Navigating the North: Exploring the Geography and Significance of Northern Germany
Related Articles: Navigating the North: Exploring the Geography and Significance of Northern Germany
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the North: Exploring the Geography and Significance of Northern Germany. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the North: Exploring the Geography and Significance of Northern Germany
Northern Germany, a region often associated with the North Sea coast, Hanseatic history, and picturesque landscapes, presents a unique and captivating tapestry of geography, culture, and economic activity. Its diverse terrain, ranging from the flat expanses of the North German Plain to the rolling hills of the Schleswig-Holstein region, offers a diverse and visually compelling landscape. This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of Northern Germany, highlighting its distinctive features, historical significance, and contemporary relevance.
A Geographic Overview
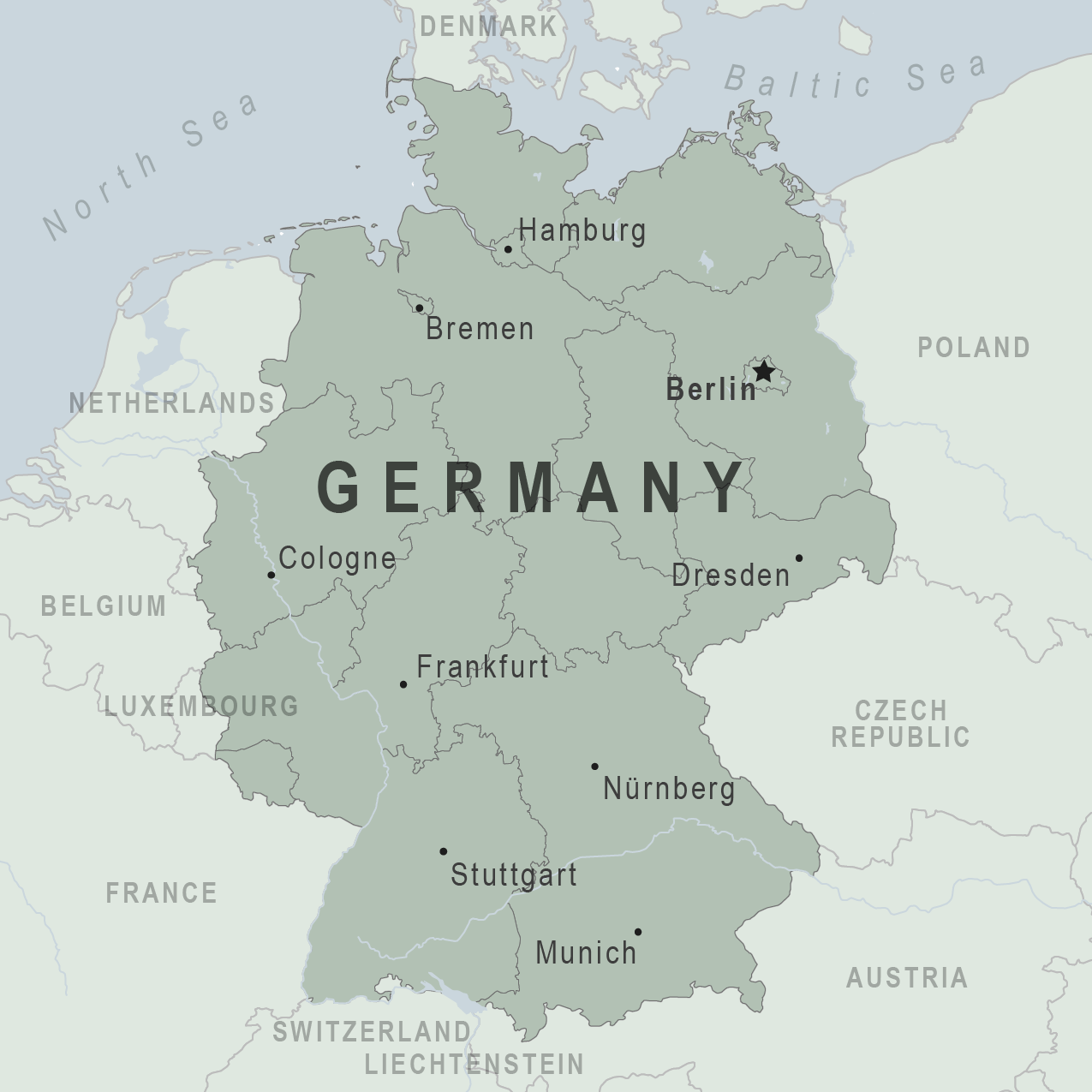
Northern Germany, encompassing the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Hamburg, Bremen, Lower Saxony, and parts of Brandenburg, occupies the northernmost portion of the Federal Republic of Germany. The region’s most defining feature is its extensive coastline, stretching along the North Sea and Baltic Sea, offering a rich tapestry of sandy beaches, picturesque islands, and bustling port cities.
The North German Plain, a vast expanse of flat land, dominates the eastern and central portions of Northern Germany. This fertile region, characterized by its rolling hills and agricultural landscapes, has been a vital source of food production for centuries. The region also features extensive forests, particularly in the north-eastern regions of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, providing important ecological services and timber resources.
The southern boundary of Northern Germany is marked by the Elbe River, a significant waterway that has historically served as a crucial trade route and transportation artery. The river’s presence has fostered the development of major cities like Hamburg and Magdeburg, shaping the region’s economic and cultural landscape.
Historical Significance
Northern Germany holds a rich and complex history, deeply intertwined with the development of the German nation. The region’s strategic location along the Baltic and North Seas has long made it a vital hub for trade and cultural exchange. The Hanseatic League, a powerful medieval trading alliance, played a crucial role in shaping the region’s economic and political landscape.
The historical city of Lübeck, located on the Baltic coast, served as the heart of the Hanseatic League, showcasing the region’s economic prowess and influence. The league’s legacy continues to be evident in the architecture, trade traditions, and cultural identity of many Northern German cities.
The region also witnessed significant events during the Reformation, with the city of Wittenberg, located in Saxony-Anhalt, serving as the birthplace of Martin Luther’s revolutionary ideas. The Reformation’s impact on Northern Germany was profound, shaping its religious landscape and fostering a sense of cultural independence.
Contemporary Relevance
Northern Germany continues to hold significant relevance in the modern era, playing a crucial role in the German economy and contributing to the nation’s cultural and social fabric.
The region’s coastal location has fostered the development of important maritime industries, including shipping, shipbuilding, and offshore wind energy. The ports of Hamburg and Bremerhaven, among the busiest in Europe, serve as vital hubs for international trade and transportation.
Northern Germany also boasts a strong manufacturing sector, with major industries including automotive production, aerospace, and electronics. The region’s well-developed infrastructure, skilled workforce, and proximity to other European markets make it an attractive location for businesses.
Cultural Tapestry
Northern Germany is renowned for its distinctive cultural identity, shaped by its maritime history, Hanseatic heritage, and unique traditions. The region’s cuisine reflects its proximity to the sea, with seafood dishes like Labskaus and Matjes herring being local favorites.
The region’s cultural landscape is also enriched by its numerous museums, theaters, and music venues. The city of Hamburg, known for its vibrant music scene, hosts world-renowned operas, ballets, and concerts. The region’s historical significance is evident in its many castles, churches, and medieval city centers, offering a glimpse into Germany’s rich past.
Exploring the Region: A Guide to Northern Germany
Hamburg: The bustling port city of Hamburg, Germany’s second-largest city, offers a vibrant blend of history, culture, and modern life. Explore the historic Speicherstadt, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, wander through the trendy HafenCity district, and enjoy the city’s lively nightlife.
Lübeck: This historic Hanseatic city, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, offers a glimpse into the region’s medieval past. Explore its well-preserved city walls, admire the iconic Holstentor gate, and delve into the city’s rich history at the Lübeck Museum.
Bremen: This charming port city, known for its unique Bremen Town Musicians statue, boasts a rich history and cultural heritage. Explore the historic Schnoor district, visit the Bremen Cathedral, and enjoy the city’s vibrant maritime atmosphere.
Schleswig-Holstein: This region, located in the north of Germany, offers a stunning coastline, picturesque islands, and charming towns. Visit the historic city of Kiel, explore the island of Sylt, and enjoy the region’s natural beauty.
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern: This region, known for its extensive coastline and tranquil lakes, offers a serene escape from the hustle and bustle of city life. Explore the Baltic Sea coast, visit the historic city of Rostock, and enjoy the region’s natural beauty.
Lower Saxony: This region, located in the heart of Northern Germany, offers a diverse landscape, from the North Sea coast to the Harz Mountains. Visit the historic city of Hannover, explore the Lüneburg Heath, and enjoy the region’s natural beauty.
FAQs about Northern Germany:
What is the climate like in Northern Germany?
Northern Germany experiences a temperate climate with mild winters and warm summers. The region is known for its frequent rainfall and occasional strong winds.
What are the main languages spoken in Northern Germany?
The main language spoken in Northern Germany is German. However, some regional dialects and Low German are also spoken in certain areas.
What are the major industries in Northern Germany?
Northern Germany’s major industries include maritime, manufacturing, tourism, and agriculture. The region is also a major hub for renewable energy, particularly offshore wind energy.
What are some popular tourist attractions in Northern Germany?
Some popular tourist attractions in Northern Germany include the city of Hamburg, the island of Sylt, the Lüneburg Heath, and the Baltic Sea coast.
Tips for Visiting Northern Germany:
- Plan your trip in advance: Northern Germany is a large region with many attractions, so it’s essential to plan your trip in advance.
- Consider the weather: Northern Germany is known for its frequent rainfall, so pack accordingly.
- Explore the region’s culinary scene: Northern Germany offers a unique and delicious cuisine, with seafood dishes being a local specialty.
- Learn some basic German phrases: While English is widely spoken, learning a few basic German phrases can enhance your travel experience.
- Take advantage of public transportation: Northern Germany has a well-developed public transportation system, making it easy to get around.
Conclusion
Northern Germany, a region steeped in history, vibrant culture, and economic dynamism, offers a compelling destination for travelers and businesses alike. Its diverse landscape, from the sandy beaches of the North Sea coast to the rolling hills of the North German Plain, presents a captivating tapestry of natural beauty and cultural heritage. The region’s historical significance, evidenced by its Hanseatic past and Reformation legacy, continues to shape its identity and influence its contemporary relevance. As a vital hub for trade, innovation, and cultural expression, Northern Germany remains an integral part of the German landscape, offering a unique and rewarding experience for those seeking to explore its diverse offerings.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the North: Exploring the Geography and Significance of Northern Germany. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!