Navigating the Landscape of Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to its Provinces
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to its Provinces
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to its Provinces. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to its Provinces

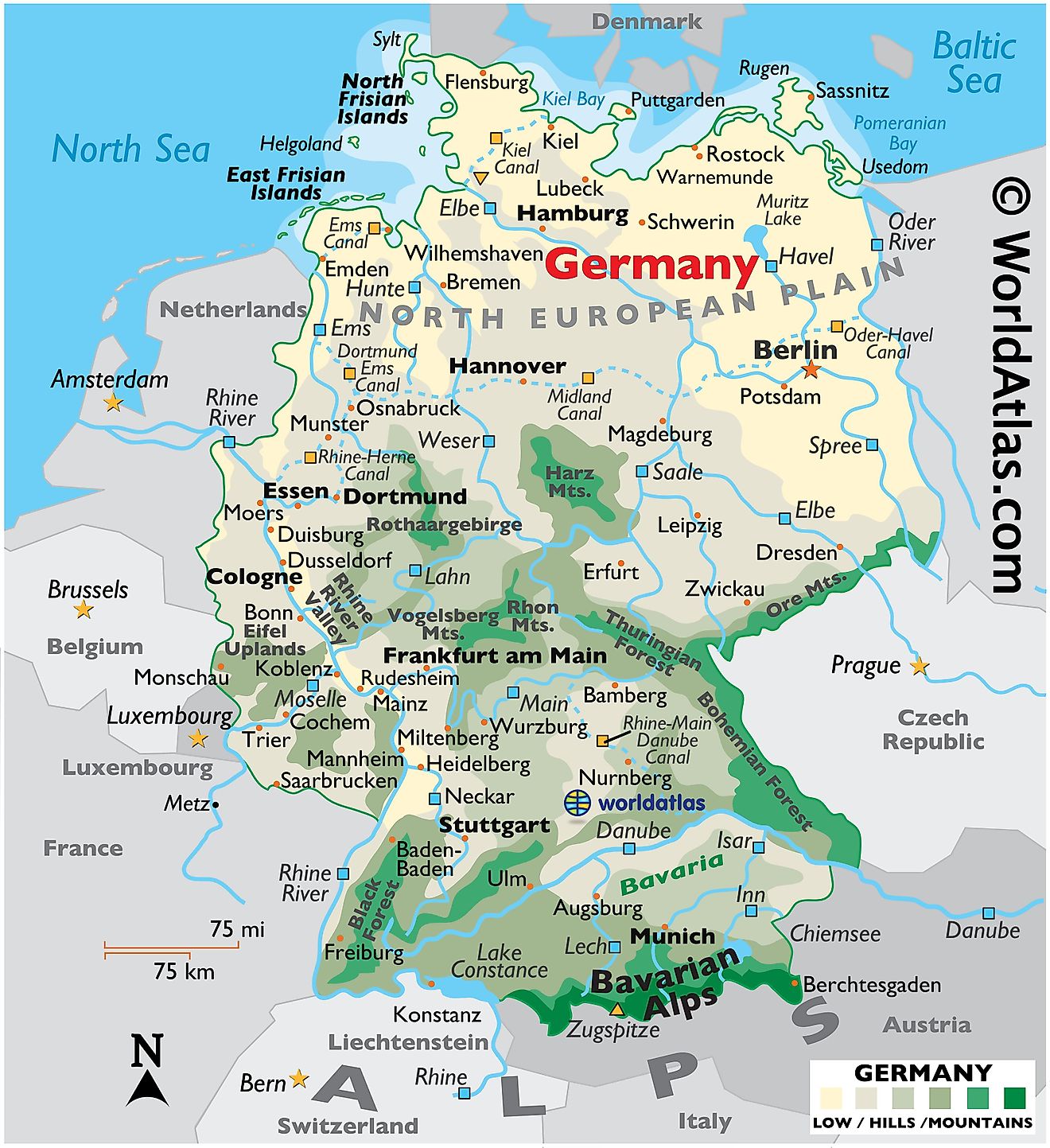
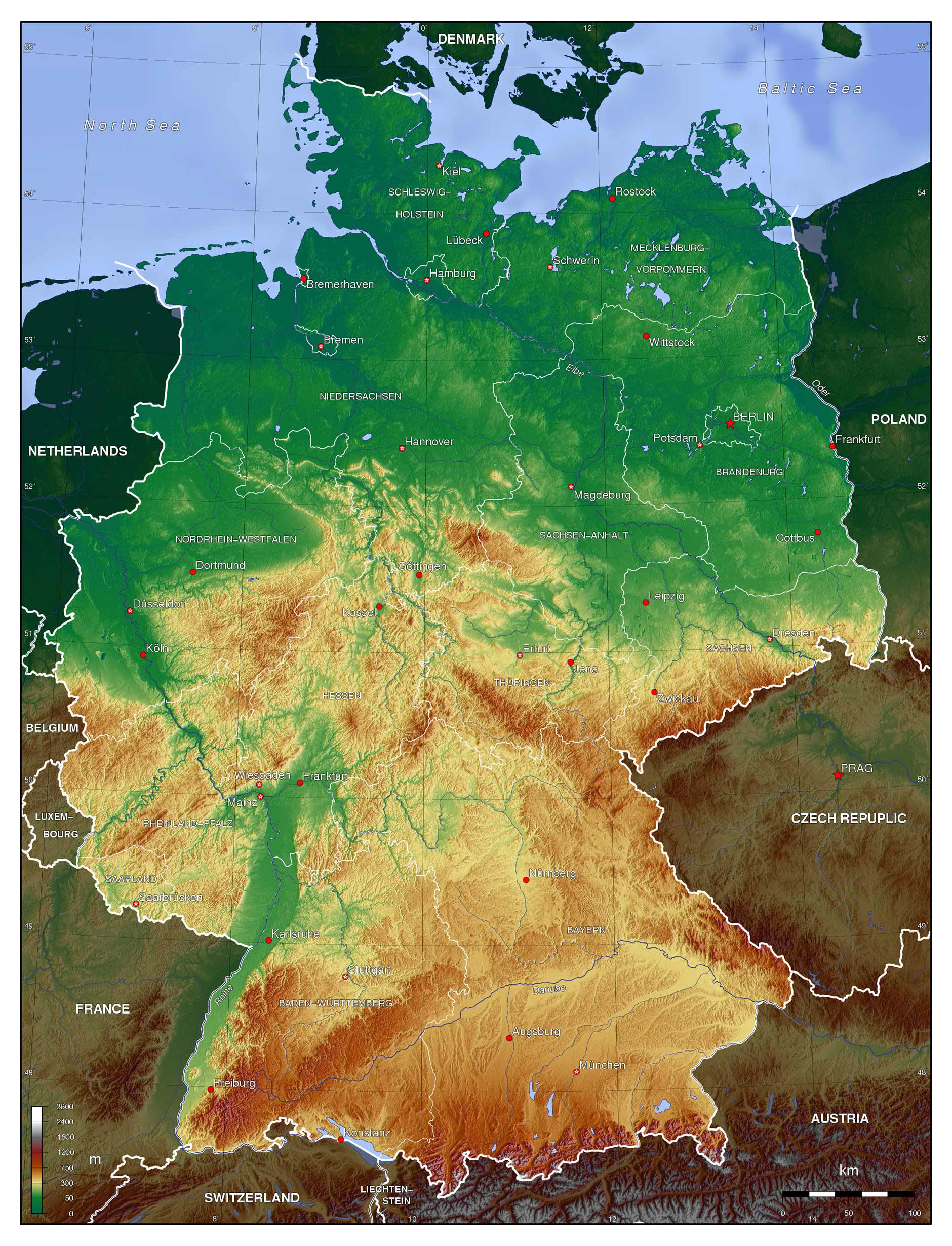
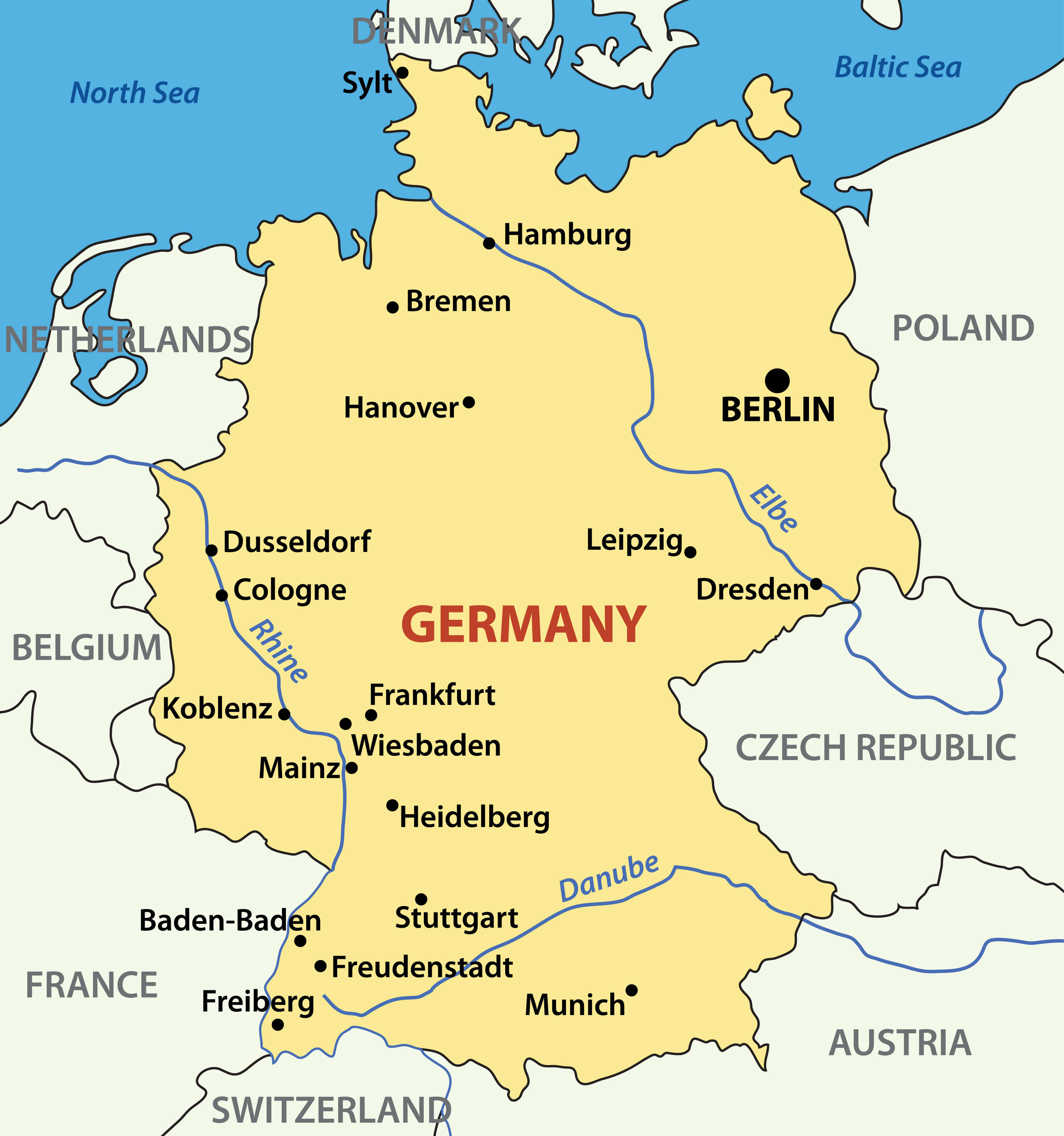
Germany, a nation renowned for its rich history, vibrant culture, and diverse landscapes, is geographically divided into 16 federal states, known as Länder. Understanding these provinces, their unique characteristics, and their relationship to the federal government is crucial for comprehending Germany’s political structure, cultural diversity, and regional identities. This article delves into the intricacies of Germany’s provinces, providing a comprehensive overview of their geographical distribution, historical significance, and distinct features.
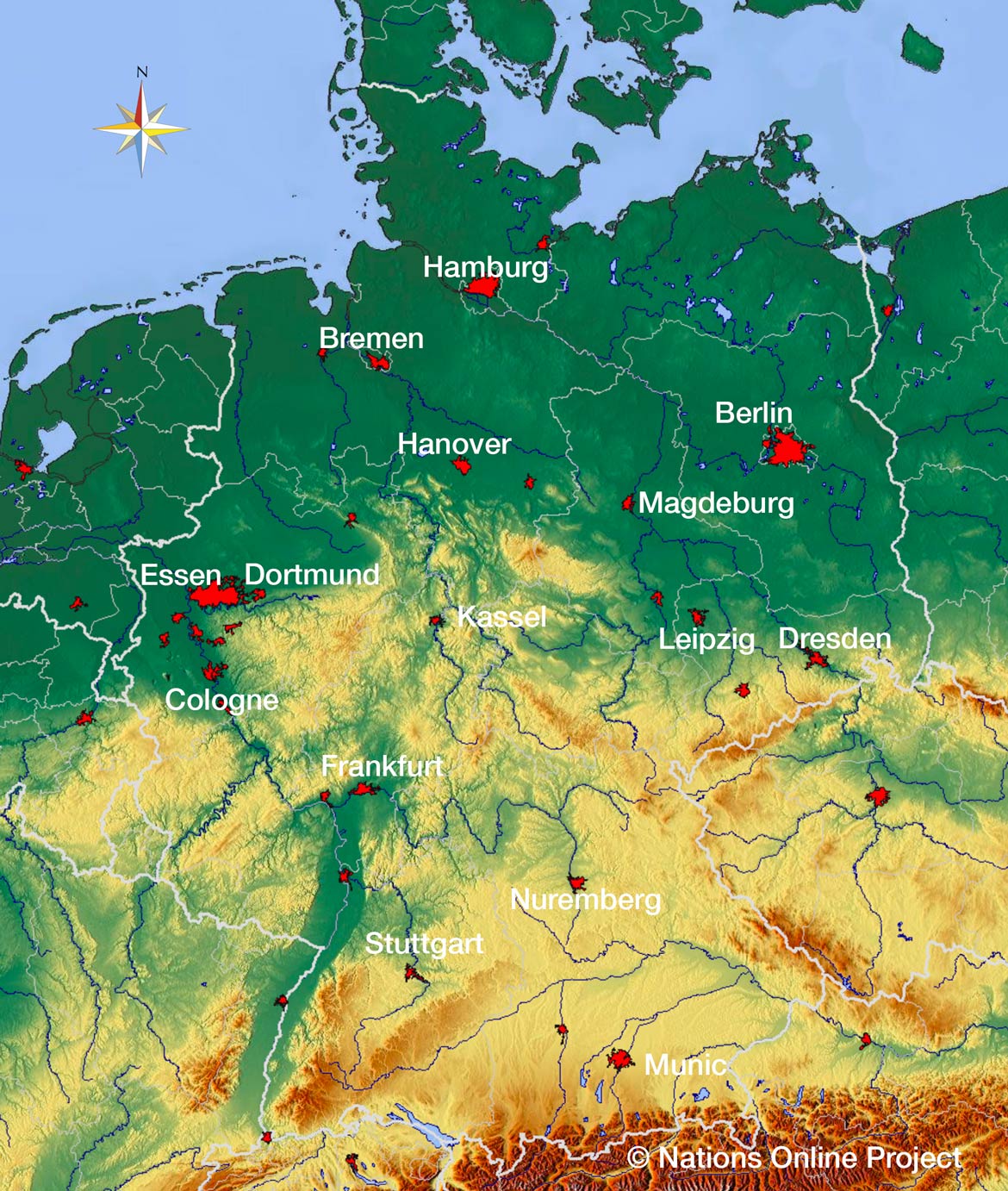
A Mosaic of Regions: The 16 Länder of Germany
The map of Germany’s provinces reveals a tapestry of distinct regions, each with its own history, culture, and economic strengths. From the bustling metropolises of Berlin and Hamburg to the picturesque countryside of Bavaria and Saxony, the German landscape offers a remarkable array of experiences.
North and East:
- Schleswig-Holstein: Located in the north, Schleswig-Holstein boasts a coastline along the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, known for its picturesque beaches and islands. Its agricultural heritage is evident in its dairy industry and its traditional farms.
- Mecklenburg-Vorpommern: This state shares a border with the Baltic Sea, offering stunning coastal landscapes and serene lakes. Its history is deeply intertwined with the Hanseatic League, a medieval trading network.
- Brandenburg: Encompassing the capital city of Berlin, Brandenburg is a state of sprawling forests, lakes, and historic castles. It plays a significant role in German agriculture and industry.
- Berlin: As the capital city, Berlin is a cultural and political hub, known for its iconic landmarks, vibrant art scene, and diverse population. It is a melting pot of history and modernity.
- Saxony-Anhalt: Located in the east, Saxony-Anhalt is a state of rolling hills, historic castles, and charming towns. It is renowned for its rich cultural heritage and its contributions to the automotive industry.
- Thuringia: This state is characterized by its picturesque countryside, historic castles, and vibrant cultural life. It is known for its traditional crafts and its contributions to the German manufacturing sector.
- Saxony: Situated in the southeast, Saxony is a state of rich industrial history, known for its mining and manufacturing industries. It is also a cultural hub, with a strong tradition in music and arts.
West and South:
- Lower Saxony: Situated in the northwest, Lower Saxony is a state of diverse landscapes, ranging from the North Sea coast to the Harz Mountains. It is known for its agricultural heritage and its automotive industry.
- North Rhine-Westphalia: As the most populous state, North Rhine-Westphalia is a major industrial and economic powerhouse, with a strong presence in the automotive, chemical, and steel industries. It is also home to a significant number of universities and research institutions.
- Hesse: Located in the center of Germany, Hesse is a state of rolling hills, historic castles, and vibrant cities. It is known for its financial sector, its manufacturing industry, and its rich cultural heritage.
- Rhineland-Palatinate: Situated in the southwest, Rhineland-Palatinate is a state of vineyards, historic castles, and scenic landscapes. It is renowned for its wine production, its tourism industry, and its cultural heritage.
- Baden-Württemberg: Located in the southwest, Baden-Württemberg is a state of rolling hills, forests, and charming towns. It is known for its automotive industry, its high-tech sector, and its vibrant cultural life.
- Bavaria: Situated in the southeast, Bavaria is the largest state in Germany, known for its stunning mountain scenery, its traditional culture, and its thriving economy. It is home to the Bavarian Alps, the famous Oktoberfest, and a strong presence in the tourism and manufacturing sectors.
- Hamburg: As a city-state, Hamburg is a major port city and a global hub for trade and commerce. It is known for its vibrant harbor, its cultural institutions, and its diverse population.
- Bremen: Another city-state, Bremen is a historic port city with a rich maritime heritage. It is known for its shipbuilding industry, its cultural institutions, and its picturesque old town.
The Importance of Federalism
Germany’s federal system, with its division into Länder, is a cornerstone of its political structure and a key factor in its economic success. Each province enjoys a significant degree of autonomy, managing its own affairs in areas such as education, culture, and infrastructure. This decentralized approach fosters regional diversity, encourages innovation, and allows for tailored solutions to local challenges.
Benefits of a Federal System:
- Regional Autonomy: Each Land has its own parliament, government, and budget, allowing for localized decision-making and tailored solutions to specific regional needs.
- Diversity and Innovation: The decentralized structure encourages diversity and innovation, as each Land can pursue its own unique strengths and priorities.
- Economic Growth: The autonomy of the Länder fosters competition and innovation, driving economic growth and creating a dynamic and adaptable economy.
- Political Stability: The federal system provides a balance of power, ensuring that no single entity holds too much authority and fostering political stability.
Understanding the Map: A Guide to Regional Identities
Beyond their political and economic significance, Germany’s provinces are also deeply rooted in cultural and historical identities. The map of Germany’s provinces is not just a geographical representation; it is a reflection of the country’s rich tapestry of traditions, dialects, and cultural expressions.
- Regional Dialects: Germany is known for its diverse dialects, and each Land often has its own unique linguistic variations, adding another layer of cultural richness to the country.
- Traditional Cuisine: Each Land has its own culinary specialties, from the hearty Bavarian dishes to the lighter fare of the north.
- Architectural Styles: From the half-timbered houses of the north to the grand Baroque palaces of the south, the architecture of each Land reflects its unique history and cultural influences.
- Cultural Events and Festivals: Each Land celebrates its own unique traditions through festivals, celebrations, and cultural events that showcase its rich heritage.
FAQs: Navigating the Provinces
Q: What is the largest Land in Germany?
A: Bavaria, with its stunning mountain scenery and vibrant culture, is the largest Land in Germany.
Q: What is the most populous Land in Germany?
A: North Rhine-Westphalia, a major industrial and economic powerhouse, is the most populous Land in Germany.
Q: What are the major industries in each Land?
A: Each Land has its own economic strengths. For example, Bavaria is known for its automotive industry, while Hamburg is a major port city and global hub for trade and commerce.
Q: How do the Länder interact with the federal government?
A: The Länder have a significant degree of autonomy, but they also work closely with the federal government on issues of national importance. The Bundesrat, the upper house of the German parliament, represents the interests of the Länder in the federal legislative process.
Tips for Exploring Germany’s Provinces
- Plan your itinerary based on your interests: Whether you’re interested in history, culture, nature, or gastronomy, each Land offers unique experiences.
- Learn a few basic phrases in the local dialect: This will enhance your interactions with locals and add an extra layer of cultural immersion to your trip.
- Sample local cuisine: Each Land has its own culinary specialties, so be sure to try some regional dishes and drinks.
- Visit local museums and cultural institutions: These offer insights into the history, art, and culture of each Land.
- Explore the countryside: Many Länder offer stunning natural landscapes, from rolling hills to mountain ranges, perfect for hiking, biking, or simply enjoying the fresh air.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Diversity and Unity
The map of Germany’s provinces is a testament to the country’s rich history, cultural diversity, and economic dynamism. Each Land, with its unique characteristics and contributions, contributes to the overall tapestry of German identity. Understanding the provinces, their individual strengths, and their relationship to the federal government is crucial for appreciating the complexity and beauty of this fascinating nation. As you navigate the diverse landscapes and vibrant cultures of Germany, remember that each province holds its own story, waiting to be discovered.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Germany: A Comprehensive Guide to its Provinces. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!