The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Volcano: A Geographic and Geological Perspective
Related Articles: The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Volcano: A Geographic and Geological Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Volcano: A Geographic and Geological Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Volcano: A Geographic and Geological Perspective
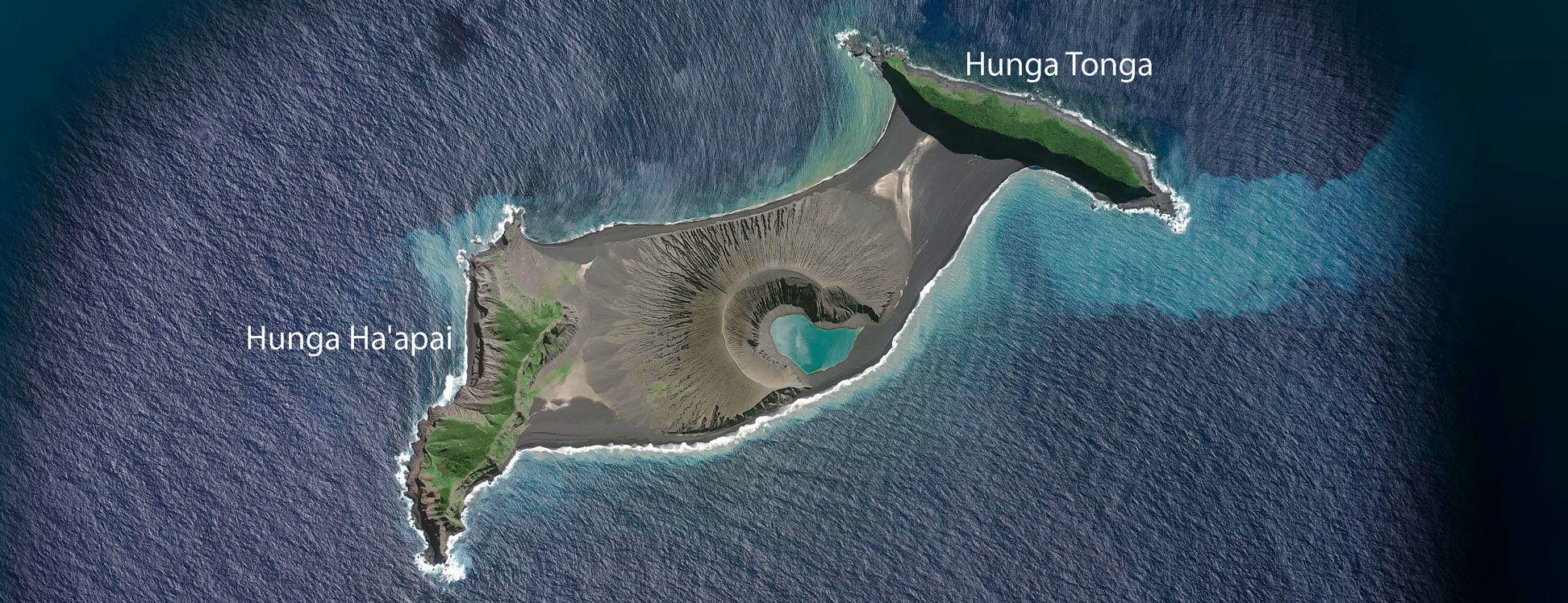
The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano, located in the South Pacific Ocean, gained global attention in January 2022 for its powerful eruption. This event, one of the most significant volcanic eruptions in recent history, had profound impacts on the surrounding region and even the global climate. Understanding the location and geological context of this volcano is crucial for comprehending the eruption’s magnitude and its implications.
Location and Geography
The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano is situated in the Tongan archipelago, a group of islands in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. Specifically, it lies approximately 65 kilometers (40 miles) north of the Tongan capital, Nuku’alofa, on the island of Tongatapu. The volcano emerges from the submerged Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone, a region of intense geological activity where the Pacific Plate dives beneath the Tonga Plate.
Geological Context
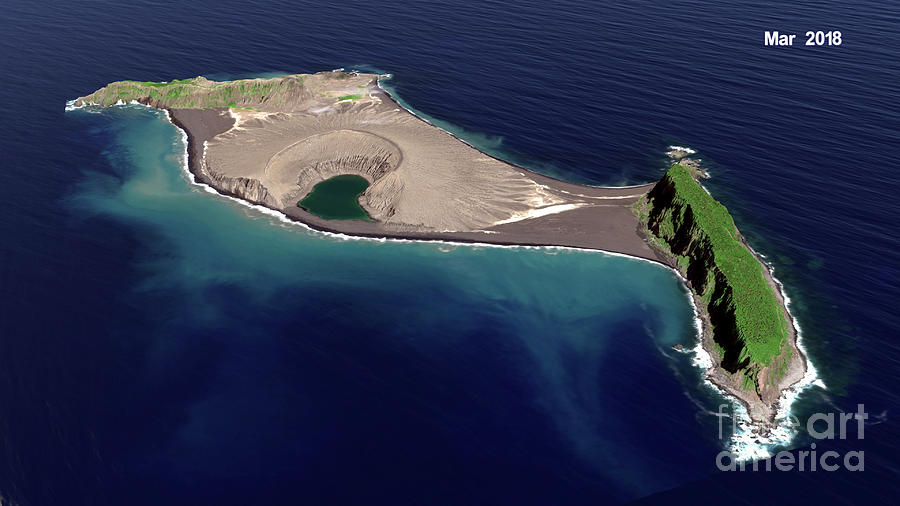
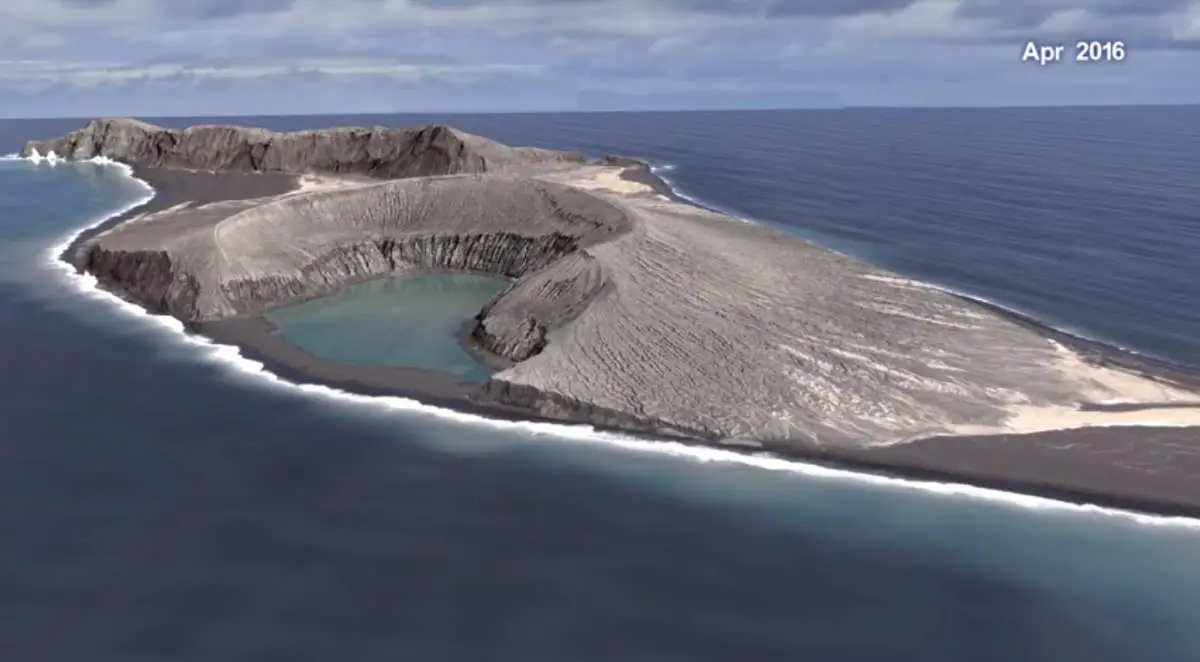
The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano is a stratovolcano, characterized by its steep conical shape formed by layers of lava flows, ash, and volcanic debris. It is part of a larger volcanic arc, a chain of volcanoes that form along the convergent boundary of two tectonic plates. In the case of the Tonga-Kermadec arc, the subduction process generates magma, which rises to the surface through volcanic vents, creating new landforms.
The volcano’s location within the subduction zone plays a crucial role in its eruptive activity. As the denser Pacific Plate descends beneath the Tonga Plate, it melts, generating magma that ascends towards the surface. This process, combined with the presence of water trapped within the subducting plate, contributes to the explosive nature of eruptions in this region.
The 2022 Eruption
The eruption of Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai in January 2022 was a significant event, categorized as a Plinian eruption, characterized by its highly explosive nature and the formation of a massive eruption column. The eruption triggered a series of devastating impacts, including:
- Tsunami: The eruption generated a powerful tsunami that reached the shores of Tonga, as well as other Pacific islands and even distant coastlines, causing widespread damage and flooding.
- Atmospheric Disturbances: The eruption released vast amounts of volcanic ash and gases into the atmosphere, creating a plume that reached stratospheric heights. This event led to disruptions in air travel and had a temporary impact on global weather patterns.
- Climate Change: The eruption’s release of sulfur dioxide and other gases into the atmosphere could potentially contribute to a cooling effect on the global climate, although the long-term impact remains uncertain.
Importance of Monitoring and Research
The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruption highlights the importance of monitoring volcanic activity and understanding the potential risks associated with these events. Studying the volcano’s history, geology, and eruptive patterns provides valuable insights for predicting future activity and mitigating potential hazards.
FAQs about the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Volcano
Q: What is the significance of the volcano’s location within the subduction zone?
A: The subduction zone provides the geological context for the volcano’s existence and its explosive nature. The convergence of tectonic plates generates magma, which rises to the surface, creating volcanic activity.
Q: What are the potential impacts of volcanic eruptions on the environment and human populations?
A: Volcanic eruptions can have significant impacts on the environment, including air pollution, climate change, and the release of harmful gases. They can also pose risks to human populations through tsunamis, ashfall, and volcanic landslides.
Q: How can scientists predict volcanic eruptions and mitigate their potential hazards?
A: Scientists monitor volcanic activity through various methods, including seismic monitoring, gas emissions, and ground deformation measurements. This data can help predict eruptions and inform evacuation plans and other mitigation strategies.
Tips for Understanding the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Volcano
- Utilize online resources: Explore interactive maps, geological data, and scientific reports about the volcano.
- Engage with scientific publications: Read research articles and reports from reputable sources to gain a deeper understanding of the volcano’s history, geology, and eruptive patterns.
- Follow news and updates: Stay informed about the volcano’s current activity and any potential risks through reliable news sources and official statements.
Conclusion
The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcano serves as a powerful reminder of the dynamic nature of our planet and the potential impact of geological events. Understanding the volcano’s location, geology, and eruptive history is crucial for mitigating risks and ensuring the safety of surrounding populations. Continued research and monitoring efforts are essential for understanding this powerful natural force and preparing for future eruptions.
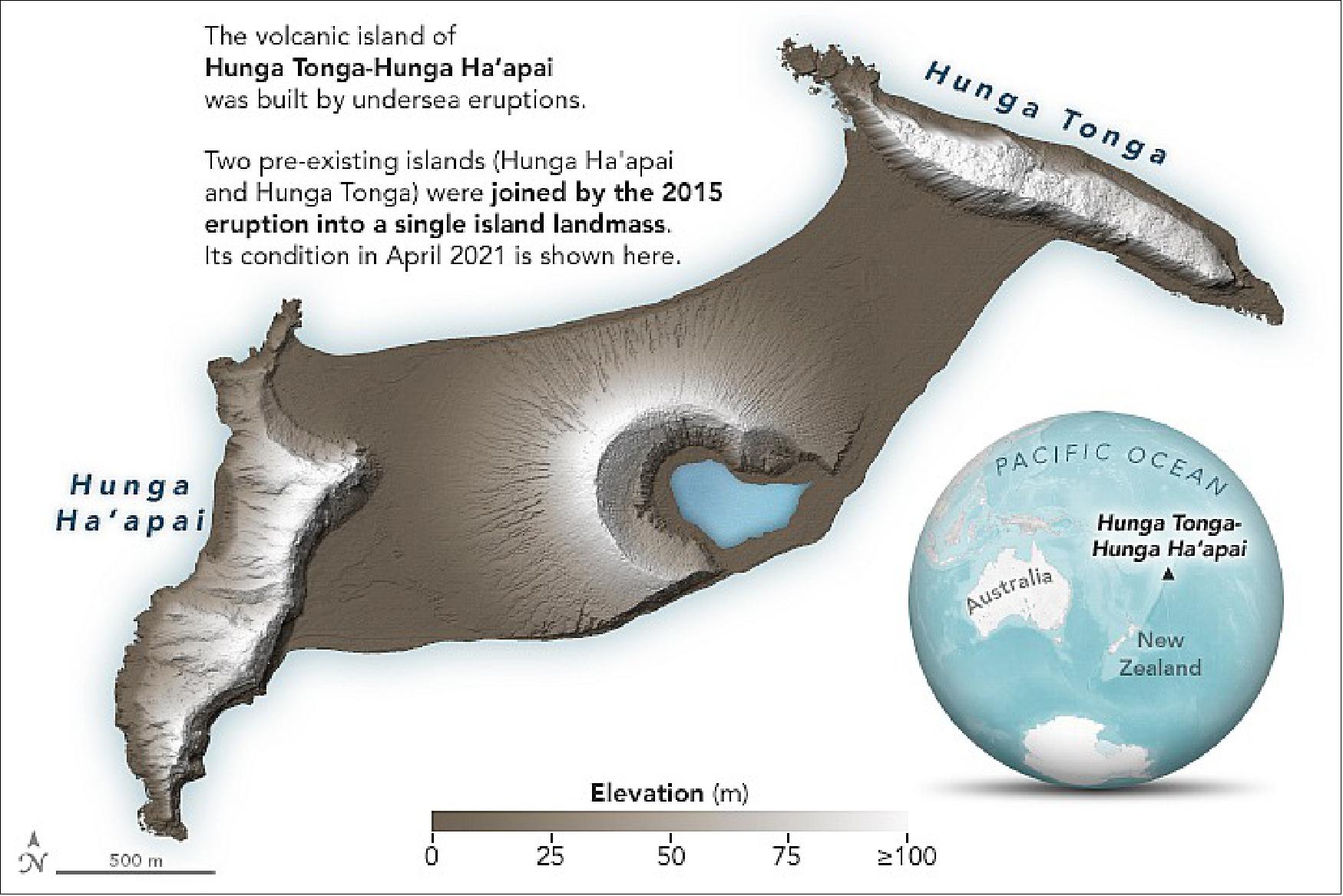
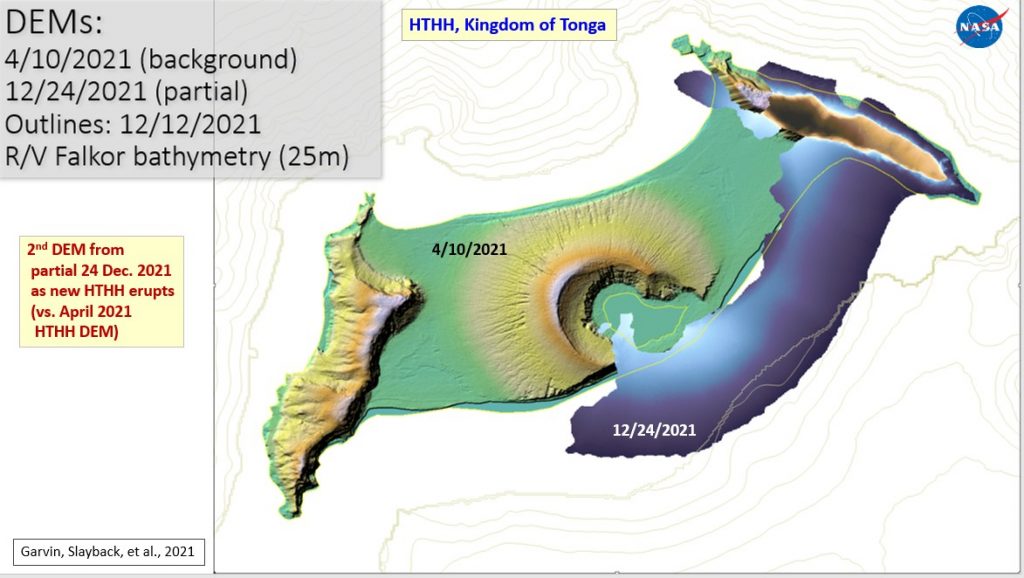
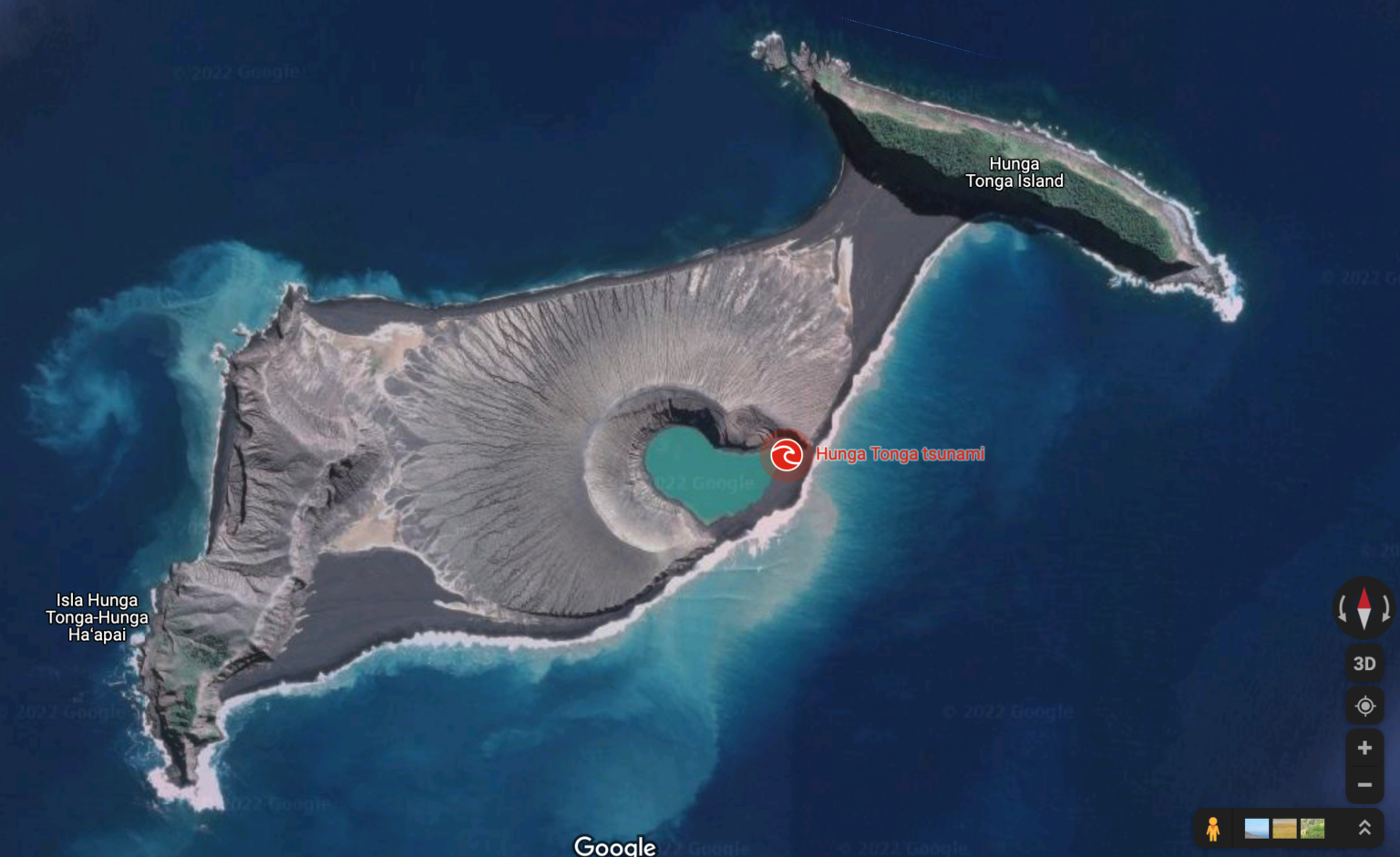




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai Volcano: A Geographic and Geological Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!