Unfolding the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Historic Maps of Europe
Related Articles: Unfolding the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Historic Maps of Europe
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unfolding the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Historic Maps of Europe. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unfolding the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Historic Maps of Europe
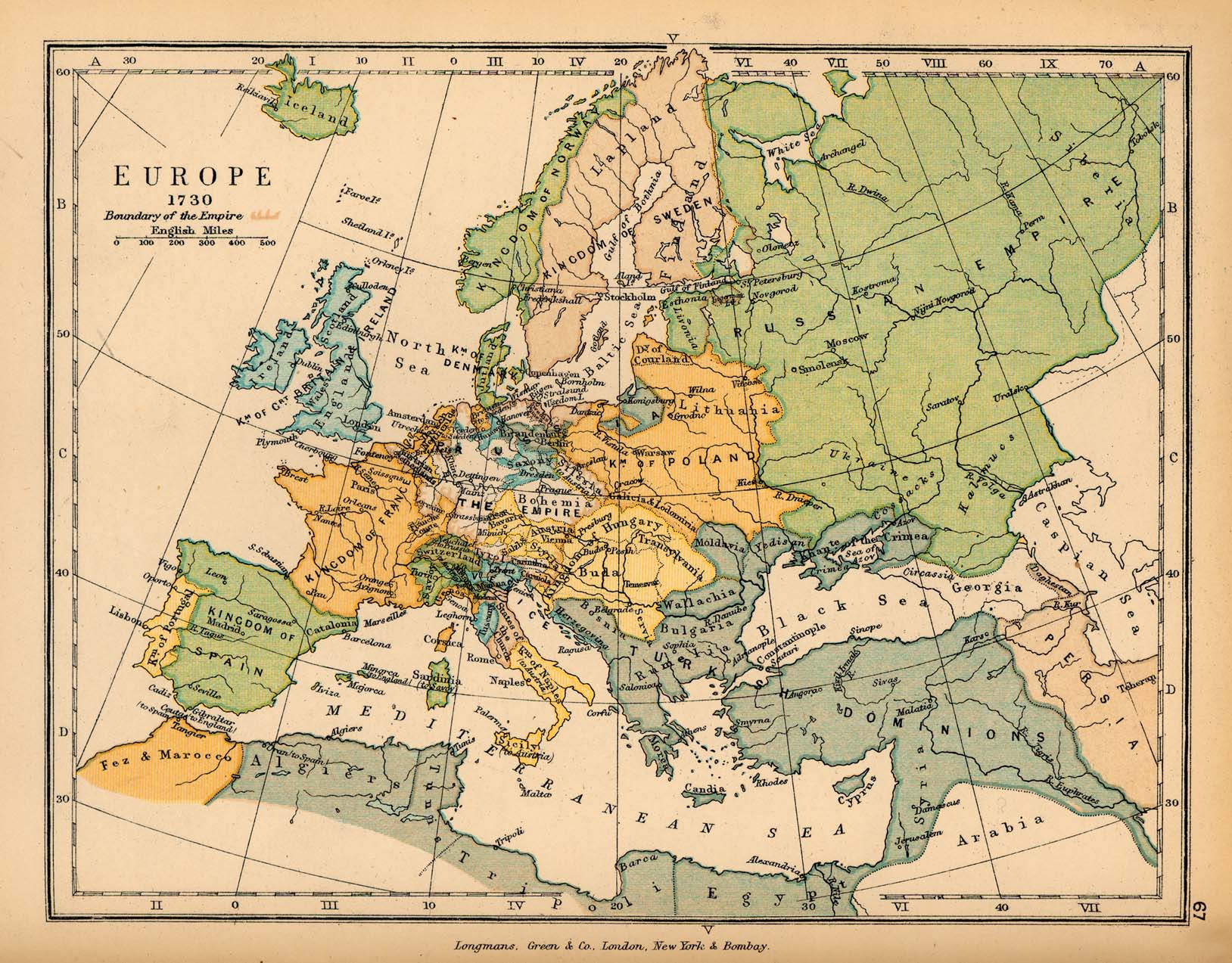
Maps, those seemingly simple representations of our world, are far more than mere navigational tools. They are windows into the past, offering glimpses into the evolution of human societies, the ebb and flow of empires, and the ever-shifting geopolitical landscape. Nowhere is this more evident than in the realm of historic maps of Europe, which provide a fascinating and intricate narrative of the continent’s rich and complex history.
A Glimpse into the Past: Tracing the Evolution of Europe
From ancient Greek cartographers to the meticulous draftsmen of the Renaissance, the history of mapmaking in Europe is a testament to human ingenuity and the insatiable desire to understand and represent the world around us. These maps, meticulously crafted over centuries, offer a unique perspective on the changing political, cultural, and geographical realities of the continent.
-
Ancient Origins: The earliest maps of Europe, often fragmented and incomplete, emerged from the ancient civilizations of Greece and Rome. These maps, primarily used for navigation and military campaigns, reflected the limited geographical knowledge of the time. For instance, the map of the world by the Greek geographer Anaximander (6th century BC), while rudimentary, is considered one of the first attempts to depict the world as a sphere.
-
Medieval Innovations: The Middle Ages witnessed a resurgence of cartography, driven by the need to map pilgrimage routes and understand the expanding Christian world. The famous "T-O" map, with its circular world centered on Jerusalem, became a dominant representation of the known world. While these maps were often infused with religious symbolism and mythical creatures, they reflected the growing awareness of the continent’s vastness and the desire to understand its diverse regions.
-
Renaissance and Reformation: The Renaissance marked a turning point in mapmaking, ushering in a period of scientific exploration and cartographic innovation. The invention of the printing press facilitated the mass production of maps, disseminating geographical knowledge to a wider audience. This era saw the rise of cartographers like Gerardus Mercator, whose projection revolutionized mapmaking and remains in use today. The Reformation, with its emphasis on biblical interpretation, further fueled cartographic activity, as scholars sought to understand the geography of the Holy Land and other biblical locations.
-
Age of Exploration: The Age of Exploration, fueled by the desire for new trade routes and territories, propelled European cartography to new heights. Explorers like Christopher Columbus and Ferdinand Magellan brought back invaluable geographical data, leading to the creation of more accurate and detailed maps. This era witnessed the development of specialized maps, including nautical charts, which played a crucial role in navigation and trade.
-
Enlightenment and Beyond: The Enlightenment, with its emphasis on reason and scientific inquiry, further advanced the field of cartography. The use of precise measurements, triangulation, and the development of new surveying tools led to increasingly accurate and detailed maps. The 18th and 19th centuries saw the creation of comprehensive atlases, covering entire continents and providing a detailed picture of the European landscape.
Beyond the Lines: Interpreting the Meaning of Historic Maps
While historic maps offer a visual representation of the physical world, they also provide insights into the cultural and social realities of the time. By analyzing the content, style, and context of these maps, historians and cartographers can glean valuable information about:
-
Political Boundaries: Historic maps are invaluable for understanding the evolution of political boundaries, tracing the rise and fall of empires, and the formation of nation-states. For example, the shifting borders of the Holy Roman Empire, the expansion of the Ottoman Empire, and the gradual unification of Italy can all be traced through the lens of historic maps.
-
Economic Activity: Maps often depict trade routes, major cities, and resource distribution, offering insights into the economic landscape of Europe. The growth of major trading centers like Venice, Amsterdam, and London can be observed through the evolution of their representations on maps.
-
Cultural Influences: The style and content of maps often reflect the prevailing cultural and intellectual trends of the time. For instance, the inclusion of religious symbols, mythical creatures, or specific geographical features can reveal the beliefs and values of the mapmakers and their intended audience.
-
Social Structures: Maps can also shed light on social structures and hierarchies. The representation of cities, towns, and villages, along with their associated demographics and economic activities, can offer insights into the distribution of wealth, power, and social mobility.
Beyond the Borders: The Global Impact of European Cartography
The influence of European cartography extends far beyond the continent’s borders. The techniques, tools, and knowledge developed by European mapmakers had a profound impact on the exploration and mapping of the world. European maps were used by explorers, traders, and missionaries to navigate unknown territories, chart new trade routes, and establish colonial empires. The global impact of European cartography is evident in the universal use of the Mercator projection, which remains a standard for world maps today.
Engaging with History: The Importance of Historic Maps
Historic maps offer a unique and engaging way to connect with the past. They provide a visual narrative of the world, allowing us to see the evolution of human societies and the changing geopolitical landscape. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper understanding of the past and its influence on the present. They serve as a powerful reminder of the interconnectedness of history, geography, and culture.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How can I find historic maps of Europe?
A: Historic maps of Europe can be found in various repositories, including:
- National and university libraries: Many libraries hold extensive collections of historic maps, often digitized and accessible online.
- Historical societies and museums: These institutions frequently exhibit and preserve historic maps as part of their collections.
- Online databases: Several online databases, such as the David Rumsey Map Collection and the Library of Congress’s Geography and Map Division, offer searchable collections of historic maps.
- Auction houses and antique dealers: Historic maps are also sometimes sold at auction or through specialized antique dealers.
Q: What are the benefits of studying historic maps?
A: Studying historic maps offers numerous benefits, including:
- Gaining a deeper understanding of history: Maps provide a visual context for historical events, allowing for a more comprehensive and engaging understanding of the past.
- Developing critical thinking skills: Analyzing and interpreting historic maps requires critical thinking skills, as they often contain multiple layers of information and require contextualization.
- Enhancing spatial awareness: Maps help to develop spatial awareness and the ability to visualize geographical relationships.
- Promoting interdisciplinary learning: Historic maps can be used in a variety of disciplines, including history, geography, art, and social studies, promoting interdisciplinary learning.
Tips for Studying Historic Maps
- Understand the context: Before studying a historic map, consider the time period, the mapmaker, and the intended audience.
- Analyze the content: Pay attention to the geographical features, political boundaries, symbols, and other details included on the map.
- Compare and contrast: Compare different historic maps to observe how representations of the world have evolved over time.
- Use technology: Utilize online tools and resources to zoom in on details, view maps in 3D, and explore interactive features.
- Engage in discussion: Share your observations and interpretations with others, fostering a deeper understanding of the maps and their historical significance.
Conclusion
Historic maps of Europe are more than just static representations of the continent’s geography. They are dynamic and multifaceted documents that offer a unique perspective on the past, revealing the intricate tapestry of political, social, cultural, and economic change. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper understanding of the forces that have shaped Europe and its place in the world. They serve as a testament to human ingenuity, the enduring power of cartography, and the importance of preserving our historical heritage. Through these maps, we can connect with the past, gain insights into the present, and imagine the possibilities of the future.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unfolding the Tapestry of Time: A Journey Through Historic Maps of Europe. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!