The Niger River: A Lifeline Through West Africa
Related Articles: The Niger River: A Lifeline Through West Africa
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Niger River: A Lifeline Through West Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Niger River: A Lifeline Through West Africa
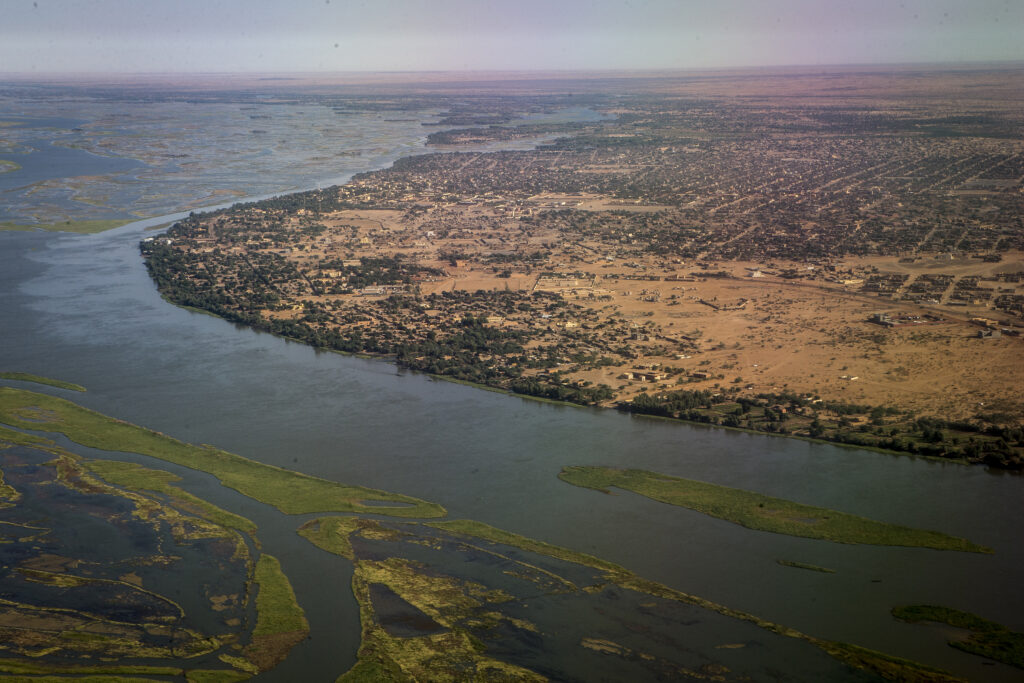

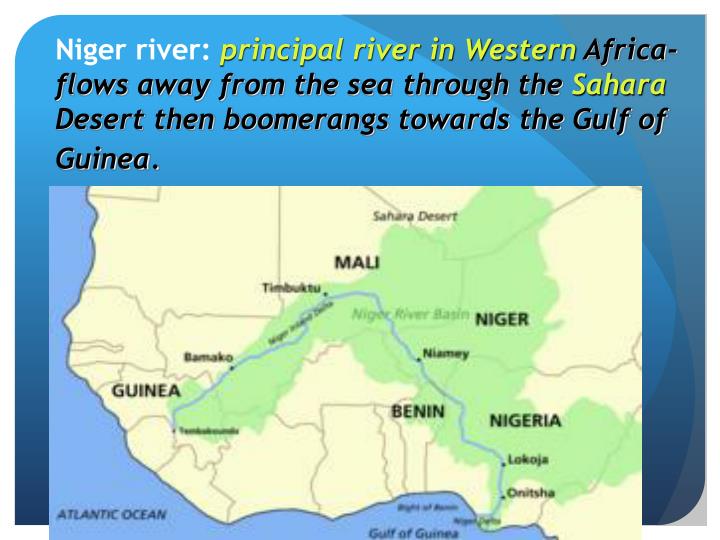
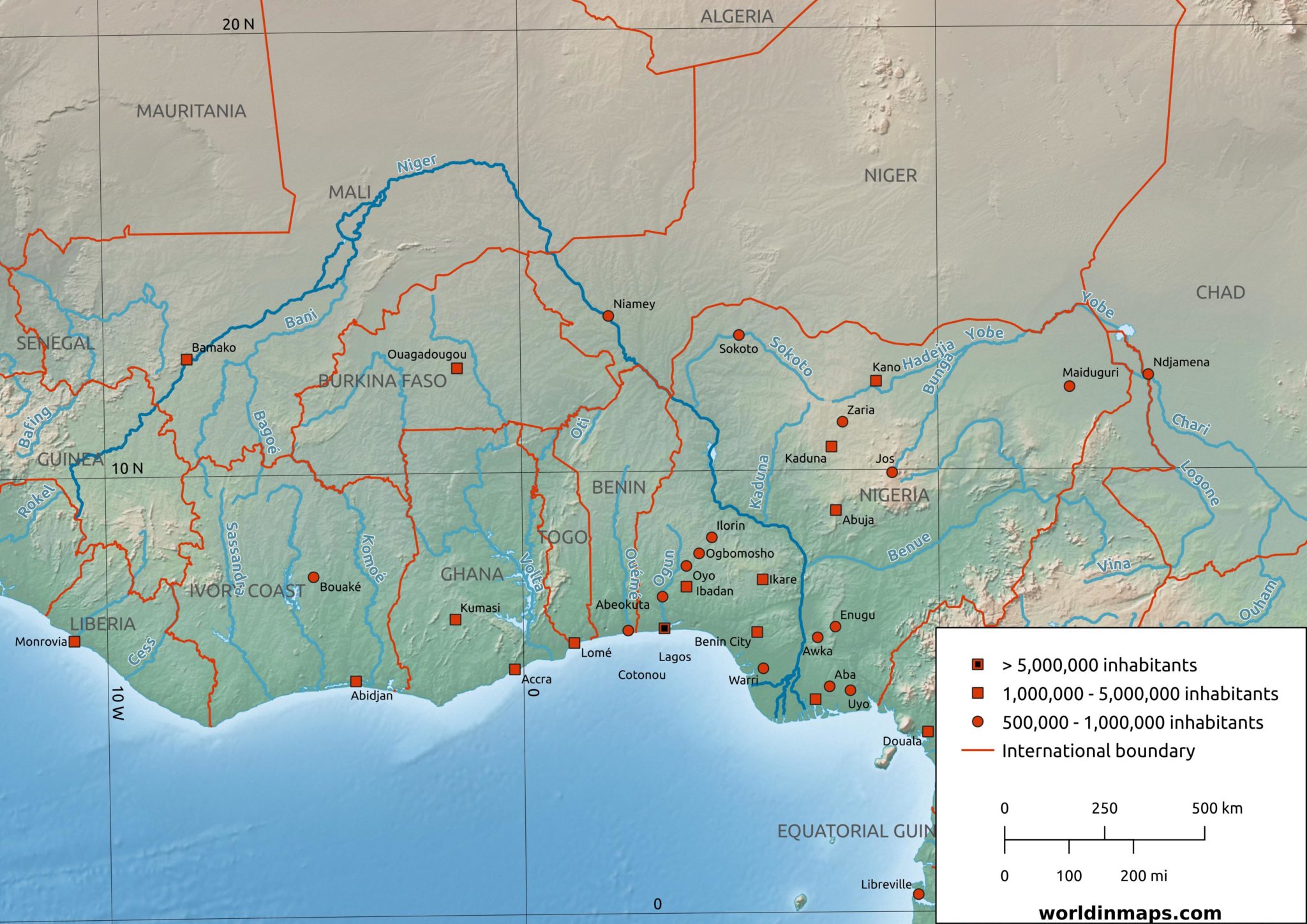
The Niger River, a vital artery of West Africa, winds its way across a vast expanse of land, traversing diverse ecosystems and supporting millions of people. Its journey, spanning over 4,180 kilometers, begins in the Guinea Highlands and concludes in the Niger Delta, where it empties into the Atlantic Ocean. This article explores the Niger River’s geographical significance, its historical and cultural impact, and its critical role in the present-day landscape of West Africa.
The Niger River: A Geographical Overview
The Niger River is the third longest river in Africa, after the Nile and Congo. Its winding course through the Sahel, Sudanian, and Guinean savannas, as well as the coastal regions of West Africa, creates a unique and diverse landscape. The river’s journey is marked by a series of dramatic features:
- The Upper Niger: This section begins in the Fouta Djallon mountains of Guinea, flowing westward before turning southward. This area is characterized by steep slopes and rugged terrain, resulting in rapids and waterfalls.
- The Middle Niger: This section encompasses a vast inland delta, stretching across Mali and Niger. The river splits into numerous channels and tributaries, creating a network of wetlands and floodplains. This area is crucial for agriculture, fishing, and livestock herding.
- The Lower Niger: This section flows through Nigeria, where it widens significantly, creating a vast delta that empties into the Atlantic Ocean. This area is characterized by mangrove forests, coastal lagoons, and fertile alluvial plains.
Historical and Cultural Significance
The Niger River has played a pivotal role in the history and culture of West Africa for centuries. Its fertile banks have provided a fertile ground for agriculture, supporting the development of numerous ancient civilizations. The river served as a vital trade route, connecting different communities and facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultural practices.
- Ancient Civilizations: The Niger River played a crucial role in the development of ancient civilizations like the Nok culture in present-day Nigeria, known for its terracotta figurines and ironworking. The Jenne-jeno, a pre-colonial city in Mali, flourished along the Niger River, showcasing sophisticated architecture and trade networks.
- Trade Routes: The Niger River served as a major trade route for centuries, connecting the interior of West Africa to the coast. Trade goods like salt, gold, kola nuts, and slaves were transported along the river, fostering economic growth and cultural exchange.
- Religious and Spiritual Significance: The Niger River holds deep religious and spiritual significance for many communities in West Africa. It is considered a sacred space, associated with fertility, abundance, and the spirits of ancestors.
The Niger River: A Vital Resource in the 21st Century
The Niger River continues to be a vital resource for West Africa in the 21st century, providing numerous benefits for its people and ecosystems:
- Agriculture: The fertile floodplains and alluvial soils along the Niger River support a significant agricultural sector. The river’s waters are crucial for irrigation, facilitating the cultivation of crops such as rice, millet, sorghum, and cotton.
- Fishing: The Niger River and its tributaries are home to a diverse range of fish species, providing a significant source of protein for local communities. Fishing is a major economic activity, contributing to food security and livelihoods.
- Transportation: The Niger River remains an important waterway for transportation, connecting communities and facilitating the movement of goods. Barges and other vessels are used to transport agricultural products, construction materials, and other goods.
- Hydroelectric Power: The Niger River’s significant water flow has been harnessed for hydroelectric power generation. Dams along the river contribute to electricity production, supporting economic development and improving living standards.
Challenges and Conservation
Despite its immense importance, the Niger River faces a range of challenges, including:
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural activities, as well as urban waste disposal, contribute to pollution of the river, threatening its ecosystem and the livelihoods of those who depend on it.
- Climate Change: Climate change is impacting the Niger River’s flow and water availability, leading to increased droughts and floods, affecting agriculture, fishing, and water supply.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices are depleting fish populations, impacting food security and livelihoods.
- Dam Construction: The construction of dams along the Niger River can disrupt natural water flow, affecting downstream ecosystems and livelihoods.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring the sustainable management of the Niger River and its ecosystem. Conservation efforts are needed to protect the river’s biodiversity, mitigate pollution, and adapt to the impacts of climate change.
FAQs about the Niger River:
1. What is the source of the Niger River?
The Niger River originates in the Fouta Djallon mountains of Guinea.
2. What countries does the Niger River flow through?
The Niger River flows through Guinea, Mali, Niger, Benin, and Nigeria.
3. What is the significance of the Niger Delta?
The Niger Delta is a vast and fertile region where the Niger River empties into the Atlantic Ocean. It is home to a rich biodiversity, including mangrove forests, coastal lagoons, and diverse wildlife. It is also a major oil-producing region, but this activity has led to environmental concerns.
4. What are the major tributaries of the Niger River?
The major tributaries of the Niger River include the Benue River, the Sokoto River, and the Bani River.
5. What is the importance of the Niger River for agriculture?
The Niger River provides vital irrigation for agriculture, supporting the cultivation of various crops and ensuring food security for millions of people.
6. How does climate change affect the Niger River?
Climate change is leading to increased droughts and floods, impacting the Niger River’s flow and water availability, affecting agriculture, fishing, and water supply.
7. What are the main threats to the Niger River’s ecosystem?
The Niger River’s ecosystem faces threats from pollution, overfishing, dam construction, and the impacts of climate change.
8. What are some of the conservation efforts to protect the Niger River?
Conservation efforts include reducing pollution, promoting sustainable fishing practices, managing dam construction, and adapting to the impacts of climate change.
Tips for Understanding the Niger River:
- Explore a map: Examining a map of the Niger River will help you visualize its course and understand its geographical significance.
- Learn about the cultures: Research the diverse cultures and communities that have thrived along the Niger River for centuries.
- Read about its history: Understanding the historical role of the Niger River in trade, politics, and the development of ancient civilizations will provide valuable context.
- Consider the environmental challenges: Explore the challenges facing the Niger River, such as pollution, climate change, and overfishing, and understand the importance of conservation efforts.
Conclusion
The Niger River is a vital lifeline for West Africa, providing a unique and diverse landscape, supporting agriculture, fishing, transportation, and hydroelectric power. Its historical and cultural significance is deeply intertwined with the lives of millions of people. However, the river faces numerous challenges, including pollution, climate change, and overfishing. Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring the sustainable management of this vital resource for generations to come. Understanding the Niger River’s importance, its challenges, and the efforts to protect it is essential for appreciating its significance in the present-day landscape of West Africa.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Niger River: A Lifeline Through West Africa. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!