The Dynamic World of Mapping: Navigating Data and Understanding Change
Related Articles: The Dynamic World of Mapping: Navigating Data and Understanding Change
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Dynamic World of Mapping: Navigating Data and Understanding Change. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Dynamic World of Mapping: Navigating Data and Understanding Change

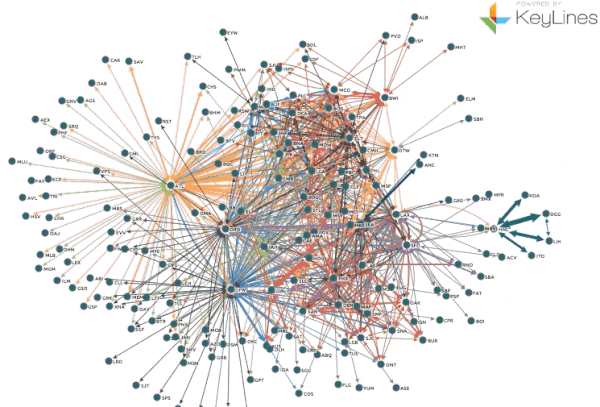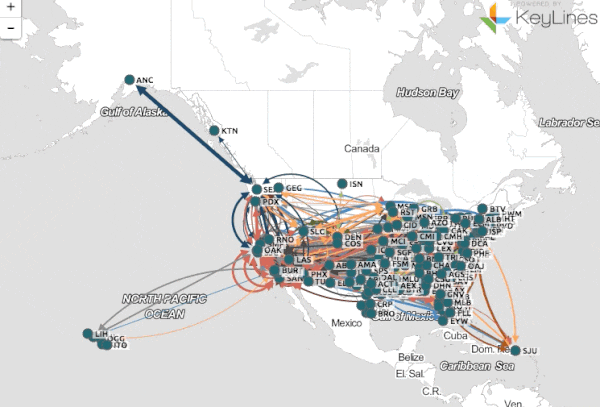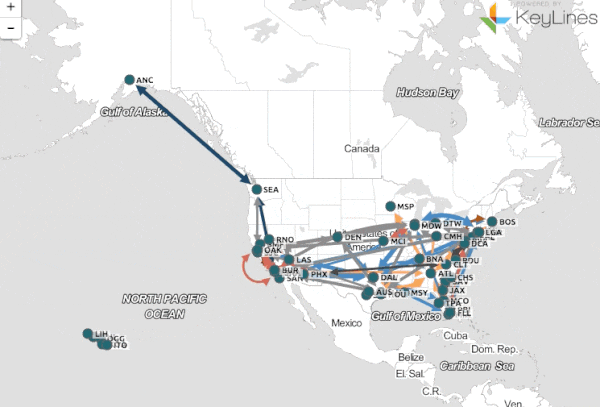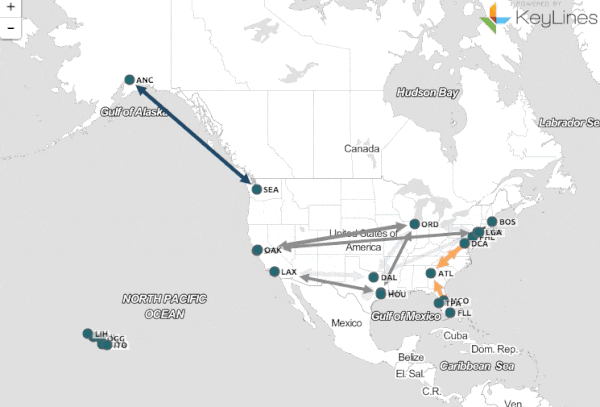
Maps, once static representations of the world, have undergone a profound transformation, evolving into dynamic, interactive, and data-rich tools. This shift, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing availability of data, has revolutionized how we perceive, analyze, and interact with the world around us.
This dynamic approach to mapping allows for a deeper understanding of our planet and its complexities. By integrating diverse data sources, incorporating real-time updates, and enabling interactive exploration, dynamic maps offer a powerful lens for visualizing, analyzing, and interpreting information across various disciplines.
Understanding the Dynamics: Key Components
The dynamism of modern mapping lies in its ability to transcend static representations and embrace constant change. This is achieved through several key components:
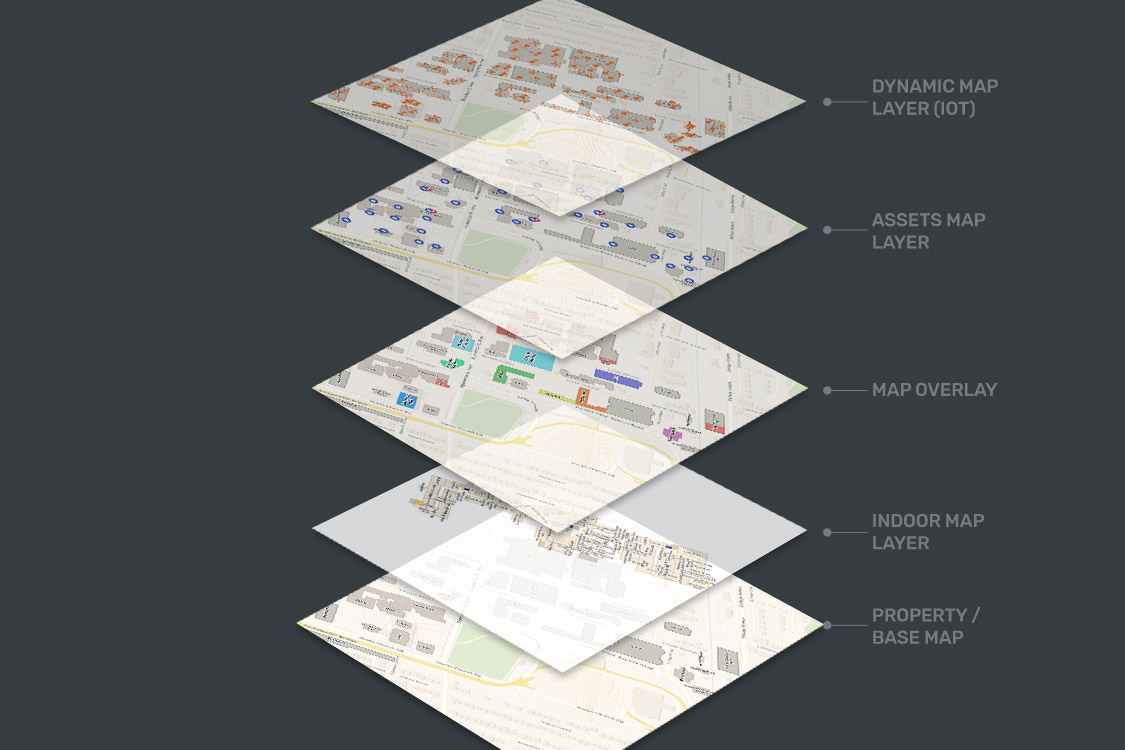
- Data Integration: Dynamic maps leverage diverse data sources, including geospatial data, sensor readings, social media feeds, and statistical information. This integration allows for the creation of comprehensive maps that offer a multifaceted view of the world.
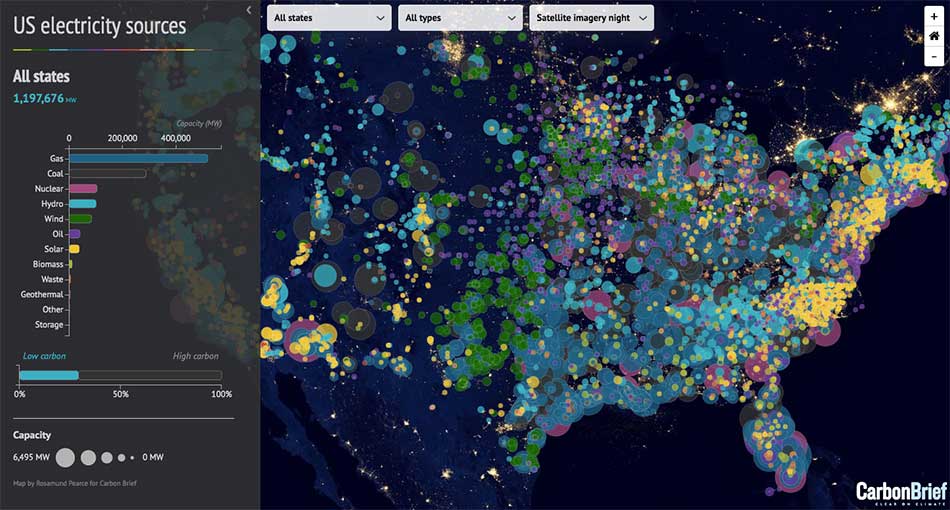
- Real-time Updates: The ability to incorporate real-time data is crucial to dynamic mapping. Traffic conditions, weather patterns, and other dynamic phenomena can be visualized in real-time, offering insights into changing situations.
- Interactive Exploration: Users are no longer passive observers of static maps. Dynamic maps empower users to explore data interactively, zooming in on specific areas, filtering data based on specific criteria, and analyzing relationships between different data points.
- Visualization and Analysis: Dynamic maps utilize advanced visualization techniques to present complex data in an intuitive and understandable manner. This allows for the identification of patterns, trends, and anomalies that might be missed in static representations.
Applications of Dynamic Mapping
The applications of dynamic mapping extend far beyond simple navigation. They are transforming various fields, including:
- Urban Planning and Development: Dynamic maps are used to analyze urban growth patterns, assess infrastructure needs, optimize traffic flow, and plan sustainable development strategies.
- Environmental Monitoring: Real-time data from sensors and satellites can be integrated into dynamic maps to monitor environmental conditions, track pollution levels, and assess the impact of climate change.
- Disaster Management: Dynamic maps play a crucial role in disaster response, providing real-time information on the extent of damage, evacuation routes, and resource allocation.
- Business and Marketing: Dynamic maps are used to analyze customer demographics, identify market trends, optimize logistics, and target marketing campaigns effectively.
- Healthcare: Dynamic maps are employed to visualize the spread of diseases, track patient data, and optimize healthcare resource allocation.
- Education: Dynamic maps provide a powerful tool for teaching geography, history, and other subjects, fostering interactive learning experiences.
Benefits of Dynamic Mapping
The dynamic approach to mapping offers numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Understanding: Dynamic maps provide a deeper and more comprehensive understanding of complex data, enabling informed decision-making.
- Improved Efficiency: Real-time data updates and interactive exploration streamline processes, leading to increased efficiency in various applications.
- Data-Driven Insights: Dynamic maps facilitate the identification of patterns, trends, and anomalies, providing valuable insights for informed decision-making.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Dynamic maps foster collaboration by providing a common platform for sharing and analyzing data, leading to more effective teamwork.
- Improved Communication: Dynamic maps effectively communicate complex data to diverse audiences, fostering understanding and engagement.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the key differences between static and dynamic maps?
A: Static maps are fixed representations of data, while dynamic maps are interactive and constantly updated with real-time data. Dynamic maps offer greater flexibility, interactivity, and insights compared to static maps.
Q: What types of data can be integrated into dynamic maps?
A: Dynamic maps can integrate a wide range of data, including geospatial data, sensor readings, social media feeds, weather data, traffic information, demographic data, and more.
Q: How can I create my own dynamic map?
A: Several online platforms and software tools offer the capability to create dynamic maps. These platforms typically require users to input data and customize map elements, such as basemaps, data layers, and visualization styles.
Q: What are some of the challenges associated with dynamic mapping?
A: Challenges include data availability, data accuracy, data security, scalability, and the need for technical expertise to create and manage dynamic maps.
Tips for Effective Dynamic Mapping
- Define the Purpose: Clearly define the objective of the map before starting the mapping process. This will guide data selection, visualization techniques, and overall design.
- Choose the Right Data: Select data that is relevant to the map’s purpose and ensure its accuracy and reliability.
- Optimize Visualization: Use clear and intuitive visualization techniques to present complex data in an understandable manner.
- Enable Interactivity: Encourage user engagement by incorporating interactive elements, such as zoom capabilities, data filtering, and information pop-ups.
- Consider Accessibility: Ensure that the map is accessible to all users, regardless of their technical skills or disabilities.
Conclusion
Dynamic mapping is revolutionizing how we perceive and interact with the world. By integrating diverse data sources, incorporating real-time updates, and enabling interactive exploration, dynamic maps offer a powerful tool for understanding complex systems, making informed decisions, and driving innovation across various fields. As technology continues to advance, dynamic maps will undoubtedly become even more sophisticated and integral to our understanding of the world around us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Dynamic World of Mapping: Navigating Data and Understanding Change. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!