The Rio Grande: A Lifeline Through the American Southwest
Related Articles: The Rio Grande: A Lifeline Through the American Southwest
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Rio Grande: A Lifeline Through the American Southwest. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Rio Grande: A Lifeline Through the American Southwest
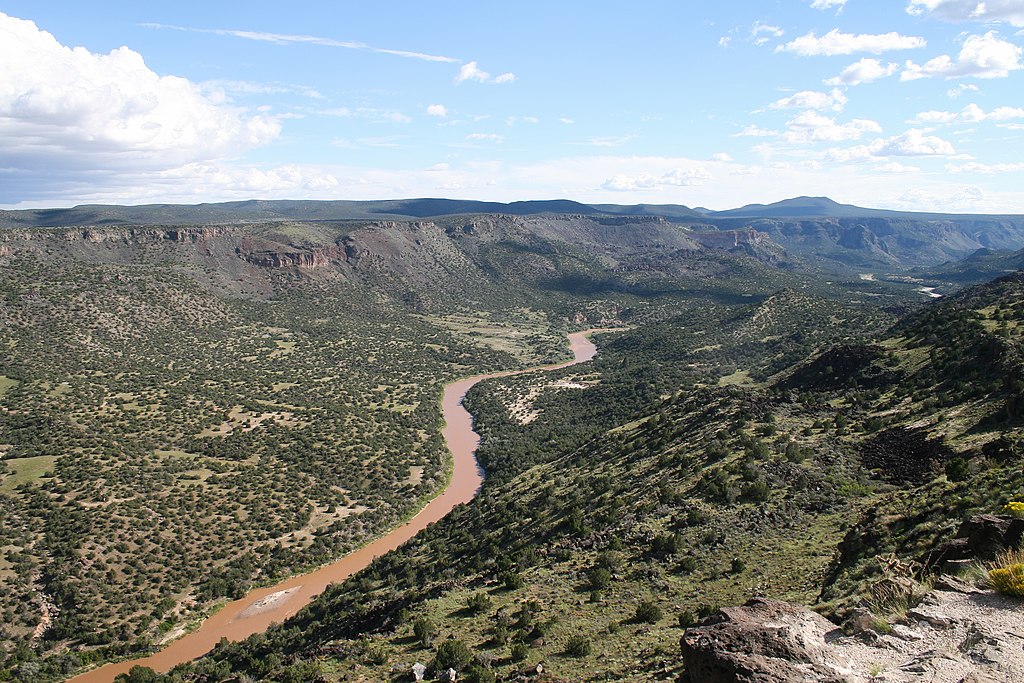

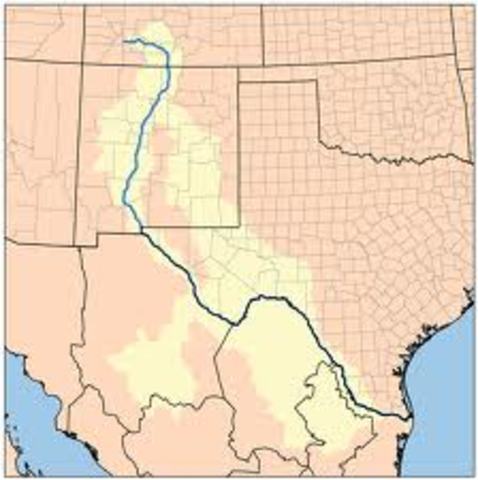
The Rio Grande, a river with a rich history and profound significance, flows for over 1,900 miles through the American Southwest and northern Mexico. Its journey begins in the San Juan Mountains of southwestern Colorado, meanders through the high plains of New Mexico, and carves its way through the rugged Texas landscape before emptying into the Gulf of Mexico. This river, a natural boundary between the United States and Mexico, is a vital resource for both countries, supporting diverse ecosystems, providing water for agriculture and urban centers, and serving as a cultural and historical landmark.
A Geographic Overview
The Rio Grande’s course can be divided into three distinct sections:
- Upper Rio Grande: Originating in the San Juan Mountains of Colorado, this section is characterized by its steep gradient and rapid flow. It flows through the San Luis Valley, a fertile agricultural region, before entering New Mexico.
- Middle Rio Grande: This section traverses the Rio Grande Rift, a geological feature that has shaped the landscape of New Mexico. The river flows through Albuquerque, the state’s largest city, and forms the Rio Grande Valley, a region known for its agricultural production and cultural heritage.
- Lower Rio Grande: The final section of the river flows through Texas, where it becomes a defining feature of the state’s landscape. It forms the border between Texas and Mexico, and its flow slows considerably as it approaches the Gulf of Mexico.
The Rio Grande: A Lifeline for Ecosystems and Communities
The Rio Grande is a vital resource for a diverse range of ecosystems, supporting a rich biodiversity of flora and fauna. Its riparian zones, the areas immediately adjacent to the river, are home to a wide variety of plant and animal species, including cottonwood trees, willows, mesquite, and numerous bird species. The river also supports a variety of fish species, some of which are endemic to the Rio Grande basin.
The river’s importance extends beyond its ecological significance. It provides a crucial source of water for agriculture, industry, and urban centers in both the United States and Mexico. The Rio Grande Valley, a region that spans both sides of the border, is known for its agricultural production, relying heavily on irrigation water from the river. Urban centers such as Albuquerque, El Paso, and Ciudad Juarez also depend on the Rio Grande for their water supply.
The Rio Grande: A Historical and Cultural Tapestry
The Rio Grande has played a significant role in the history and culture of the Southwest. Indigenous peoples have inhabited the region for centuries, utilizing the river’s resources and shaping their lives around its rhythms. The Spanish conquistadors arrived in the 16th century, establishing settlements along the river and claiming the region for Spain. The Rio Grande became a focal point for trade and cultural exchange between different groups, shaping the region’s unique cultural heritage.
The river also played a crucial role in the development of the United States and Mexico. It served as a natural boundary between the two countries, shaping their relationship and influencing their development. The Rio Grande’s history is marked by periods of cooperation and conflict, reflecting the complex dynamics of the US-Mexico border.
Challenges and Opportunities
The Rio Grande faces numerous challenges, including water scarcity, pollution, and the impacts of climate change. The river’s flow has been significantly impacted by human activities, such as dam construction, irrigation, and urban development. These activities have reduced the river’s natural flow, leading to water scarcity and conflicts over water allocation.
Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and urban wastewater has also affected the Rio Grande’s water quality. These pollutants threaten the health of the river’s ecosystems and the well-being of communities that depend on it. Climate change is exacerbating these challenges, leading to increased droughts, hotter temperatures, and more extreme weather events, further stressing the river’s resources.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities to protect and restore the Rio Grande. Collaborative efforts between the United States and Mexico are crucial for addressing the transboundary nature of the river’s challenges. Conservation and restoration initiatives, including water conservation programs, pollution control measures, and habitat restoration projects, can help to improve the river’s health and sustainability.
FAQs
1. What is the length of the Rio Grande?
The Rio Grande is approximately 1,900 miles long, making it one of the longest rivers in North America.
2. What is the source of the Rio Grande?
The Rio Grande originates in the San Juan Mountains of southwestern Colorado, specifically in the headwaters of the Rio Grande National Forest.
3. Where does the Rio Grande flow?
The Rio Grande flows through the states of Colorado, New Mexico, and Texas in the United States, and the states of Chihuahua, Coahuila, and Tamaulipas in Mexico.
4. What are the major cities located along the Rio Grande?
Some of the major cities located along the Rio Grande include Albuquerque, New Mexico; El Paso, Texas; and Ciudad Juarez, Mexico.
5. What are some of the environmental challenges facing the Rio Grande?
The Rio Grande faces several environmental challenges, including water scarcity, pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial waste, and urban wastewater, and the impacts of climate change.
6. What are some of the cultural and historical aspects of the Rio Grande?
The Rio Grande has played a significant role in the history and culture of the Southwest. Indigenous peoples have inhabited the region for centuries, utilizing the river’s resources and shaping their lives around its rhythms. The river also served as a natural boundary between the United States and Mexico, shaping their relationship and influencing their development.
7. What are some of the efforts being made to protect and restore the Rio Grande?
Collaborative efforts between the United States and Mexico are crucial for addressing the transboundary nature of the river’s challenges. Conservation and restoration initiatives, including water conservation programs, pollution control measures, and habitat restoration projects, can help to improve the river’s health and sustainability.
Tips
- Visit a National Park or Wildlife Refuge: Explore the beauty and importance of the Rio Grande by visiting one of the many National Parks or Wildlife Refuges located along its banks.
- Learn about the history and culture of the region: Immerse yourself in the rich history and culture of the Southwest by visiting museums, historical sites, and cultural centers.
- Support conservation efforts: Contribute to organizations working to protect and restore the Rio Grande’s ecosystems.
- Reduce your water consumption: Conserve water in your daily life to help alleviate water scarcity in the region.
- Advocate for sustainable practices: Support policies and initiatives that promote sustainable water management and pollution control.
Conclusion
The Rio Grande, a river that has shaped the landscape, history, and culture of the American Southwest, is a vital resource for both the United States and Mexico. It supports diverse ecosystems, provides water for agriculture and urban centers, and serves as a cultural and historical landmark. While facing challenges related to water scarcity, pollution, and climate change, the Rio Grande also presents opportunities for collaboration, conservation, and restoration. By recognizing the river’s importance and working together to address its challenges, we can ensure its continued health and sustainability for generations to come.
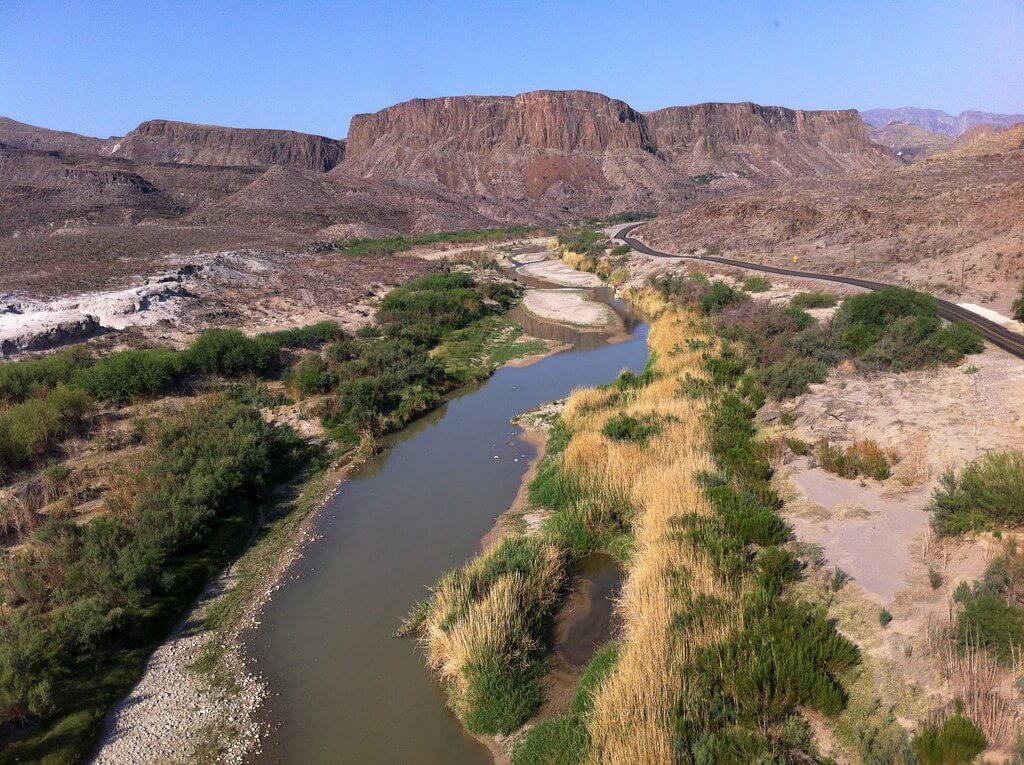
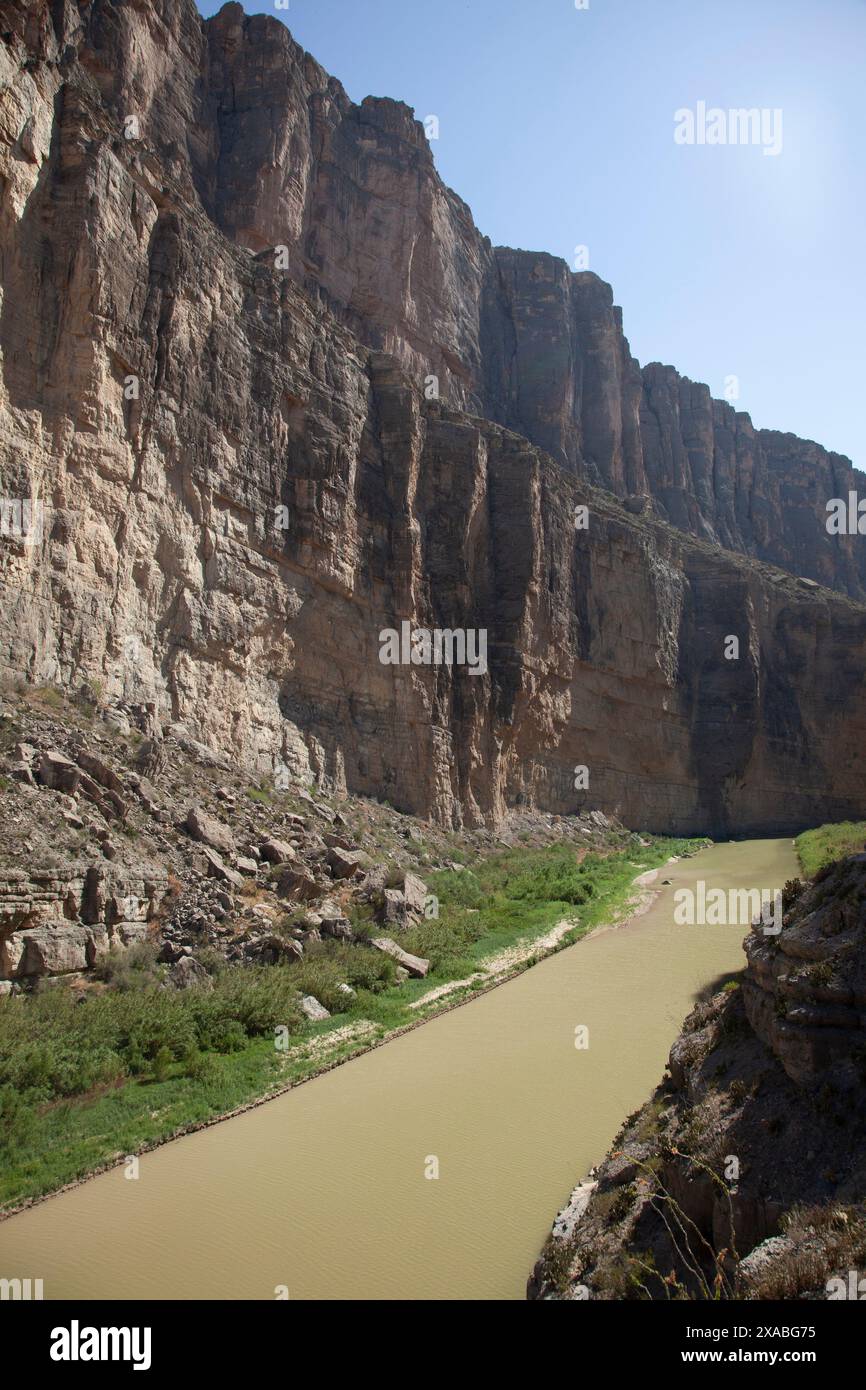
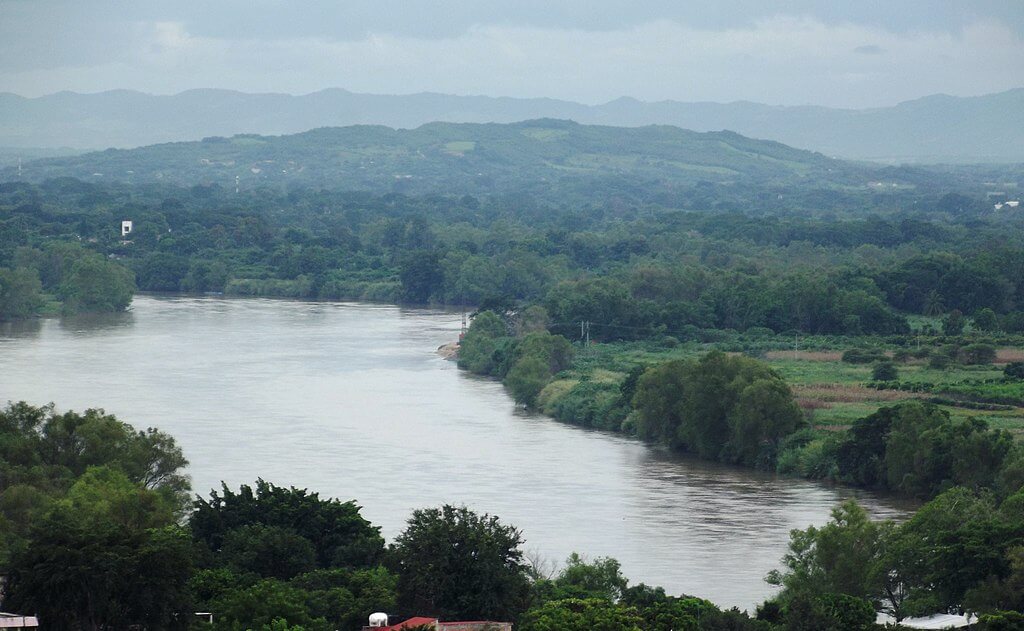







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Rio Grande: A Lifeline Through the American Southwest. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!