Navigating West Africa: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry
Related Articles: Navigating West Africa: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating West Africa: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating West Africa: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry

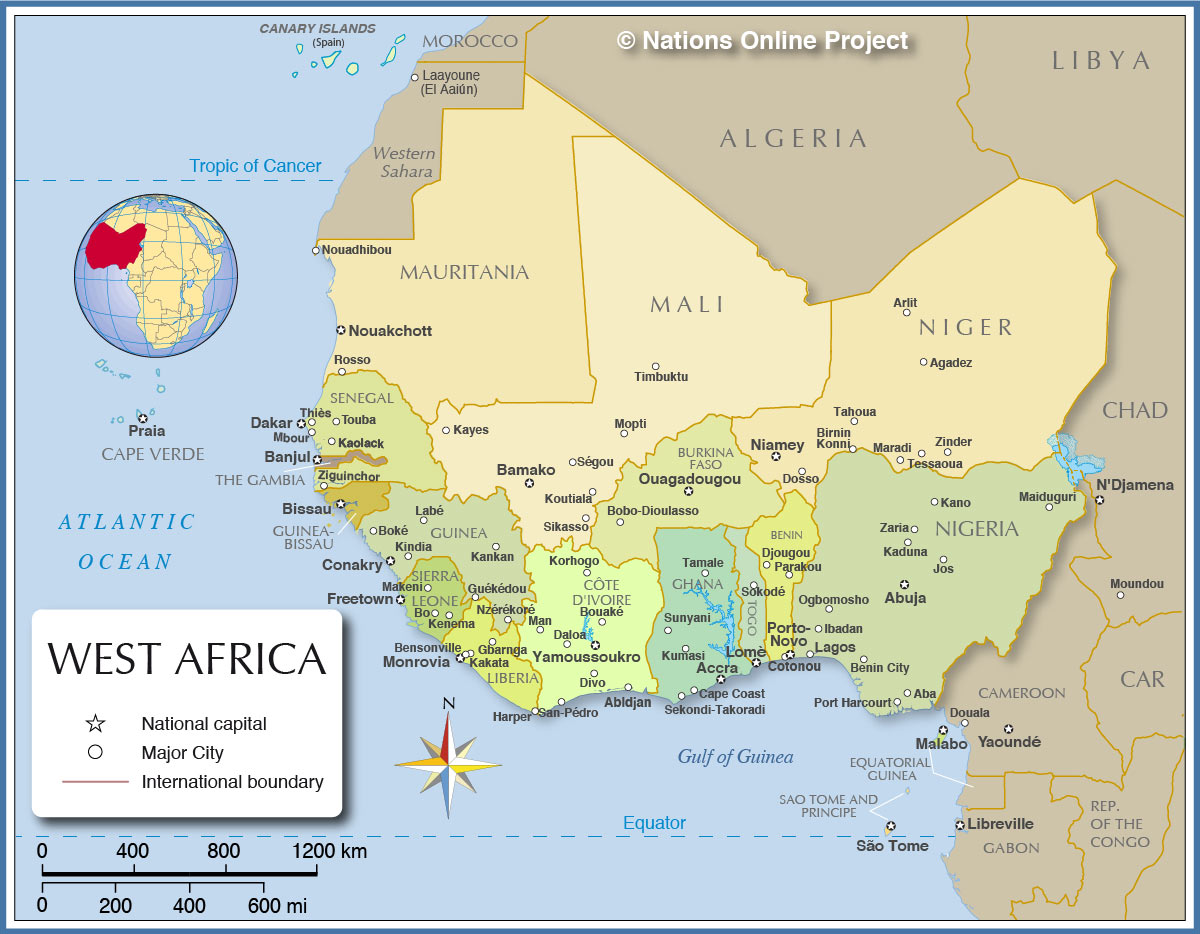
West Africa, a vibrant and diverse region on the westernmost edge of the African continent, boasts a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and landscapes. Understanding the geographical layout of this region, with its intricate network of countries, is crucial for appreciating its unique history, economic potential, and cultural heritage.
A Geographic Overview:
The map of West Africa reveals a diverse landscape. Its northern reaches are dominated by the Sahara Desert, a vast expanse of sand and rock. Moving southward, the landscape transitions to the Sahel, a semi-arid zone characterized by grasslands and savannas. Further south, lush rainforests and coastal plains dominate, interspersed with rivers, lakes, and mountains.
The Countries of West Africa:
West Africa is home to 16 distinct countries, each with its own unique character and history. These countries, from north to south, are:
- Mauritania: Situated on the Atlantic coast, Mauritania is largely desert with a rich history of nomadic cultures.
- Western Sahara: A disputed territory claimed by Morocco, Western Sahara possesses a unique cultural identity and remains a focus of international attention.
- Senegal: Known for its vibrant culture, diverse landscapes, and bustling capital Dakar, Senegal is a significant player in West African politics and economics.
- Gambia: A small, narrow country bordering Senegal, Gambia is home to diverse ethnicities and a rich cultural heritage.
- Guinea-Bissau: A coastal nation with a history of Portuguese influence, Guinea-Bissau is known for its beautiful beaches and diverse flora and fauna.
- Guinea: A mountainous nation with a rich cultural heritage, Guinea is a major producer of bauxite, a key ingredient in aluminum production.
- Sierra Leone: A coastal nation with a tragic history of civil war, Sierra Leone is working towards rebuilding its economy and society.
- Liberia: Founded by freed American slaves, Liberia has a unique history and culture, and is striving to overcome the challenges of poverty and instability.
- Côte d’Ivoire: A major economic powerhouse in West Africa, Côte d’Ivoire is known for its cocoa and coffee production, as well as its vibrant cultural scene.
- Ghana: An influential nation with a rich history, Ghana is a major producer of gold and cocoa, and is a key player in regional politics.
- Togo: A small, coastal nation with a diverse landscape, Togo is known for its vibrant markets and its commitment to sustainable development.
- Benin: A nation with a rich cultural heritage, Benin is known for its traditional arts and crafts, and its efforts to promote tourism.
- Nigeria: The most populous country in West Africa, Nigeria is a major oil producer and a significant force in regional politics and economics.
- Niger: A landlocked country with a vast desert landscape, Niger is a major producer of uranium and is working to diversify its economy.
- Chad: A landlocked country with a diverse landscape, Chad faces challenges from poverty, instability, and climate change.
- Cameroon: A diverse nation with a coastline on the Atlantic Ocean and a mountainous interior, Cameroon is known for its rich biodiversity and its vibrant cultural scene.
Importance and Benefits of Understanding the Map:
Understanding the map of West Africa provides numerous benefits, including:
- Promoting Cultural Understanding: The map highlights the diverse cultures, languages, and traditions that exist within the region. This understanding fosters respect and appreciation for the unique heritage of each country.
- Facilitating Economic Development: The map facilitates the identification of key resources, infrastructure, and trade routes, enabling businesses and governments to develop sustainable economic strategies.
- Enhancing Security and Stability: The map provides a framework for understanding regional dynamics, conflicts, and potential threats, facilitating the development of effective security measures and conflict resolution strategies.
- Encouraging Environmental Conservation: The map reveals the diverse ecosystems and natural resources of West Africa, emphasizing the importance of sustainable development and conservation efforts.
- Strengthening Regional Integration: The map facilitates collaboration and cooperation between countries, promoting regional integration and fostering shared economic and political goals.
FAQs:
1. What is the largest country in West Africa?
Nigeria is the largest country in West Africa in terms of both population and land area.
2. What are the major languages spoken in West Africa?
English, French, Portuguese, and various indigenous languages are spoken throughout West Africa.
3. What are the major economic sectors in West Africa?
Agriculture, mining, oil and gas production, and tourism are major economic sectors in West Africa.
4. What are the main challenges facing West Africa?
Challenges include poverty, instability, conflict, climate change, and lack of infrastructure.
5. What are some of the key organizations promoting regional cooperation in West Africa?
The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) and the West African Monetary Institute (WAMI) are key organizations promoting regional cooperation.
Tips for Understanding the Map:
- Use a good quality map: Look for maps that clearly delineate borders, major cities, and geographical features.
- Study the physical features: Pay attention to the different landscapes, including mountains, rivers, deserts, and rainforests.
- Research each country: Explore the history, culture, economy, and challenges of each country in West Africa.
- Utilize online resources: Websites like Google Maps, Wikipedia, and the World Bank provide valuable information about the region.
- Engage in discussions: Participate in discussions about West Africa to deepen your understanding of its complexities.
Conclusion:
The map of West Africa is more than just a geographical representation; it is a window into a rich and diverse region brimming with potential. Understanding its intricate network of countries, their unique cultures, and the challenges they face is essential for promoting economic development, fostering peace and stability, and celebrating the vibrant heritage of West Africa. By engaging with this map and its complexities, we can contribute to a brighter future for this remarkable region.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating West Africa: A Geographic and Cultural Tapestry. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!