The Power of Spatial Data: Understanding and Utilizing Well Maps
Related Articles: The Power of Spatial Data: Understanding and Utilizing Well Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Power of Spatial Data: Understanding and Utilizing Well Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Spatial Data: Understanding and Utilizing Well Maps
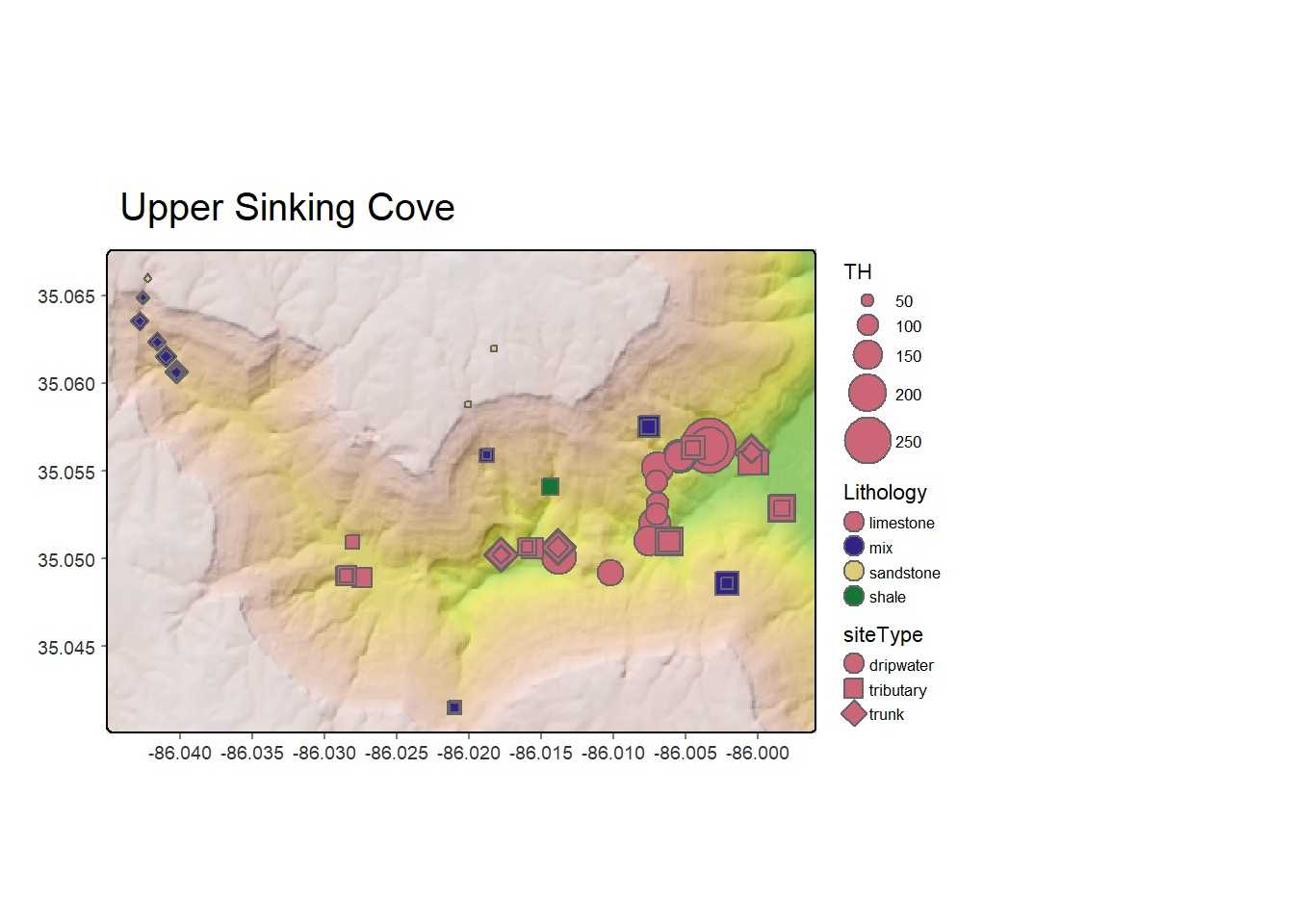
In the realm of resource management, particularly in the context of water, soil, and energy extraction, a powerful tool emerges: well maps. These maps, often digital and interactive, are more than simple representations of well locations. They are intricate repositories of data, providing a comprehensive understanding of subsurface activities, resource distribution, and potential environmental impacts.
Understanding the Essence of Well Maps
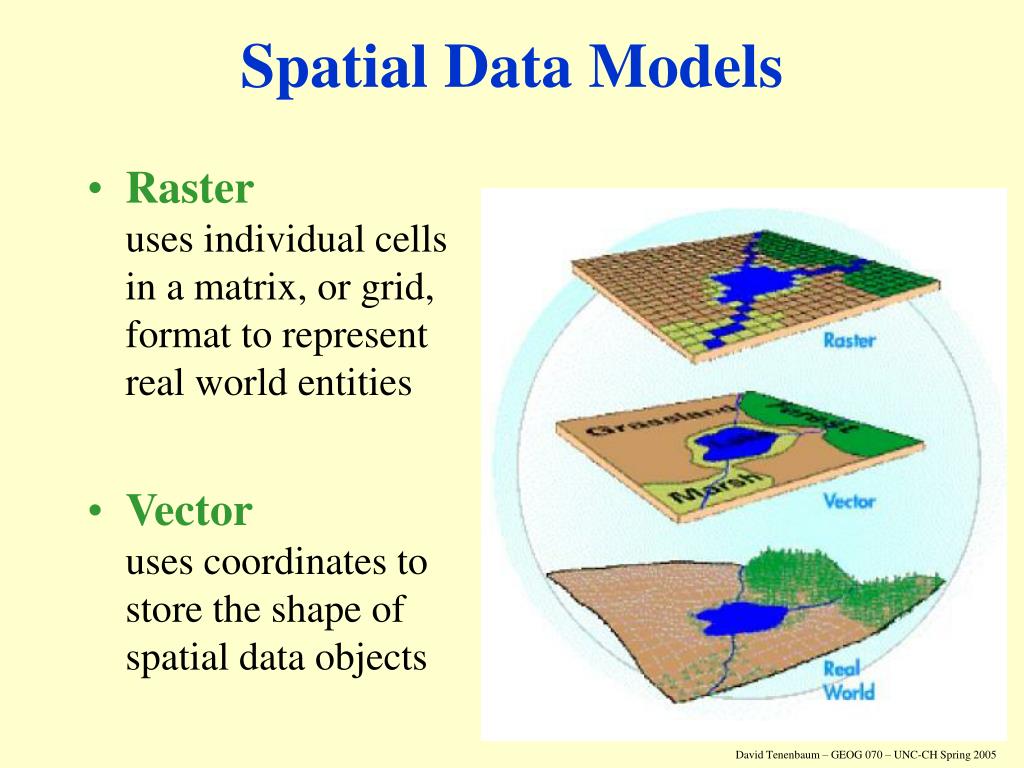
Well maps serve as a visual and informational bridge between the surface and the subsurface. They are essentially spatial databases that integrate various types of data, including:
- Well Location: Latitude, longitude, and elevation of each well, providing accurate spatial positioning.
- Well Type: Categorization of wells based on their purpose, such as water supply, oil extraction, geothermal energy, or monitoring.
- Well Depth: The vertical extent of each well, indicating the depth at which resources are accessed.
- Well Construction: Details about the materials and methods used in well construction, impacting resource extraction and potential environmental risks.
- Well Status: Information about the current state of each well, such as active, inactive, abandoned, or under construction.
- Well History: Records of past activities related to each well, including drilling dates, production data, and maintenance records.
- Geospatial Data: Integration with other spatial data layers, such as geological formations, soil types, and hydrological boundaries, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the context surrounding wells.
The Benefits of Utilizing Well Maps
The value of well maps lies in their ability to:
- Enhance Resource Management: Well maps provide valuable insights into the distribution and availability of resources, facilitating informed decision-making for resource extraction, allocation, and conservation.
- Improve Environmental Monitoring: By visualizing well locations and associated data, well maps enable the tracking of potential environmental impacts, such as groundwater contamination or land subsidence, facilitating early detection and mitigation efforts.
- Support Regulatory Compliance: Well maps serve as a crucial tool for regulatory agencies to monitor compliance with environmental regulations, ensuring responsible and sustainable resource utilization.
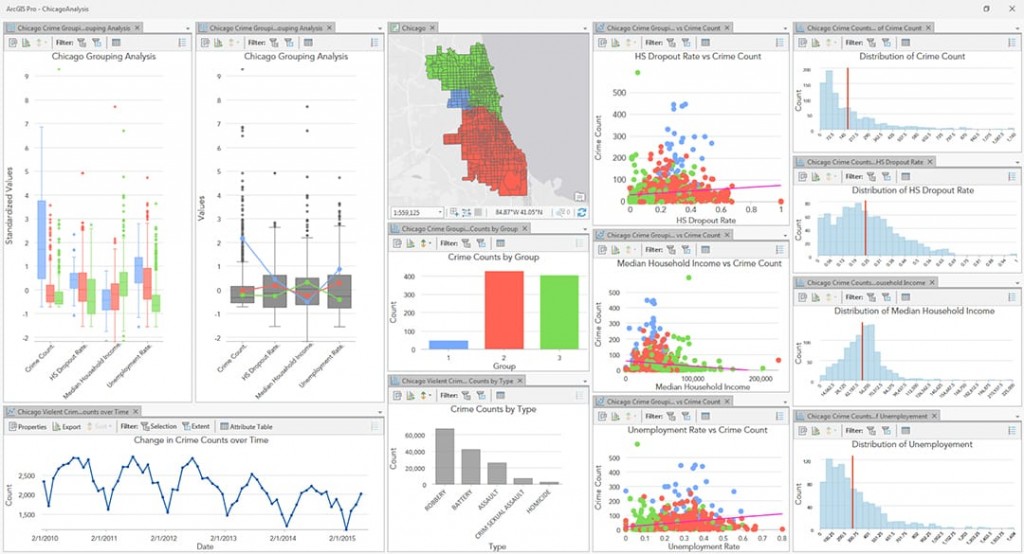
- Facilitate Research and Analysis: Well maps provide a rich dataset for researchers and scientists to study subsurface processes, analyze resource potential, and assess the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Promote Transparency and Public Engagement: Well maps can enhance transparency by making information about subsurface activities readily accessible to the public, fostering informed discussions and community engagement.
Examples of Well Map Applications
The applications of well maps extend across various sectors:
- Water Resource Management: Well maps assist in identifying optimal locations for new wells, optimizing water extraction, and monitoring groundwater levels to ensure sustainable water use.
- Oil and Gas Exploration: Well maps aid in identifying potential oil and gas reserves, planning drilling operations, and monitoring production activities, maximizing resource recovery and minimizing environmental risks.
- Geothermal Energy Development: Well maps facilitate the exploration and development of geothermal energy resources, identifying suitable locations for geothermal power plants and monitoring their performance.
- Environmental Protection: Well maps enable the monitoring of potential contamination sources, assessing the impact of industrial activities on groundwater, and implementing mitigation strategies to protect water resources.
FAQs about Well Maps
Q: What is the difference between a well map and a geological map?
A: While both maps provide information about the subsurface, well maps focus specifically on the locations and characteristics of wells, while geological maps depict the distribution of different rock formations and geological features.
Q: Are well maps publicly accessible?
A: The accessibility of well maps varies depending on the jurisdiction and the specific data being shared. In many regions, well location data is publicly available, while other data, such as production records, might be considered confidential.
Q: How are well maps updated?
A: Well maps are typically updated regularly as new wells are drilled, existing wells are modified, or new data becomes available. The frequency of updates depends on the specific purpose and the availability of data.
Q: What are the limitations of well maps?
A: Well maps can only depict what is known about the subsurface. They may not capture all existing wells, especially those that are unregistered or abandoned. Additionally, the accuracy of data depends on the quality of information collected and the methods used for data acquisition.
Tips for Utilizing Well Maps Effectively
- Understand the Data: Familiarize yourself with the types of data included in the well map and their units of measurement.
- Explore the Tools: Utilize the interactive features of digital well maps, such as zoom, pan, and filtering options, to explore specific areas of interest.
- Combine with Other Data: Integrate well map data with other spatial data layers, such as geological maps, soil maps, or population density maps, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the context.
- Consult Experts: Seek guidance from experts in relevant fields, such as hydrologists, geologists, or environmental engineers, to interpret well map data and draw informed conclusions.
Conclusion
Well maps are invaluable tools for understanding and managing subsurface activities, resources, and environmental impacts. Their ability to integrate diverse data sources, provide visual representations of spatial information, and facilitate analysis and decision-making makes them essential for sustainable resource management, environmental protection, and responsible development. As our understanding of the subsurface continues to evolve and data collection techniques advance, well maps will play an increasingly crucial role in shaping our interactions with the Earth’s resources.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Spatial Data: Understanding and Utilizing Well Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!