Navigating the Political Landscape of Western Europe: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating the Political Landscape of Western Europe: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Political Landscape of Western Europe: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Political Landscape of Western Europe: A Comprehensive Guide
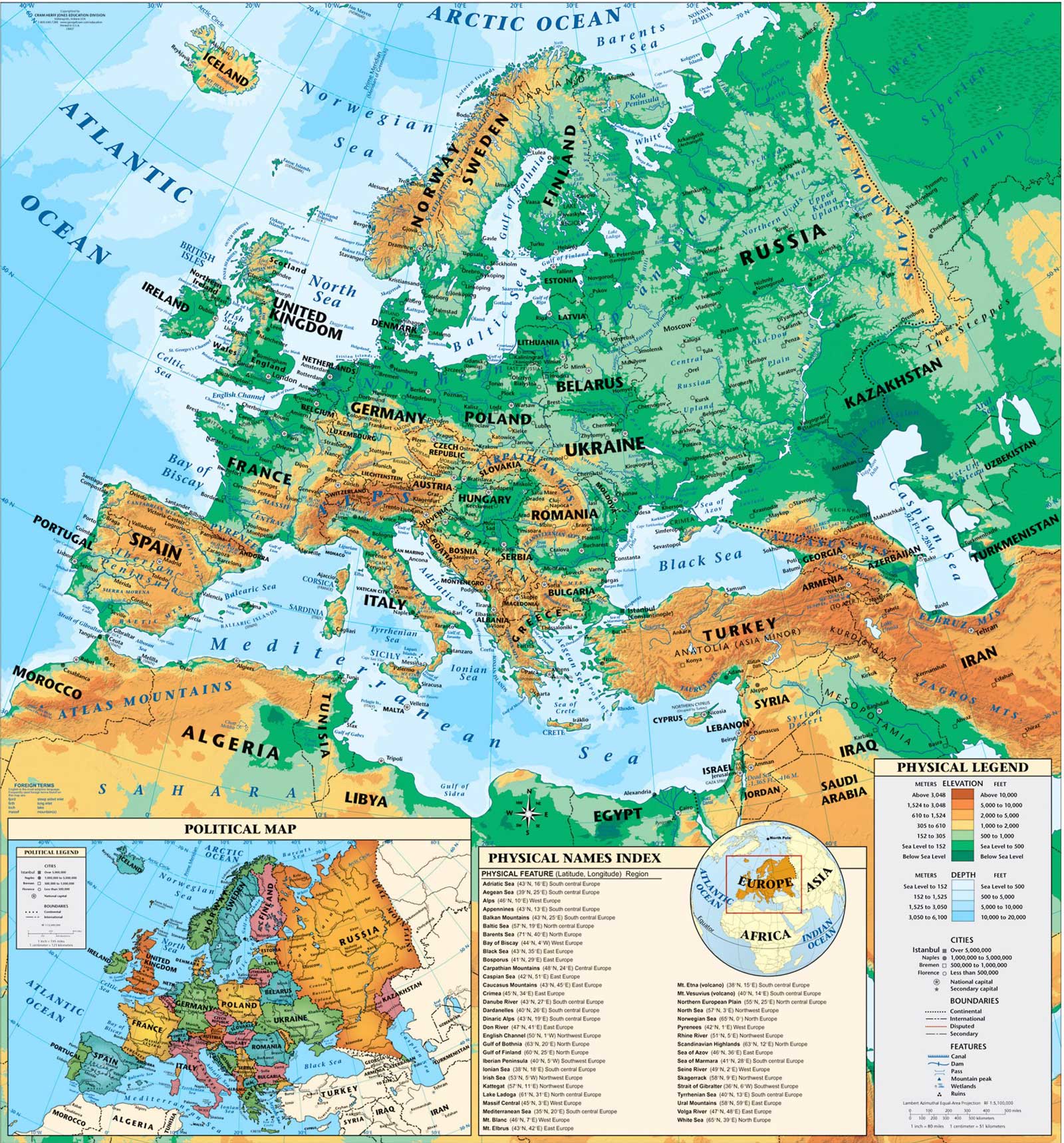
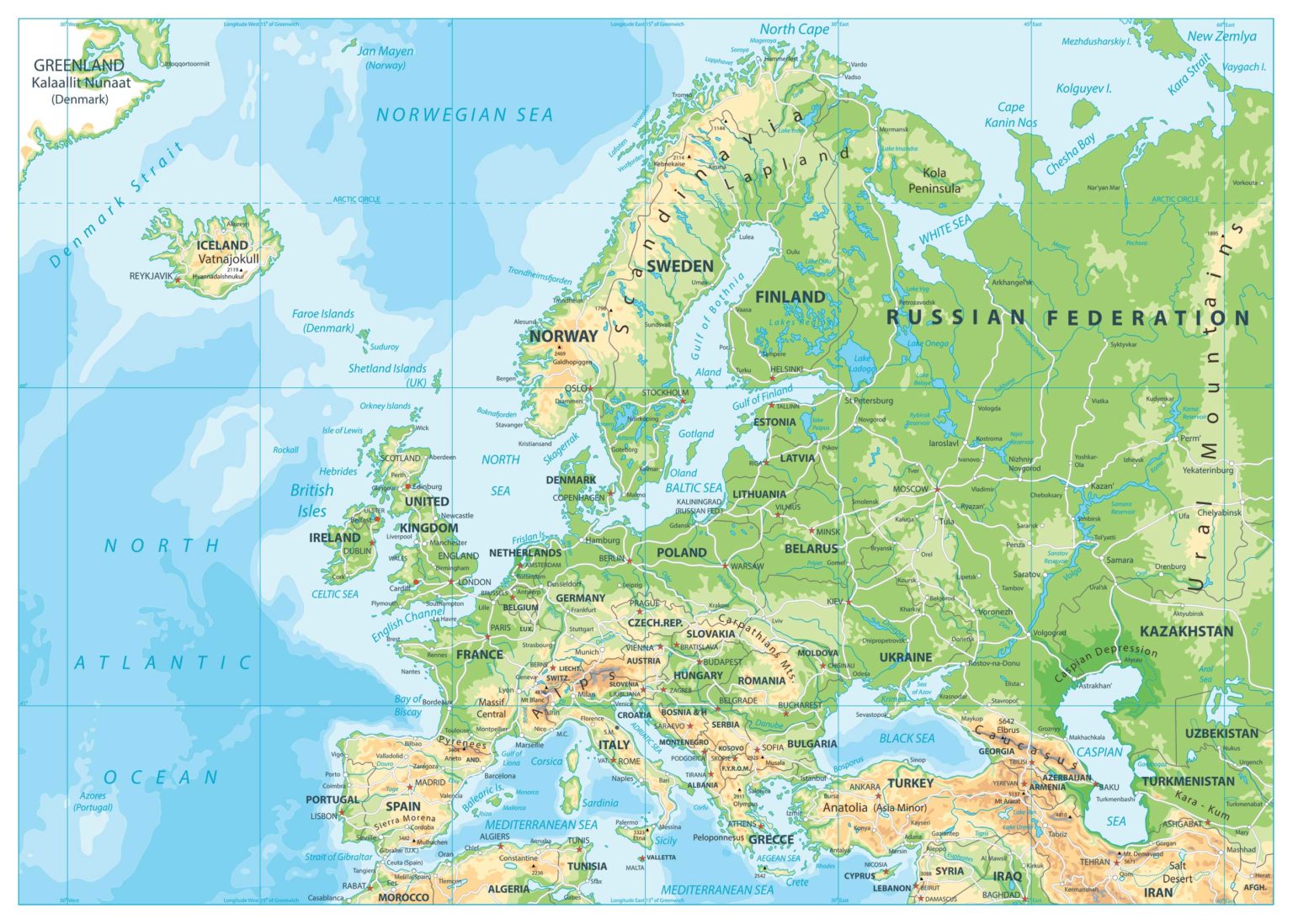
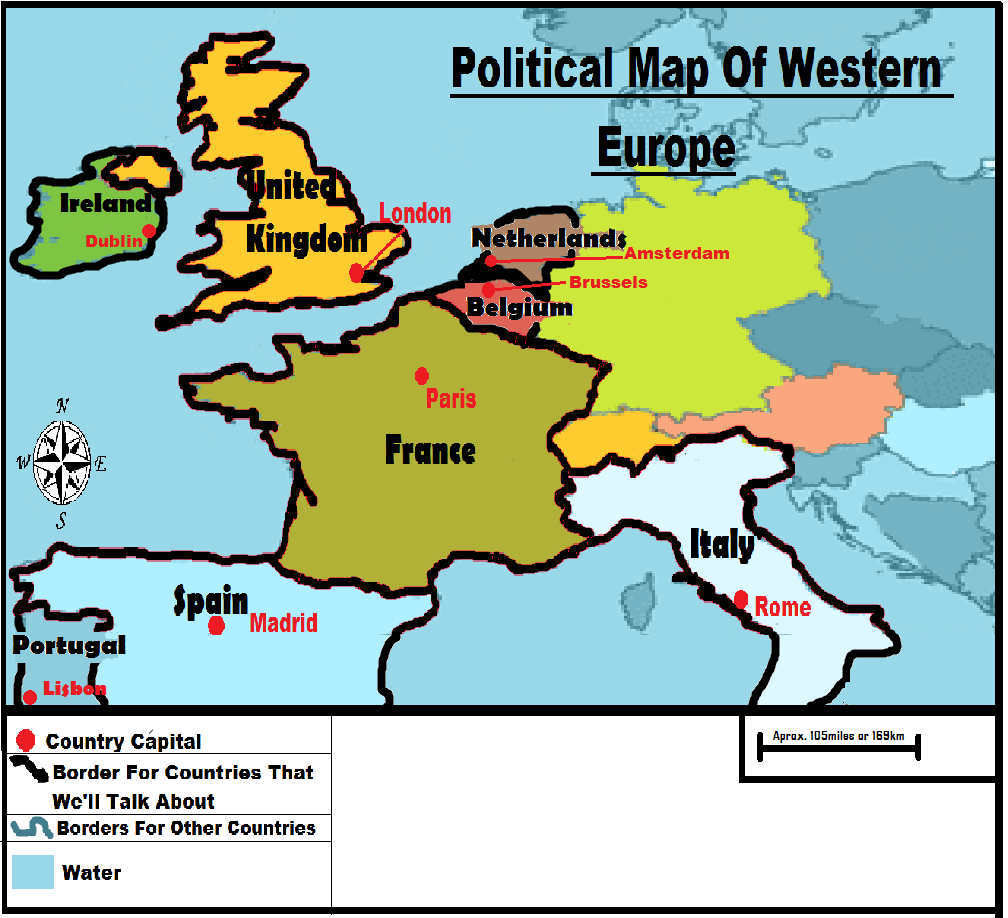
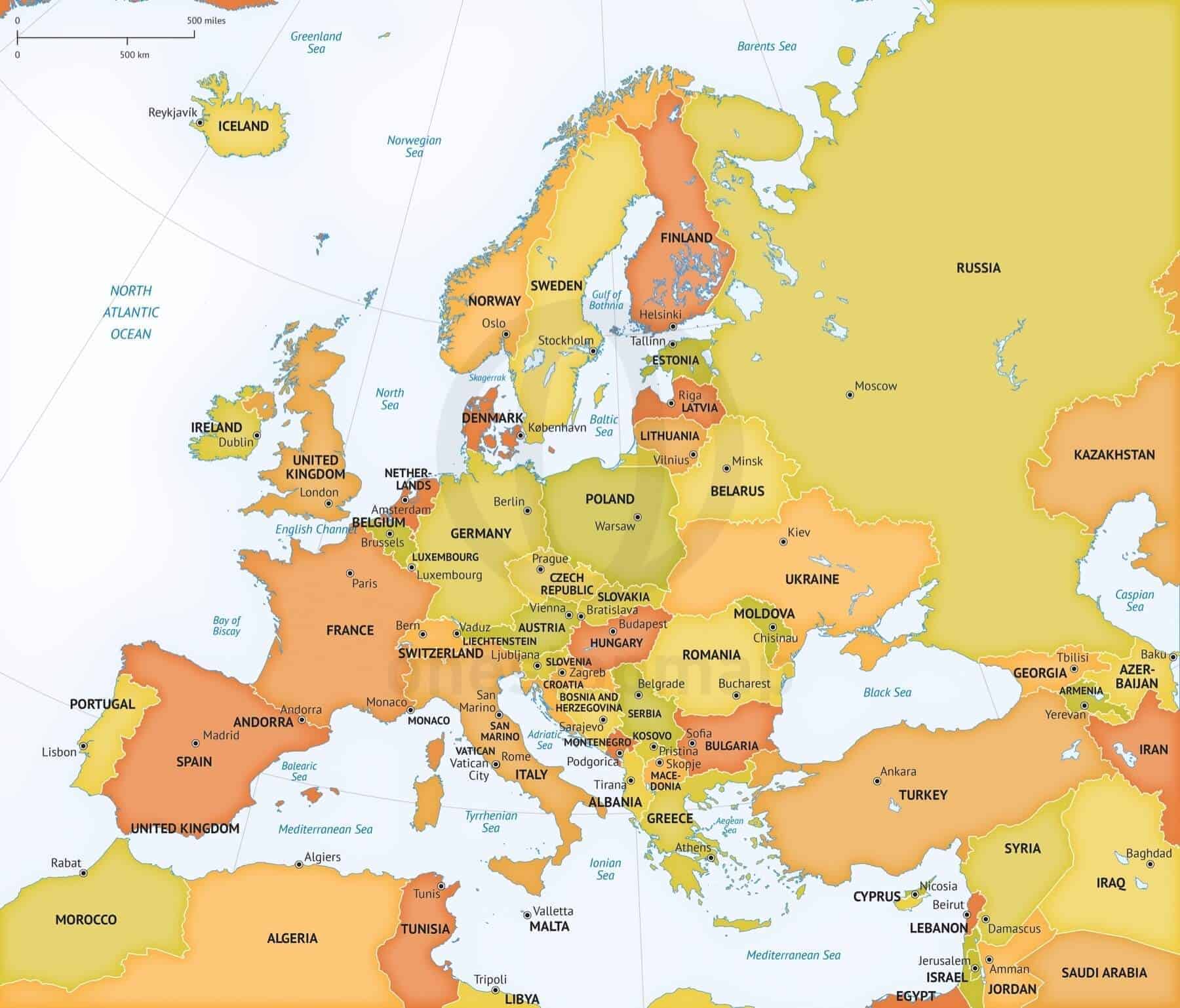
Western Europe, a region teeming with history, culture, and diverse political systems, presents a fascinating tapestry of nations and their intricate relationships. Understanding the political map of Western Europe is crucial for comprehending the region’s political dynamics, its role in global affairs, and the challenges it faces. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the region’s political landscape, highlighting its key features and complexities.
A Mosaic of Political Systems:
Western Europe boasts a diverse array of political systems, reflecting its rich history and evolving political landscape. The region is predominantly home to parliamentary democracies, where the executive branch (government) is accountable to the legislative branch (parliament). This system is prevalent in countries like the United Kingdom, France, Germany, and Italy, where the head of government, usually a Prime Minister, is appointed by the parliament and can be removed by a vote of no confidence.
However, Western Europe also features constitutional monarchies, such as the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Belgium, Spain, and Denmark, where a monarch serves as the head of state, though their powers are largely ceremonial. These countries have evolved to combine a strong tradition of monarchy with democratic principles, with the monarch acting as a symbol of national unity and stability.
Furthermore, some countries, such as Switzerland, operate under a direct democracy model, where citizens directly participate in decision-making through referendums and initiatives. This system allows for greater citizen involvement in shaping the political landscape, fostering a sense of direct accountability.
Key Political Actors and their Interplay:
The political map of Western Europe is not merely a static representation of borders and governments; it encompasses a complex interplay of actors and institutions that shape regional and global affairs.
- The European Union (EU): The EU stands as a significant force in Western European politics, integrating its member states through economic, political, and social cooperation. The EU’s institutions, such as the European Parliament, the European Commission, and the European Council, play a crucial role in shaping policies on trade, immigration, and security, influencing the political landscape of its member states.
- NATO: The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), a military alliance formed after World War II, remains a key player in Western European security. NATO’s commitment to collective defense ensures the security of its members, while its involvement in international peacekeeping and crisis management operations has significant global implications.
- National Governments: Each Western European nation possesses its own unique political system, with distinct political parties, ideologies, and priorities. The interactions between these governments shape the region’s policies, with agreements and disagreements influencing everything from trade negotiations to environmental protection.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The political map of Western Europe is not without its challenges. The region grapples with issues like:
- Economic Inequality: Despite its overall economic strength, Western Europe faces growing economic inequality, with disparities in wealth and income persisting across nations and within individual countries.
- Immigration and Integration: The influx of migrants from various parts of the world has sparked debates on immigration policies and the integration of newcomers into society, posing complex challenges for governments.
- Political Polarization: The rise of populism and nationalist movements across Western Europe has led to increased political polarization, with diverging views on issues like globalization, immigration, and national identity.
- Climate Change: The impact of climate change poses significant challenges for Western European nations, requiring coordinated efforts to mitigate its effects and adapt to its consequences.
However, Western Europe also possesses remarkable strengths and opportunities:
- Strong Economic Foundation: The region’s robust economies, characterized by technological innovation, skilled labor, and a highly developed infrastructure, provide a platform for growth and prosperity.
- Democratic Values: Western Europe’s commitment to democratic principles, including free and fair elections, the rule of law, and human rights, serves as a beacon of hope for other regions struggling with authoritarianism and political instability.
- International Cooperation: The EU and NATO provide frameworks for Western European nations to collaborate on shared challenges and promote common interests on the global stage.
- Cultural Diversity: The region’s rich cultural tapestry, encompassing a variety of languages, traditions, and perspectives, fosters innovation and creativity, contributing to its dynamic character.
FAQs by Political Map of Western Europe:
1. What is the most common political system in Western Europe?
The most prevalent political system in Western Europe is parliamentary democracy, where the executive branch (government) is accountable to the legislative branch (parliament).
2. How does the EU influence the political landscape of Western Europe?
The EU’s institutions play a significant role in shaping policies on trade, immigration, and security, influencing the political landscape of its member states. It promotes economic integration and cooperation, while also setting standards for human rights and environmental protection.
3. What are the key challenges facing Western Europe?
Western Europe faces challenges related to economic inequality, immigration and integration, political polarization, and climate change.
4. What are the strengths and opportunities of Western Europe?
Western Europe boasts a strong economic foundation, a commitment to democratic values, a framework for international cooperation, and cultural diversity.
Tips by Political Map of Western Europe:
- Focus on Key Actors: When studying the political map of Western Europe, pay attention to the major actors, including national governments, the EU, and NATO, and their interactions.
- Understand Historical Context: The political landscape of Western Europe is deeply rooted in its history, so understanding key historical events and their impact is crucial.
- Explore Different Perspectives: Recognize that diverse perspectives exist on political issues, and explore different viewpoints to gain a comprehensive understanding.
- Engage with Current Events: Stay informed about current events in Western Europe to stay up-to-date on the evolving political landscape.
Conclusion by Political Map of Western Europe:
The political map of Western Europe is a dynamic and evolving landscape, reflecting the region’s complex history, diverse political systems, and ongoing challenges. Understanding its intricate tapestry of nations, institutions, and political ideologies is crucial for grasping the region’s role in global affairs and the challenges it faces. By focusing on key actors, historical context, diverse perspectives, and current events, individuals can develop a comprehensive understanding of Western Europe’s political landscape and its significance in the world.

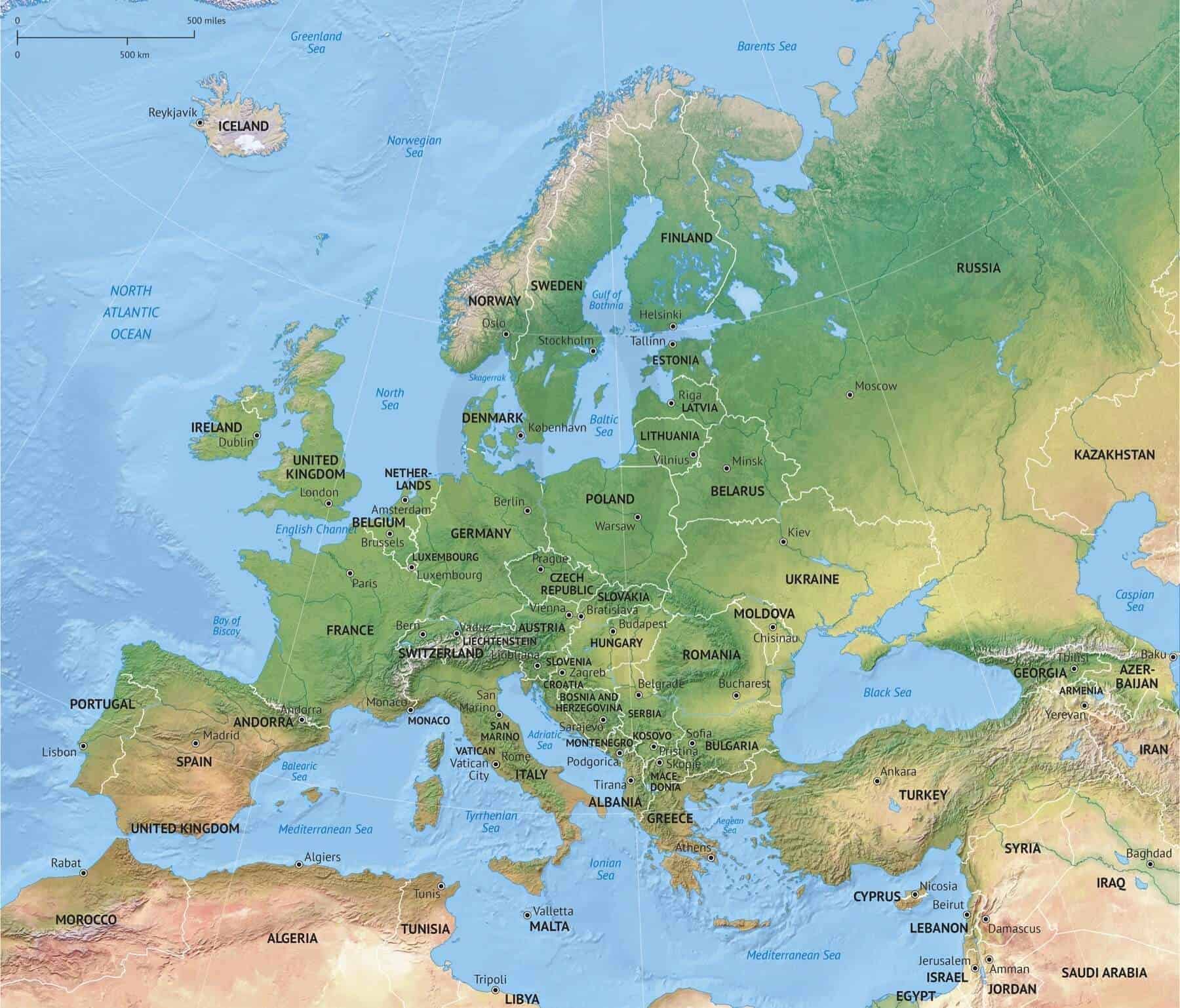
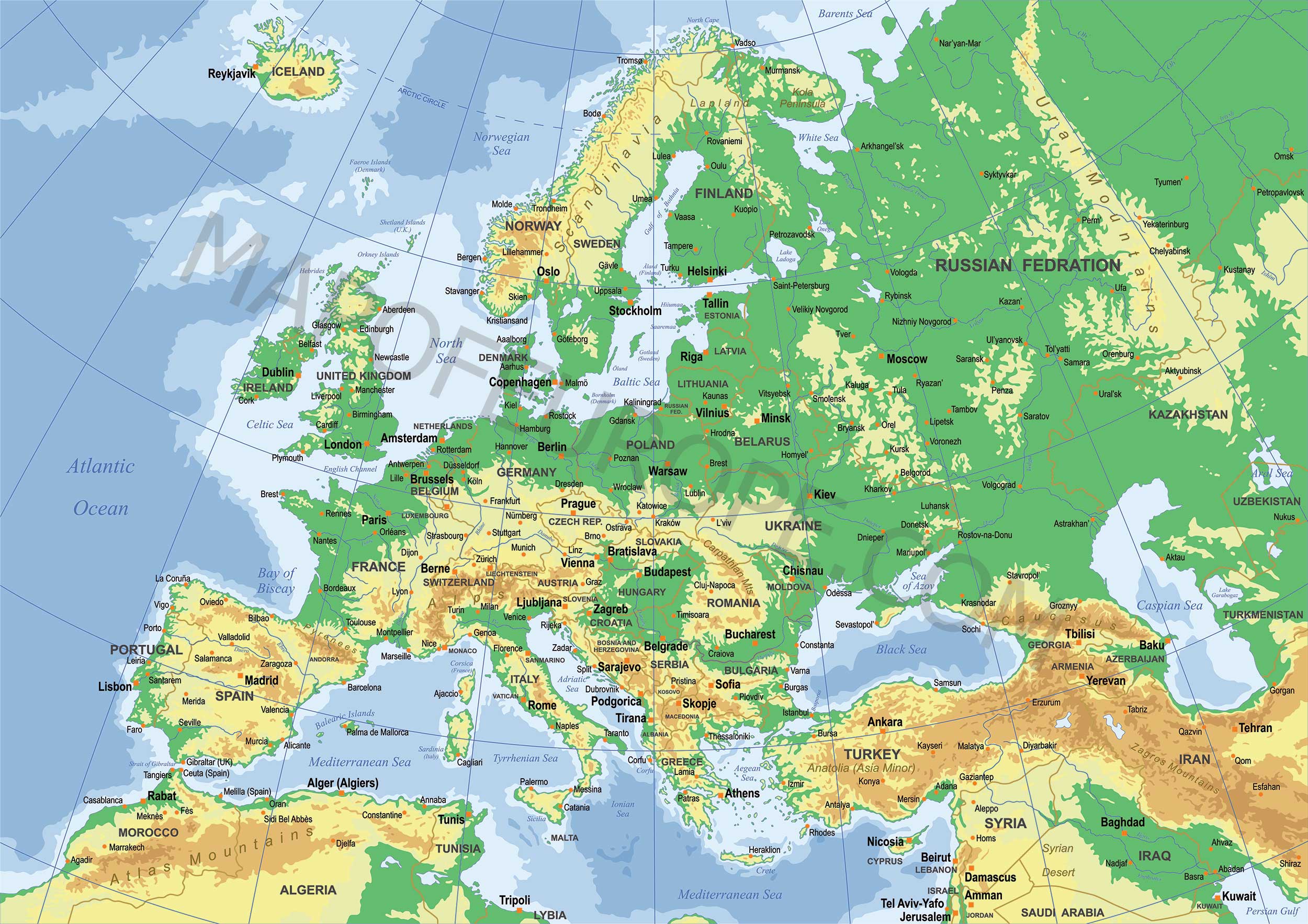
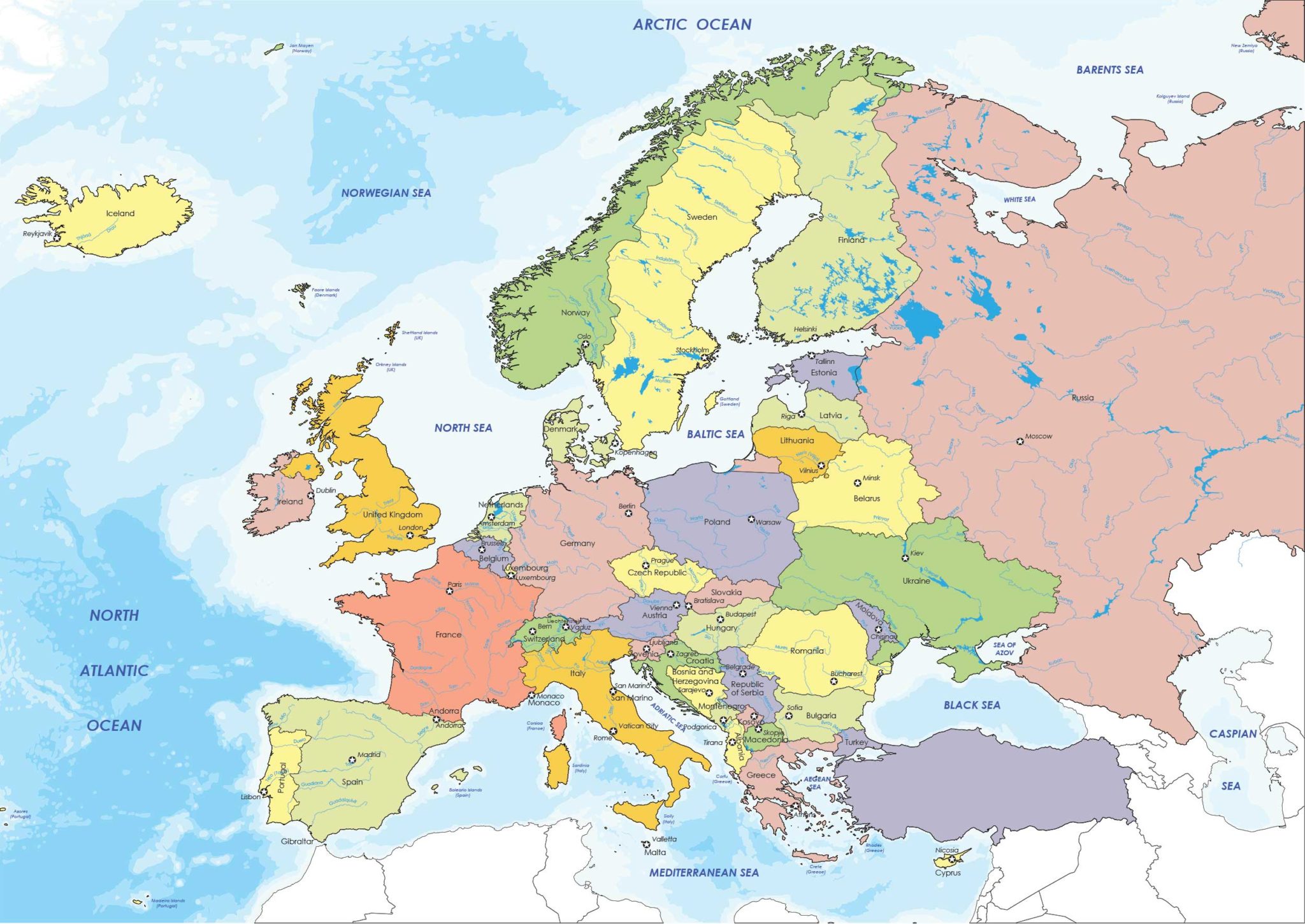

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Political Landscape of Western Europe: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!