated against pneumococcal and influenza viruses, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and avoid exposure to smoke and other irritants.
- Seek Support: Reach out to family, friends, or support groups for emotional and practical assistance during recovery.
Conclusion
Concept maps offer a powerful visual tool for understanding and communicating the complex nature of pneumonia. By organizing key concepts and highlighting their interconnectedness, these maps facilitate learning, retention, and communication of crucial information about this common and potentially serious illness. By embracing the power of visual representation, we can navigate the labyrinth of pneumonia with greater clarity and confidence, ultimately improving patient care and promoting health outcomes.



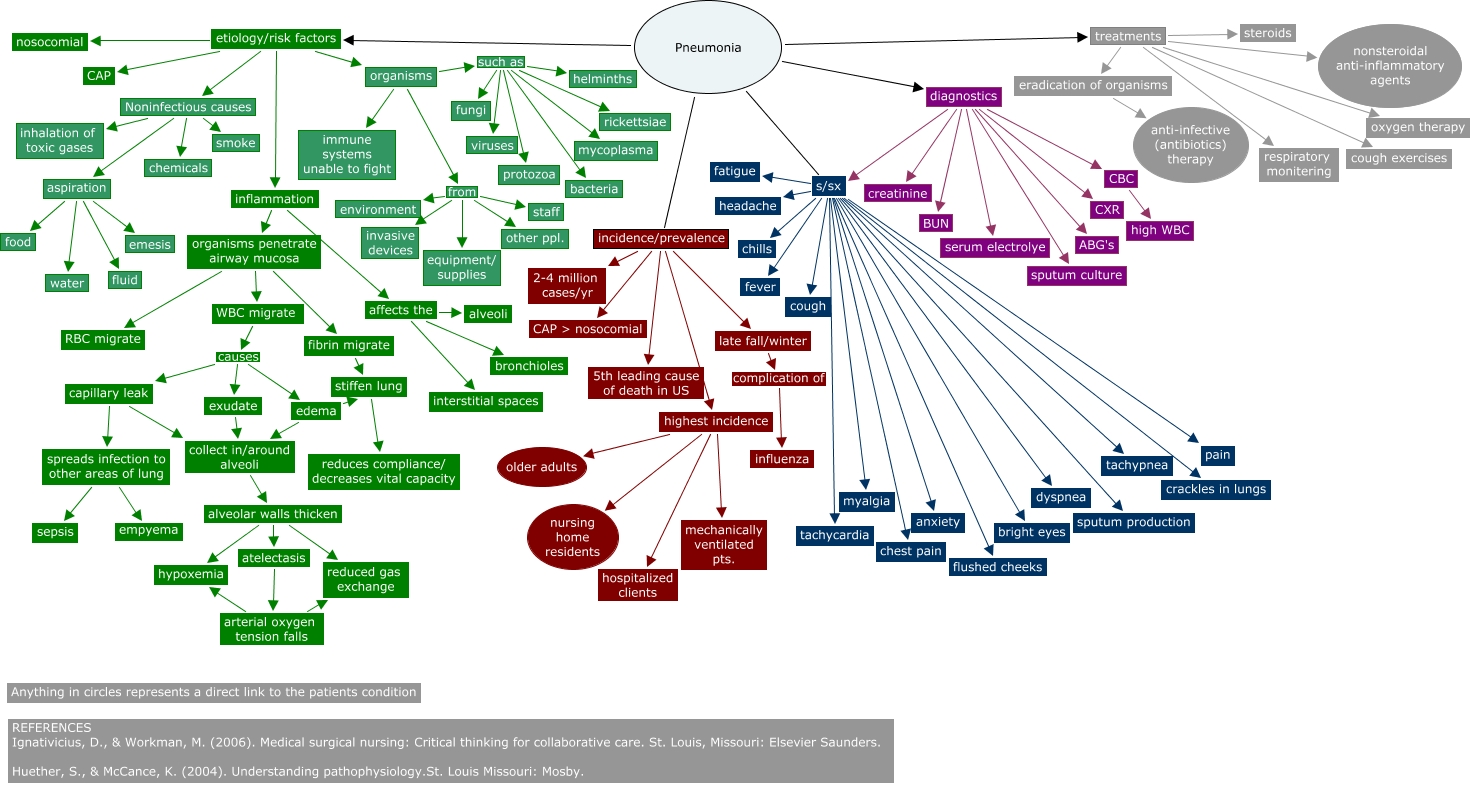


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Labyrinth of Pneumonia: A Visual Guide with Concept Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!