Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the United States Railway Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the United States Railway Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the United States Railway Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the United States Railway Map

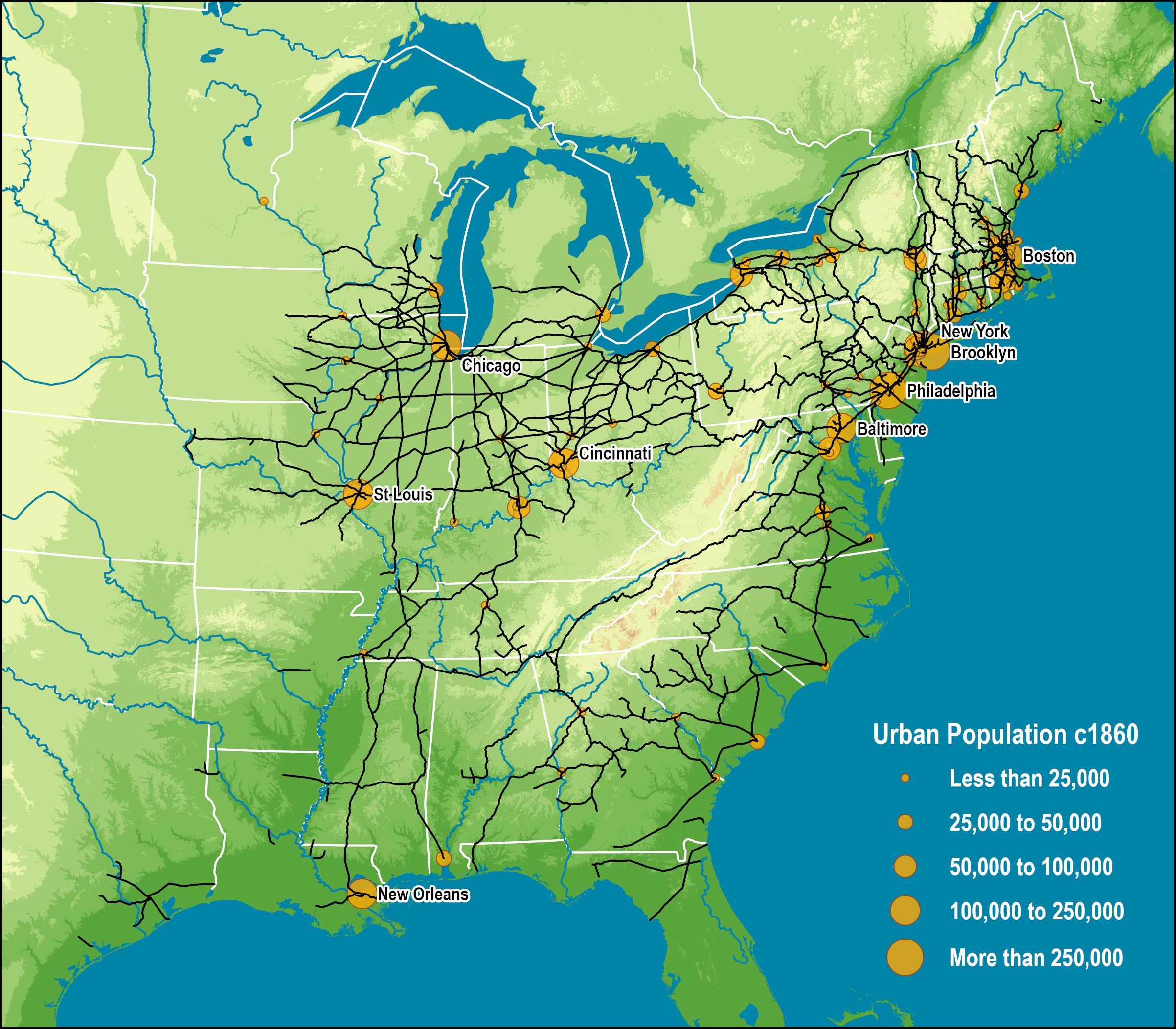
The United States railway map, a complex web of steel lines crisscrossing the vast landscape, represents more than just a network of transportation. It embodies the nation’s historical development, economic vitality, and the intricate connections that bind its diverse regions. Understanding this map offers a window into the country’s past, present, and future, revealing its potential for growth and the challenges it faces in maintaining a robust and efficient rail system.
A Historical Perspective: From Iron Horses to Modern Networks
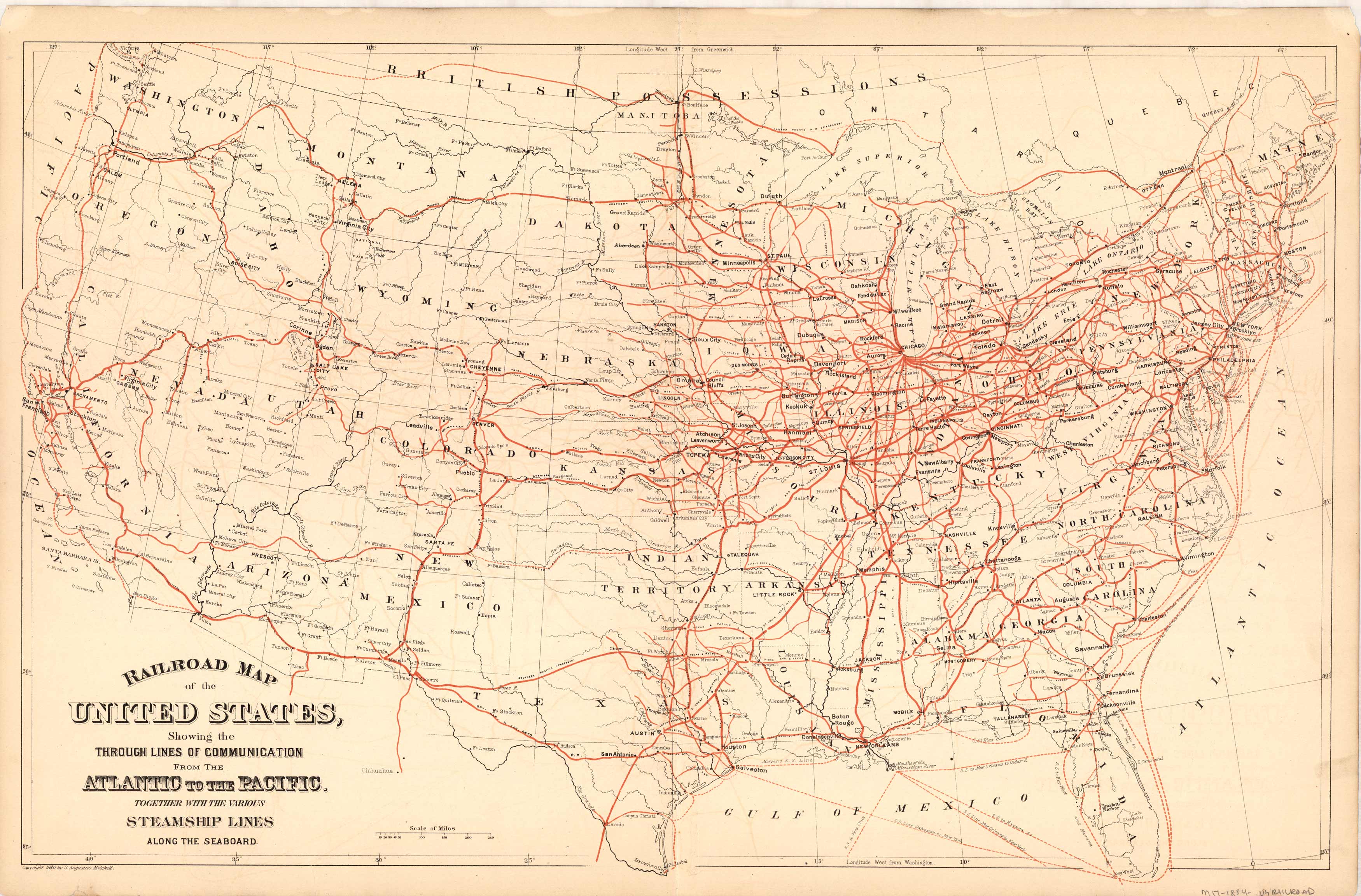
The story of American railways began in the early 19th century, with the construction of short, isolated lines primarily for transporting goods and passengers within local areas. However, the 1860s witnessed a pivotal shift with the transcontinental railroad, connecting the East Coast to the West Coast and ushering in a new era of national integration. This ambitious project spurred westward expansion, facilitated the movement of goods and people, and played a crucial role in the industrialization of the nation.
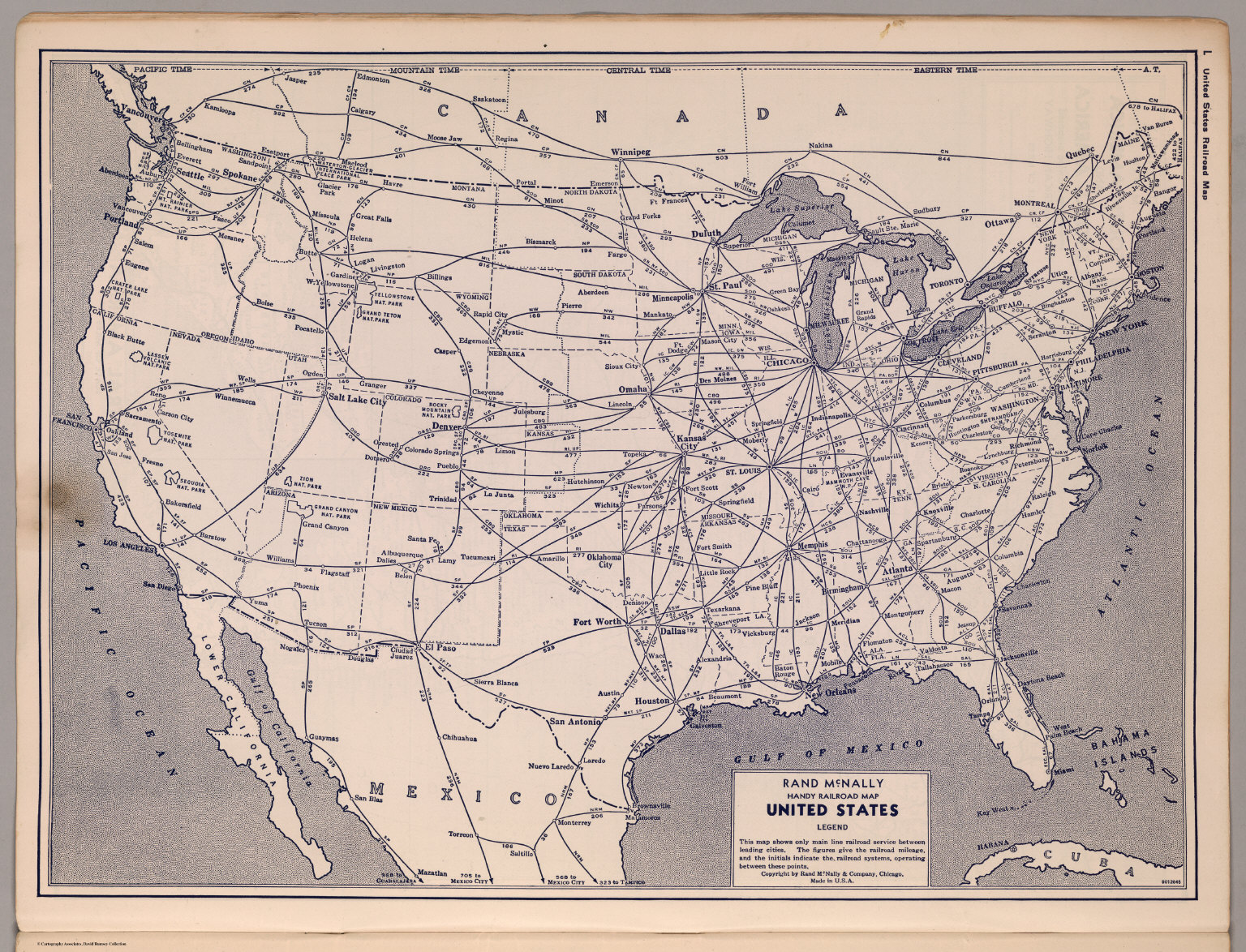
The 20th century saw further expansion and consolidation, with major railway companies merging to form the vast networks we see today. Technological advancements like electrification, diesel engines, and high-speed rail brought about significant improvements in efficiency and speed. However, the rise of the automobile and air travel in the latter half of the century posed challenges to the railway industry, leading to a decline in passenger traffic and a shift towards freight transportation.
The Modern Railway Landscape: A Complex Network of Lines and Operators
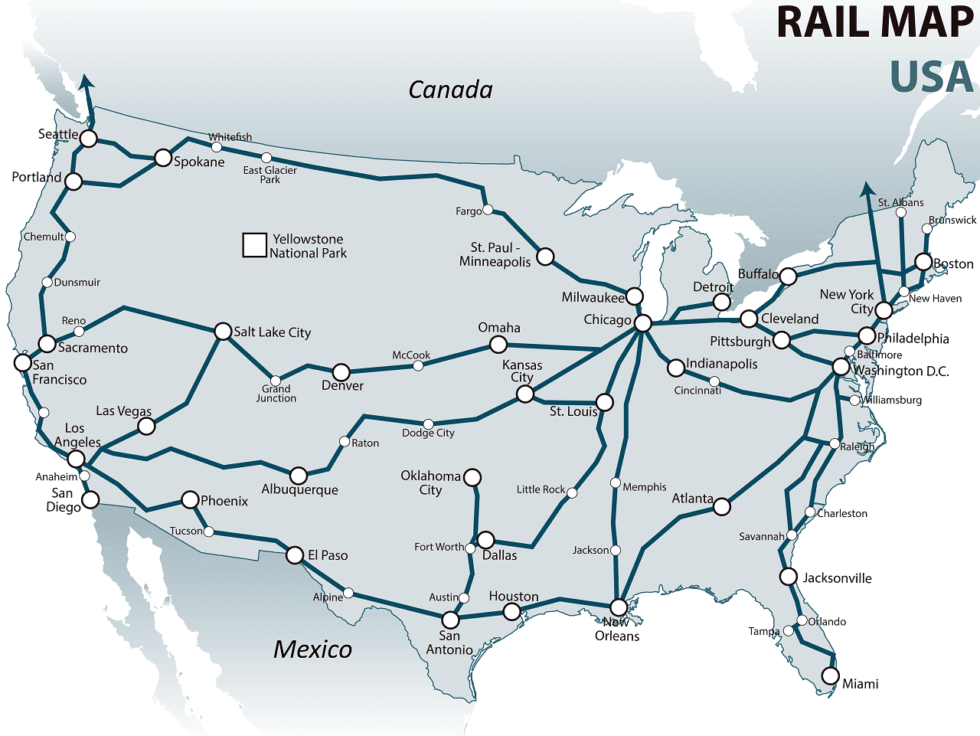
Today, the United States boasts a network of over 225,000 miles of freight and passenger rail lines, operated by a diverse mix of private companies, government agencies, and regional authorities. Major freight carriers like Union Pacific, BNSF, CSX, and Norfolk Southern dominate the industry, transporting goods across the country, while Amtrak, the national passenger rail service, operates lines connecting major cities and towns.
The railway map reveals a complex tapestry of routes, with major lines running along coastlines, traversing the Great Plains, and winding through mountain passes. This intricate network reflects the geographic and economic realities of the United States, connecting major industrial centers, agricultural regions, and port cities.
Importance and Benefits: A Vital Infrastructure for Economic Growth and Sustainability
The United States railway system plays a critical role in the nation’s economy and sustainability. Here are some key benefits:
- Efficient Freight Transportation: Railways are highly efficient in transporting large quantities of goods over long distances, reducing road congestion and fuel consumption. This is particularly important for heavy and bulky commodities like coal, grain, and manufactured goods.
- Economic Growth and Development: Railways facilitate the movement of goods and people, supporting industries, creating jobs, and stimulating economic growth in various regions.
- Environmental Sustainability: Compared to road transportation, railways have a lower carbon footprint, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to a more sustainable transportation system.
- Intermodal Connectivity: Railways connect seamlessly with other modes of transportation, such as trucking and shipping, facilitating the movement of goods across various networks.
- Passenger Transportation: While passenger rail service in the United States faces challenges, it offers a viable alternative to air travel for shorter distances, reducing congestion and offering a more sustainable mode of transportation.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Future of American Railways
Despite its crucial role, the United States railway system faces several challenges:
- Aging Infrastructure: Many lines require significant investment in maintenance and modernization to ensure safety and efficiency.
- Competition from Other Modes of Transportation: The rise of trucking and air travel has led to a decline in passenger rail traffic and increased competition for freight transportation.
- Funding and Investment: Securing sufficient funding for infrastructure improvements and expansion remains a challenge, requiring government support and private investment.
- Safety and Security: Ensuring the safety and security of passengers and freight is paramount, requiring ongoing efforts to improve infrastructure, implement safety protocols, and combat terrorism.
- Sustainability: Reducing the environmental impact of rail operations is essential, requiring investments in cleaner technologies and sustainable practices.
However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth:
- Investing in High-Speed Rail: Expanding high-speed rail networks can offer a viable alternative to air travel, reducing travel times and improving connectivity between major cities.
- Promoting Intermodal Transportation: Integrating railways with trucking and shipping networks can create more efficient and sustainable transportation systems.
- Enhancing Freight Efficiency: Implementing technologies like precision scheduling and automated freight handling can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Investing in Green Technologies: Utilizing renewable energy sources and reducing emissions can improve the environmental sustainability of rail operations.
- Promoting Passenger Rail Service: Investing in passenger rail infrastructure and services can attract more passengers and offer a viable alternative to air travel.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the United States Railway Map
1. What are the major railway companies in the United States?
The major freight carriers include Union Pacific, BNSF, CSX, and Norfolk Southern. Amtrak is the national passenger rail service.
2. How are railways important for the economy?
Railways facilitate the movement of goods and people, supporting industries, creating jobs, and stimulating economic growth.
3. What are the environmental benefits of railways?
Railways have a lower carbon footprint than road transportation, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to a more sustainable transportation system.
4. What are the challenges facing the United States railway system?
Challenges include aging infrastructure, competition from other modes of transportation, funding constraints, safety concerns, and environmental impacts.
5. What are the opportunities for the future of American railways?
Opportunities include expanding high-speed rail networks, promoting intermodal transportation, enhancing freight efficiency, investing in green technologies, and promoting passenger rail service.
Tips for Understanding the United States Railway Map:
- Focus on Major Lines: Pay attention to the major freight and passenger lines that connect major cities and industrial centers.
- Consider Geographic Features: Observe how railways navigate different terrains, mountains, rivers, and coastal areas.
- Identify Hubs and Interchanges: Look for major hubs where different lines converge, facilitating the transfer of goods and passengers.
- Research Historical Context: Understand the historical development of the railway network and its impact on the nation’s growth.
- Explore Online Resources: Utilize online maps, databases, and resources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the railway system.
Conclusion: A Vital Infrastructure for the Future
The United States railway map, a testament to the nation’s history, innovation, and ambition, represents a vital infrastructure for economic growth and sustainability. As the nation navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, investing in and modernizing its railway system will be crucial for maintaining its economic competitiveness, fostering sustainable development, and ensuring the smooth flow of goods and people across the vast landscape. By understanding and engaging with this intricate network of steel lines, we can contribute to shaping a future where railways play an even greater role in the nation’s progress.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Guide to the United States Railway Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!