Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at the Georgian Railway Network
Related Articles: Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at the Georgian Railway Network
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at the Georgian Railway Network. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at the Georgian Railway Network
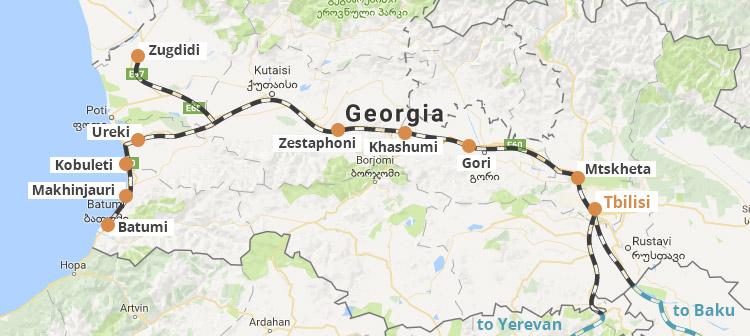
The Georgian railway network, a vital artery connecting cities, towns, and regions, plays a pivotal role in the country’s economic and social development. Understanding its intricate layout and operational nuances provides valuable insights into the country’s infrastructure, transportation dynamics, and potential for future growth. This article offers a comprehensive exploration of the Georgian railway map, delving into its history, current state, and future prospects.
Historical Roots and Modern Evolution
The origins of the Georgian railway system can be traced back to the 19th century, with the first railway line opening in 1872, connecting Poti on the Black Sea coast to Tbilisi, the capital. This marked the beginning of a transformative era, facilitating trade, communication, and passenger movement across the country.
Over the following decades, the network expanded, connecting major cities like Kutaisi, Batumi, and Rustavi. However, the Soviet period witnessed a significant shift in the railway’s focus, emphasizing its role in transporting goods and resources for the Soviet Union’s industrial needs. This resulted in a network primarily focused on freight transport, with limited passenger services and infrastructure.
Following Georgia’s independence in 1991, the railway system faced numerous challenges, including infrastructure deterioration, declining investment, and a lack of modernization. However, the past two decades have seen a gradual revival, with significant investments in infrastructure upgrades, modernization efforts, and the development of new passenger services.
The Network in Detail: A Geographical Overview
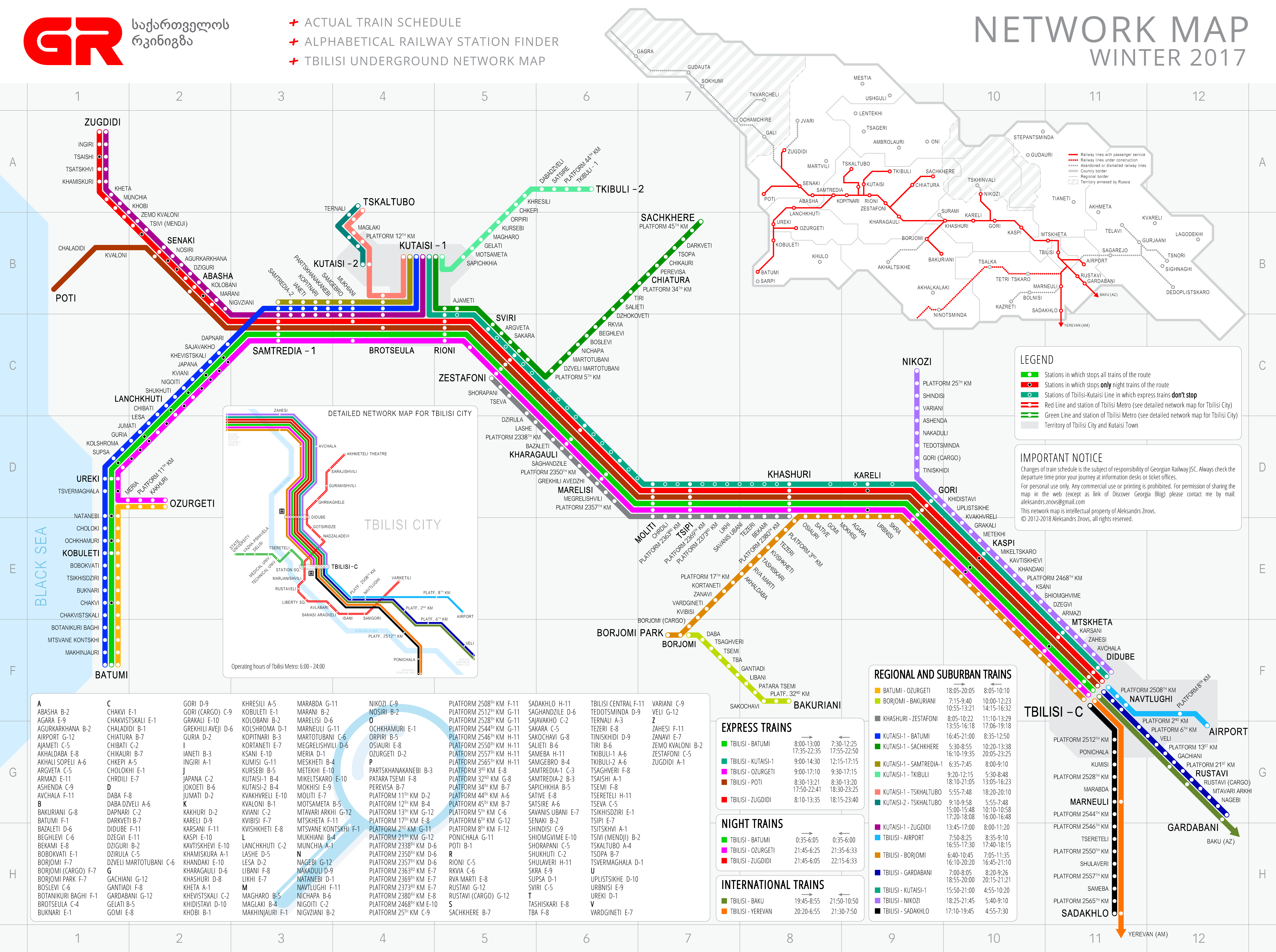
The Georgian railway network, spanning over 1,500 kilometers, comprises a complex web of lines connecting major cities, industrial centers, and border crossings. The network can be broadly divided into the following sections:
- The East-West Corridor: This is the backbone of the Georgian railway system, connecting the Black Sea port of Poti to the Caspian Sea port of Baku, Azerbaijan, via Tbilisi. This line plays a crucial role in international trade, facilitating the transportation of goods between Europe and Asia.
- The South Caucasus Railway: This line connects Tbilisi to Yerevan, Armenia, and is a vital link for regional trade and passenger transport.
- The Black Sea Coast Line: This line connects Poti to Batumi, a major port city on the Black Sea. It plays a vital role in transporting goods to and from the Black Sea region.
- The Tbilisi-Rustavi Line: This line connects the capital city of Tbilisi to the industrial city of Rustavi, a major center for steel production.
Beyond the Lines: Key Features and Challenges
The Georgian railway system faces several challenges, including:
- Infrastructure Modernization: Despite recent upgrades, much of the network still requires significant investment to modernize infrastructure, including tracks, signaling systems, and rolling stock.
- Competition from Road Transport: The development of road infrastructure and the growth of private transportation have led to increased competition for the railway sector.
- Safety Concerns: The railway system faces challenges related to safety, particularly in areas with aging infrastructure and outdated safety standards.
The Future of Georgian Railways: Prospects for Growth and Development
Despite these challenges, the Georgian railway system holds significant potential for growth and development. Several key initiatives are underway to revitalize the network and improve its efficiency:
- Investment in Infrastructure: The Georgian government and international partners are investing heavily in infrastructure upgrades, including track renewal, modernization of signaling systems, and the acquisition of new rolling stock.
- Development of High-Speed Rail: Plans are underway to develop a high-speed rail line connecting Tbilisi to Batumi, which would significantly reduce travel time and boost tourism.
- Integration with Regional Networks: The Georgian government is actively pursuing the integration of the country’s railway network with regional networks, particularly in the Caucasus and Central Asia, to facilitate cross-border trade and passenger transport.
FAQs on the Georgian Railway Network
1. What is the main purpose of the Georgian railway system?
The Georgian railway system serves both freight and passenger transport. Its primary purpose is to facilitate the movement of goods and people across the country and to connect Georgia with its neighboring countries.
2. What are the major challenges faced by the Georgian railway system?
The main challenges include infrastructure modernization, competition from road transport, and safety concerns.
3. What steps are being taken to improve the Georgian railway system?
The Georgian government and its partners are investing in infrastructure upgrades, developing high-speed rail lines, and integrating the network with regional networks.
4. What are the future prospects for the Georgian railway system?
The Georgian railway system has significant potential for growth and development, driven by increased investment, modernization efforts, and regional integration.
5. What are the benefits of a well-developed railway system for Georgia?
A well-developed railway system offers numerous benefits, including:
- Economic Growth: It facilitates trade and transportation, boosting economic activity and creating employment opportunities.
- Social Development: It provides reliable and efficient transportation for passengers, improving connectivity and accessibility.
- Environmental Sustainability: It reduces reliance on road transport, mitigating carbon emissions and promoting sustainable development.
Tips for Traveling on the Georgian Railway
- Plan your journey in advance: Check timetables and ticket availability online or at railway stations.
- Purchase tickets online or at stations: Online ticket purchase is often more convenient and allows for advance booking.
- Arrive at the station early: Allow ample time for check-in and security procedures.
- Be aware of safety regulations: Follow safety guidelines and instructions provided by railway staff.
- Enjoy the scenic views: The Georgian railway network offers stunning views of the country’s diverse landscapes.
Conclusion
The Georgian railway network, a vital component of the country’s infrastructure, is undergoing a period of transformation. With investments in modernization, expansion, and integration, the railway system is poised to play an increasingly important role in Georgia’s economic and social development. By facilitating trade, connecting communities, and promoting sustainable transportation, the Georgian railway network is paving the way for a brighter future for the country.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tracks: A Comprehensive Look at the Georgian Railway Network. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!