Navigating the Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Ancient Egypt’s Map with Labels
Related Articles: Navigating the Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Ancient Egypt’s Map with Labels
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Ancient Egypt’s Map with Labels. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Ancient Egypt’s Map with Labels
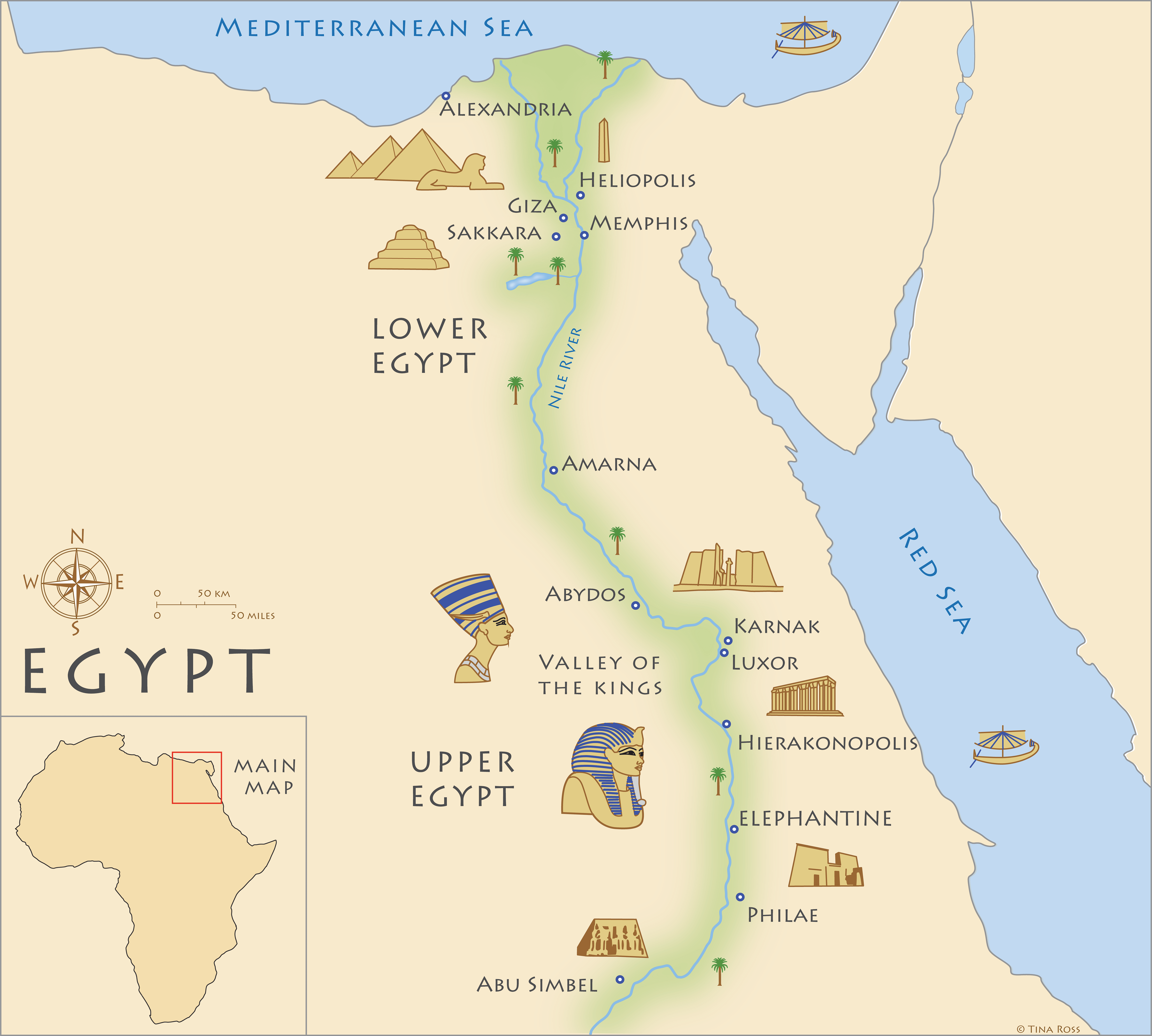
Ancient Egypt, a civilization renowned for its architectural marvels, intricate hieroglyphs, and enduring legacy, continues to captivate the imaginations of historians, archaeologists, and the general public alike. Understanding the geography of this ancient land is crucial to comprehending its history, culture, and the interconnectedness of its various regions. A map of Ancient Egypt, meticulously labeled with its key features, serves as an invaluable tool for navigating this fascinating world.
The Nile River: The Lifeline of Ancient Egypt
The most prominent feature on any map of Ancient Egypt is the Nile River, the lifeblood of the civilization. This mighty river, stretching for over 6,650 kilometers, flows from its source in the highlands of East Africa to its delta in the Mediterranean Sea. The annual flooding of the Nile, a predictable and fertile event, provided the fertile soil that sustained agriculture and allowed the Egyptians to develop a complex and sophisticated society.
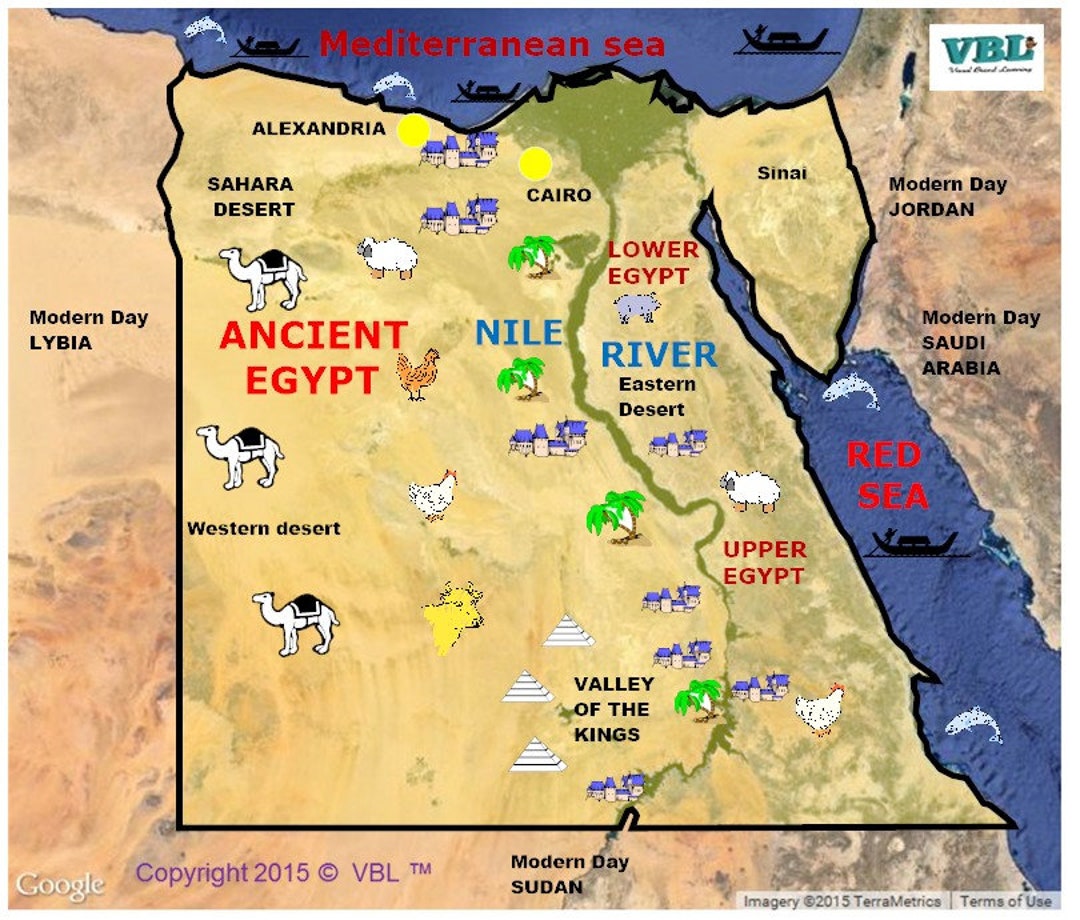
Upper and Lower Egypt: A Geographical and Cultural Divide
The Nile River naturally divides Ancient Egypt into two distinct regions: Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt. Upper Egypt, located south of the modern-day city of Cairo, is characterized by its narrow valley and steep cliffs. This region was the birthplace of the ancient Egyptian civilization, and its cities, such as Thebes (modern-day Luxor), were centers of religious and political power.
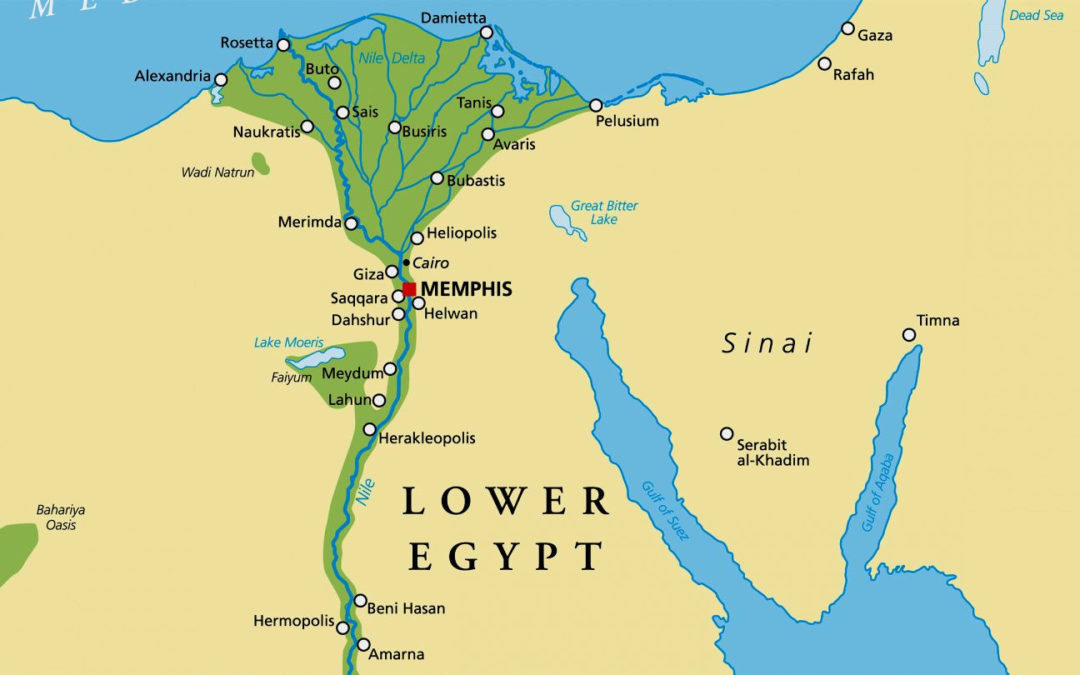
Lower Egypt, situated north of Cairo, encompasses the Nile Delta, a vast expanse of fertile land created by the river’s sediment. This region was known for its dense population, bustling cities, and its strategic location, connecting Egypt to the Mediterranean Sea. The ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis, was located in Lower Egypt, signifying its economic and political importance.
Key Cities and Sites: Centers of Power and Culture
Ancient Egypt was home to numerous cities and sites that played significant roles in its history and culture. A labeled map highlights these locations, providing a visual representation of their interconnectedness and their significance:
-
Memphis: Located at the apex of the Nile Delta, Memphis was the first capital of Ancient Egypt and a major center of trade and administration. It was also a significant religious center, housing the temple of Ptah, the creator god.
-
Thebes: Located in Upper Egypt, Thebes was the capital of the New Kingdom and a prominent religious center. Its monumental temples, such as Karnak and Luxor, are some of the most impressive architectural achievements of ancient Egypt.
-
Abydos: A sacred site in Upper Egypt, Abydos was known for its elaborate temple complex dedicated to the god Osiris. It was also a royal burial ground, containing the tombs of numerous pharaohs.
-
Saqqara: Located near Memphis, Saqqara was the necropolis of the Old Kingdom pharaohs. It is home to the iconic Step Pyramid of Djoser, the first monumental stone structure in Egypt, and numerous other pyramid complexes.
-
Giza: Located on the outskirts of Cairo, Giza is famous for its three Great Pyramids, built for the pharaohs Khufu, Khafre, and Menkaure. The Great Sphinx, a monumental statue with the head of a human and the body of a lion, also stands at Giza.
-
Luxor: Situated on the west bank of the Nile in Upper Egypt, Luxor is a modern city built on the ancient site of Thebes. It is home to the Temple of Luxor, the Karnak Temple Complex, and the Valley of the Kings, a royal burial ground.
-
Abu Simbel: Located in southern Egypt, Abu Simbel is famous for its two massive rock-cut temples dedicated to Pharaoh Ramesses II. These temples were relocated in the 1960s to protect them from the rising waters of Lake Nasser, a testament to the preservation efforts of the ancient Egyptian heritage.
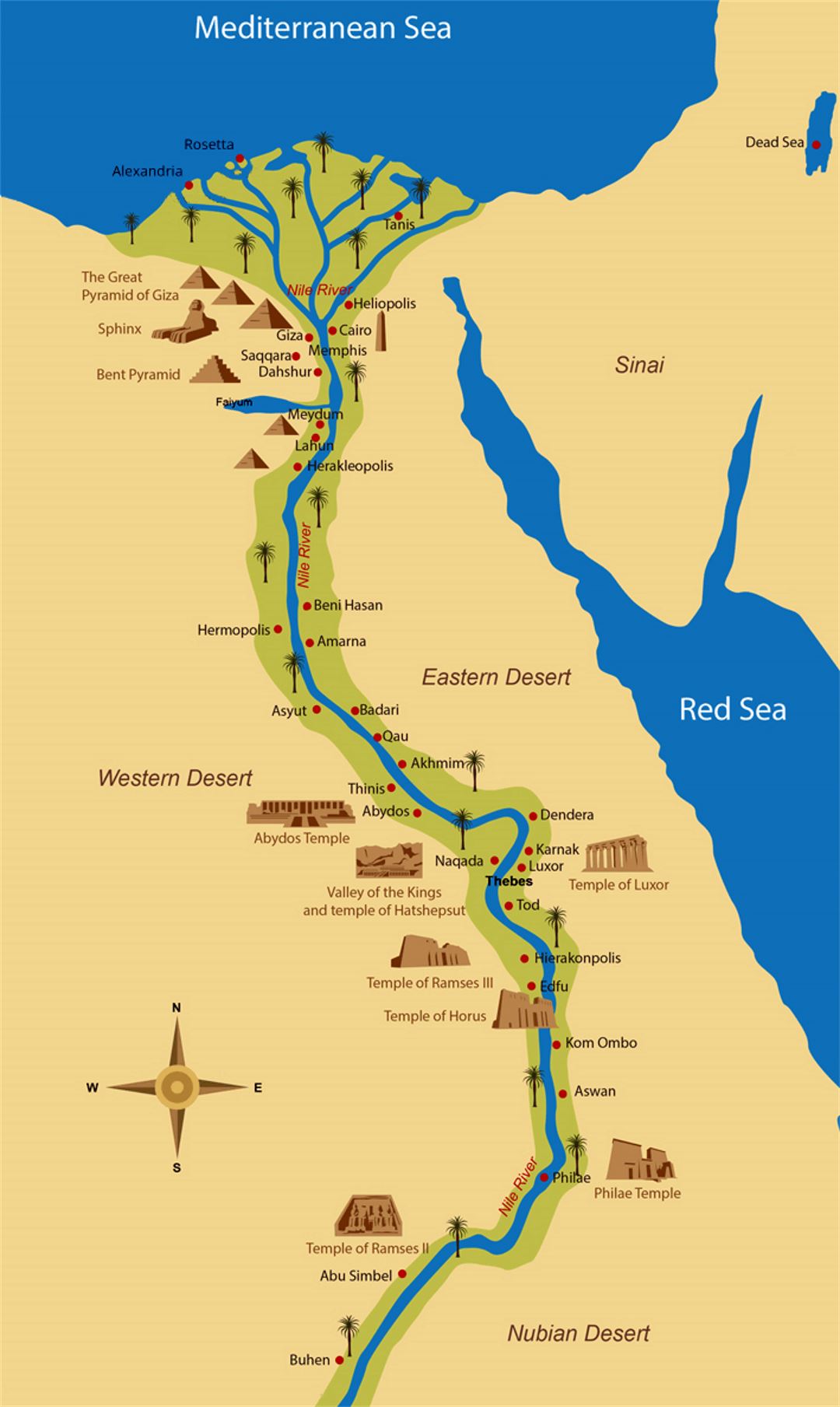
Beyond the Nile: The Deserts and Oases
While the Nile River is the central element of Ancient Egypt, the surrounding deserts and oases played important roles in the civilization’s development. The Western Desert, stretching west of the Nile, was a source of natural resources, including gold, copper, and precious stones. Oases, such as Siwa and Bahariya, provided vital water sources and allowed for the development of small settlements.
The Importance of the Labeled Map
A labeled map of Ancient Egypt provides a crucial visual framework for understanding the civilization’s geography, history, and culture. It allows us to:
-
Visualize the relationship between key cities and sites: The map reveals the interconnectedness of ancient Egyptian settlements, highlighting the flow of goods, ideas, and people throughout the land.
-
Understand the influence of the Nile River: The map emphasizes the importance of the Nile as a lifeline for the civilization, showcasing its role in agriculture, transportation, and the development of urban centers.
-
Appreciate the diversity of the Egyptian landscape: The map demonstrates the varied terrain of Ancient Egypt, from the fertile Nile Valley to the vast deserts and oases.
-
Gain context for historical events and developments: The map provides a spatial framework for understanding the rise and fall of dynasties, the expansion of the Egyptian Empire, and the interactions with neighboring civilizations.
-
Engage with the ancient world in a new way: By visually representing the physical geography of Ancient Egypt, the map allows us to imagine ourselves in the world of the pharaohs, priests, and commoners who once inhabited this land.
FAQs About Ancient Egypt’s Map with Labels
Q: Why is the Nile River so important to Ancient Egypt?
A: The Nile River provided the fertile soil that sustained Egyptian agriculture, allowing the development of a complex society. It also served as a major transportation route, connecting different regions of the country and facilitating trade.
Q: What are the main differences between Upper and Lower Egypt?
A: Upper Egypt was the cradle of ancient Egyptian civilization, known for its narrow valley and steep cliffs. Lower Egypt, encompassing the Nile Delta, was characterized by its fertile land and dense population.
Q: What are some of the most important cities and sites in Ancient Egypt?
A: Some of the most significant cities and sites include Memphis, Thebes, Abydos, Saqqara, Giza, Luxor, and Abu Simbel, each playing a vital role in the civilization’s history and culture.
Q: What role did the deserts and oases play in Ancient Egypt?
A: The deserts provided natural resources and served as a barrier against invaders. Oases provided vital water sources and allowed for the development of small settlements.
Q: How can a labeled map of Ancient Egypt help us understand the civilization?
A: A labeled map provides a visual framework for understanding the geography, history, and culture of Ancient Egypt, allowing us to visualize the relationships between key cities and sites, appreciate the diversity of the landscape, and gain context for historical events.
Tips for Using a Labeled Map of Ancient Egypt
-
Start with the Nile River: Focus on the Nile as the central feature of the map and understand its importance in shaping the civilization.
-
Identify key cities and sites: Locate the major cities and sites, understanding their roles in the civilization’s history and culture.
-
Explore the surrounding landscape: Pay attention to the deserts, oases, and other geographical features that influenced the development of Ancient Egypt.
-
Use the map as a guide for further research: Use the map to identify specific locations that interest you and delve deeper into their history and significance.
Conclusion
A labeled map of Ancient Egypt is an invaluable tool for understanding this fascinating civilization. It allows us to visualize the geography of the land, appreciate the interconnectedness of its various regions, and gain a deeper understanding of its history and culture. By engaging with the map, we can step back in time and explore the world of the pharaohs, the pyramids, and the enduring legacy of Ancient Egypt.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Sands of Time: A Comprehensive Guide to Ancient Egypt’s Map with Labels. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!