The Power of Sharing: Exploring the Significance of Map Distribution
Related Articles: The Power of Sharing: Exploring the Significance of Map Distribution
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Sharing: Exploring the Significance of Map Distribution. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Power of Sharing: Exploring the Significance of Map Distribution
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Power of Sharing: Exploring the Significance of Map Distribution
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of Map Sharing
- 3.2 Unlocking the Potential: Benefits of Map Sharing
- 3.3 Navigating the Landscape: Types of Map Sharing
- 3.4 Addressing Concerns: FAQs about Map Sharing
- 3.5 Charting the Course: Tips for Effective Map Sharing
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Future of Map Sharing
- 4 Closure
The Power of Sharing: Exploring the Significance of Map Distribution
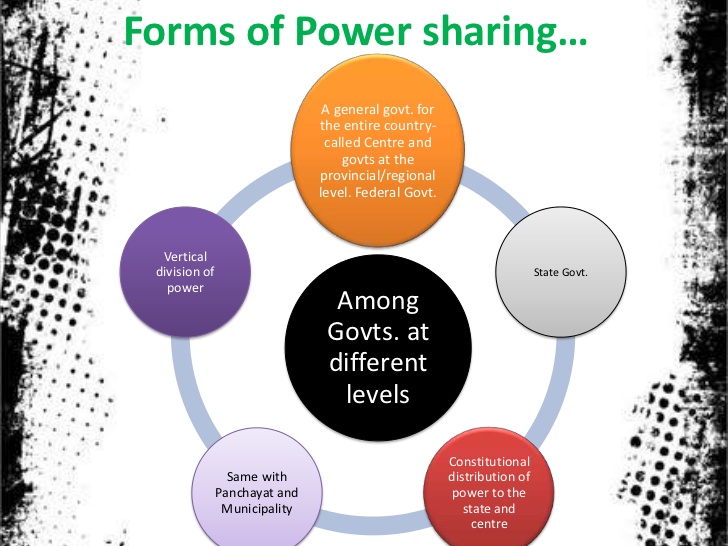
Maps have long been instrumental in navigating the physical world, guiding travelers, explorers, and everyday individuals alike. However, the advent of digital technology has revolutionized the way maps are created, accessed, and shared. Map sharing, the act of distributing and making maps accessible to others, has emerged as a powerful tool with profound implications for various sectors, from scientific research to public safety, and even personal exploration.
Understanding the Essence of Map Sharing
At its core, map sharing is the process of disseminating geographic information, often in the form of digital maps, to a wider audience. This distribution can take various forms, from simple email attachments to sophisticated online platforms that enable interactive exploration and collaborative editing.
The significance of map sharing lies in its ability to bridge the gap between data and understanding. Maps provide a visual representation of complex spatial information, making it easier for individuals to grasp patterns, relationships, and trends that might otherwise be obscured by raw data.
Unlocking the Potential: Benefits of Map Sharing
The benefits of map sharing are multifaceted and extend far beyond the realm of traditional navigation. Here are some key advantages:
1. Enhanced Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Map sharing facilitates collaboration among individuals and organizations, enabling them to share insights, data, and perspectives on a particular location or geographic area. This collaborative environment fosters innovation and accelerates progress in various fields, such as urban planning, disaster management, and environmental research.
2. Improved Decision-Making: By providing access to relevant geographic data, map sharing empowers individuals and organizations to make informed decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of the spatial context. This is particularly crucial for sectors such as transportation planning, resource management, and public health, where data-driven decision-making is paramount.
3. Increased Transparency and Accountability: Map sharing promotes transparency and accountability by making geographic information readily accessible to the public. This openness allows for greater scrutiny of government policies, infrastructure projects, and environmental impacts, fostering a more participatory and accountable society.
4. Empowerment of Individuals and Communities: Map sharing empowers individuals and communities by providing them with the tools to navigate their surroundings, understand their environment, and advocate for their needs. This is especially crucial for marginalized communities who may lack access to traditional mapping resources.
5. Advancements in Research and Development: Map sharing plays a vital role in scientific research and development by facilitating the sharing of data and insights, accelerating the discovery of new knowledge, and fostering collaboration among researchers across the globe.
6. Enhanced Public Safety and Emergency Response: Map sharing is crucial for public safety and emergency response, enabling the rapid dissemination of critical information, such as evacuation routes, hazard zones, and resource locations, during natural disasters or other emergencies.
7. Fostering Citizen Engagement and Participation: Map sharing encourages citizen engagement and participation in community planning and development by providing platforms for individuals to share their perspectives, contribute data, and participate in decision-making processes.
Navigating the Landscape: Types of Map Sharing
The world of map sharing encompasses a diverse range of approaches, each tailored to specific needs and objectives. Here are some prominent types of map sharing:
1. Static Map Sharing: This involves sharing maps as static images, often in formats like PNG or JPG. While simple to share, static maps lack interactivity and are limited in their ability to convey dynamic information.
2. Interactive Map Sharing: This approach utilizes web-based platforms to create interactive maps that allow users to zoom, pan, and explore the map content. Interactive maps often feature additional layers of information, such as points of interest, data visualizations, and user-generated content.
3. Collaborative Map Sharing: Collaborative map sharing platforms enable users to work together to create, edit, and share maps, fostering a collaborative environment for data collection, analysis, and dissemination.
4. Open Data Map Sharing: Open data map sharing involves the publication of geographic data under open licenses, allowing users to freely access, use, and distribute the data. This approach promotes transparency, innovation, and the development of new applications and services.
5. Data Visualization Map Sharing: This type of map sharing focuses on using maps to visualize complex data sets, highlighting patterns, trends, and relationships that might otherwise be hidden. Data visualization maps are powerful tools for communication, analysis, and decision-making.
Addressing Concerns: FAQs about Map Sharing
1. What are the security concerns associated with map sharing?
Security concerns are a legitimate consideration in map sharing, especially when sensitive data is involved. To mitigate these risks, it is essential to:
- Employ strong security measures: Implement robust authentication and authorization protocols to control access to sensitive data.
- Use encryption: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Implement data anonymization techniques: Remove personally identifiable information from data sets before sharing to protect user privacy.
- Establish clear data governance policies: Define guidelines for data access, use, and distribution to ensure responsible data sharing practices.
2. How can I ensure the accuracy and reliability of shared maps?
The accuracy and reliability of shared maps are paramount. To ensure data integrity, consider these measures:
- Use reputable data sources: Rely on trusted organizations and institutions for data collection and validation.
- Implement data validation and quality control procedures: Establish processes for verifying data accuracy and consistency.
- Provide clear metadata: Include detailed information about data sources, collection methods, and potential limitations.
- Encourage community feedback: Solicit feedback from users to identify and address potential errors or inconsistencies.
3. What are the ethical considerations involved in map sharing?
Ethical considerations are crucial in map sharing, especially when dealing with sensitive data or potentially harmful information. It is vital to:
- Respect privacy and confidentiality: Protect user privacy and sensitive information by obtaining consent and anonymizing data where appropriate.
- Avoid perpetuating biases and stereotypes: Ensure that maps are presented in a way that does not reinforce harmful stereotypes or biases.
- Promote inclusivity and accessibility: Make maps accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities or background.
- Consider potential unintended consequences: Evaluate the potential risks and benefits of sharing specific data to avoid negative impacts.
Charting the Course: Tips for Effective Map Sharing
1. Define your purpose and target audience: Clearly identify the purpose of sharing the map and the intended audience to tailor the content and presentation accordingly.
2. Choose the appropriate map format and platform: Select a map format and platform that best suit the purpose, audience, and data being shared.
3. Provide clear and concise metadata: Include detailed information about the map’s data sources, collection methods, and any relevant limitations.
4. Ensure accessibility and usability: Design maps for accessibility, considering users with disabilities and diverse technological capabilities.
5. Promote engagement and collaboration: Encourage feedback, contributions, and collaboration to foster a vibrant community around the shared map.
6. Regularly review and update content: Ensure that maps are up-to-date and accurate, reflecting any changes in the underlying data or environment.
Conclusion: The Future of Map Sharing
Map sharing is a powerful tool that is transforming the way we understand, interact with, and shape the world around us. As technology continues to advance and data becomes increasingly ubiquitous, the role of map sharing in fostering collaboration, innovation, and progress will only become more significant. By embracing responsible and ethical practices, we can harness the power of map sharing to create a more informed, engaged, and equitable society.






![[Power Sharing] Introduction - Power Sharing - Political Science](https://d1avenlh0i1xmr.cloudfront.net/426c1a68-d690-402f-bbfc-88d4c2b127f0/power-sharing-part-1--teachoo.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Sharing: Exploring the Significance of Map Distribution. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!