Unveiling California’s Temperature Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling California’s Temperature Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling California’s Temperature Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling California’s Temperature Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps

California, a state renowned for its diverse landscapes and climates, experiences a wide range of temperatures throughout the year. Understanding these temperature variations is crucial for various sectors, from agriculture and tourism to public health and infrastructure planning. This is where heat maps come into play, offering a visual representation of temperature distribution across the state, providing valuable insights into the spatial patterns of heat.
Understanding Heat Maps: A Visual Representation of Temperature
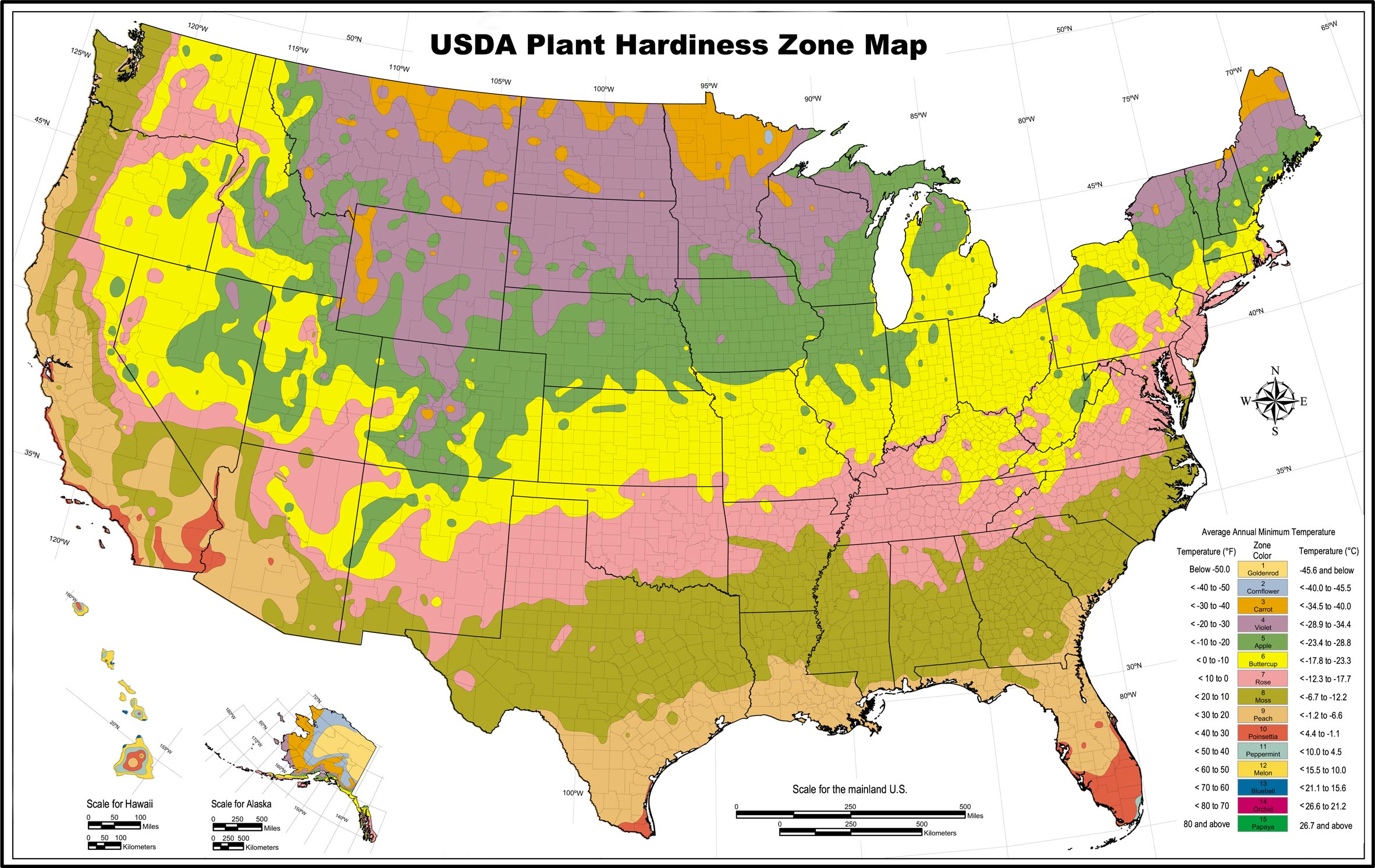
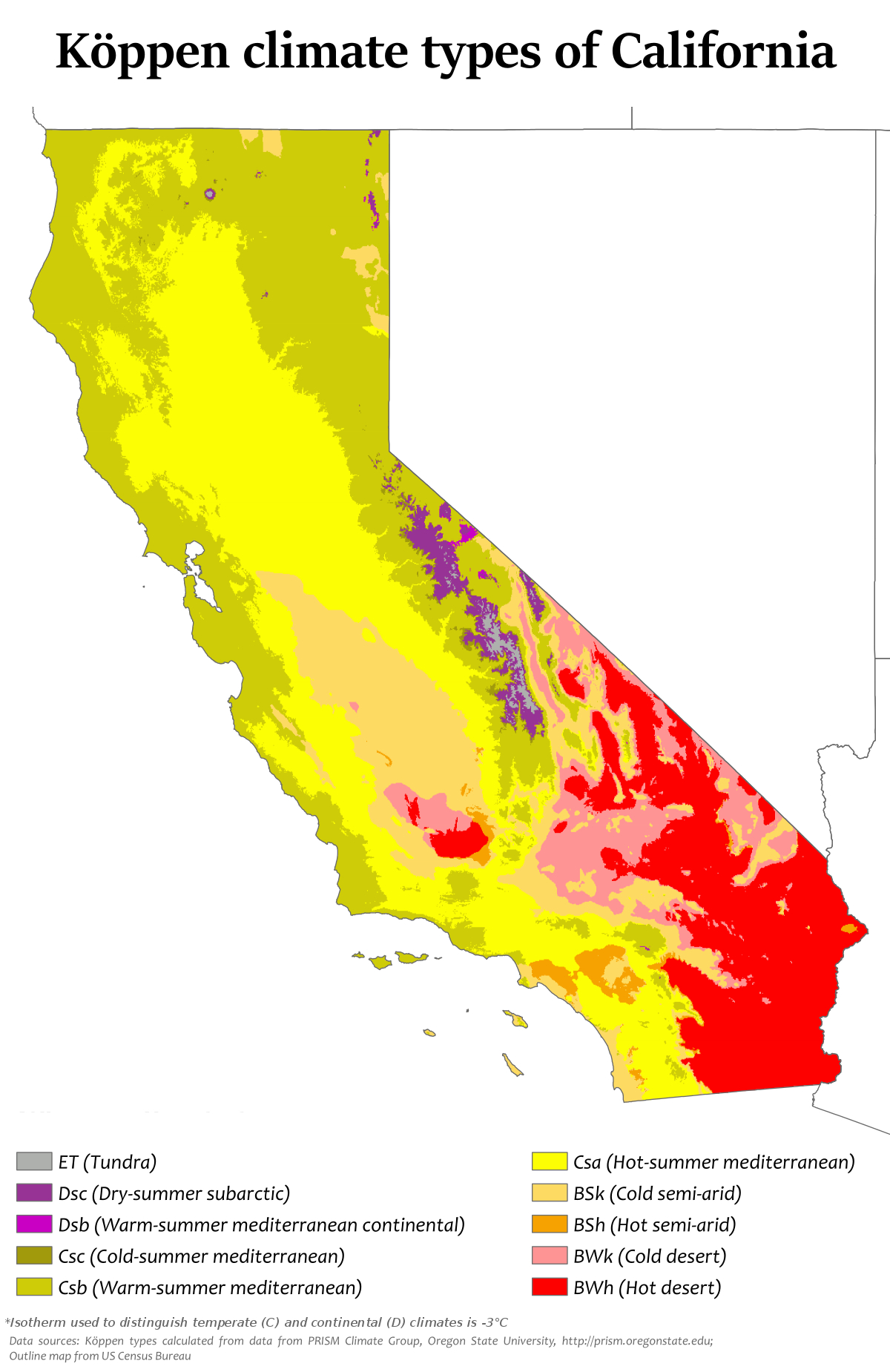
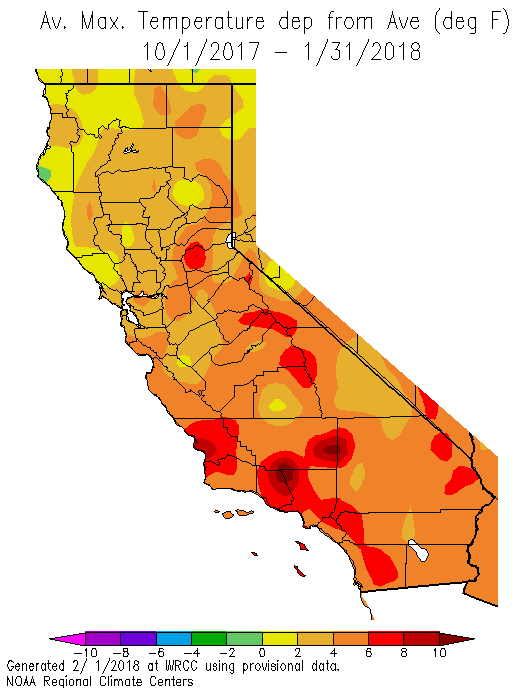
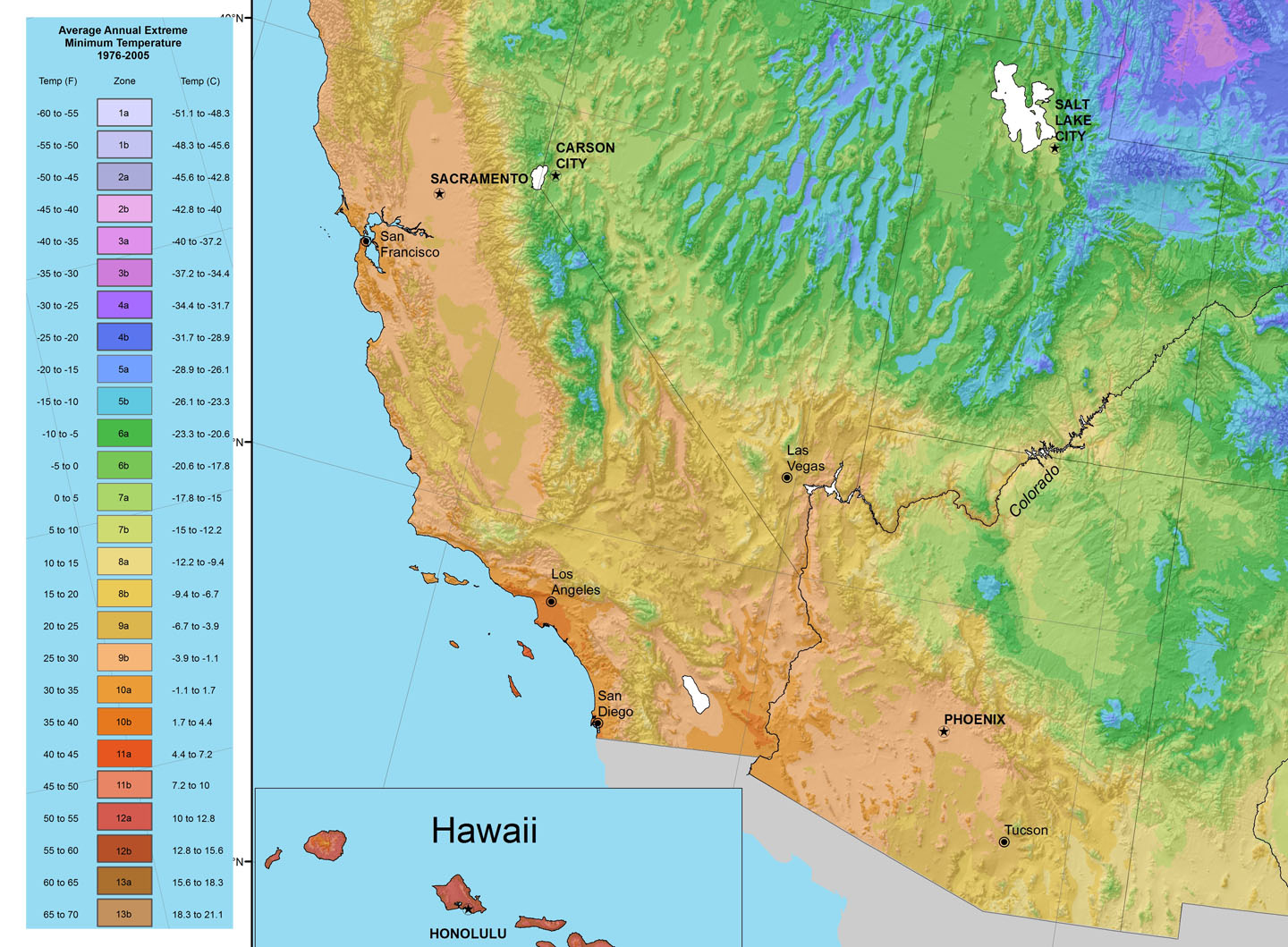
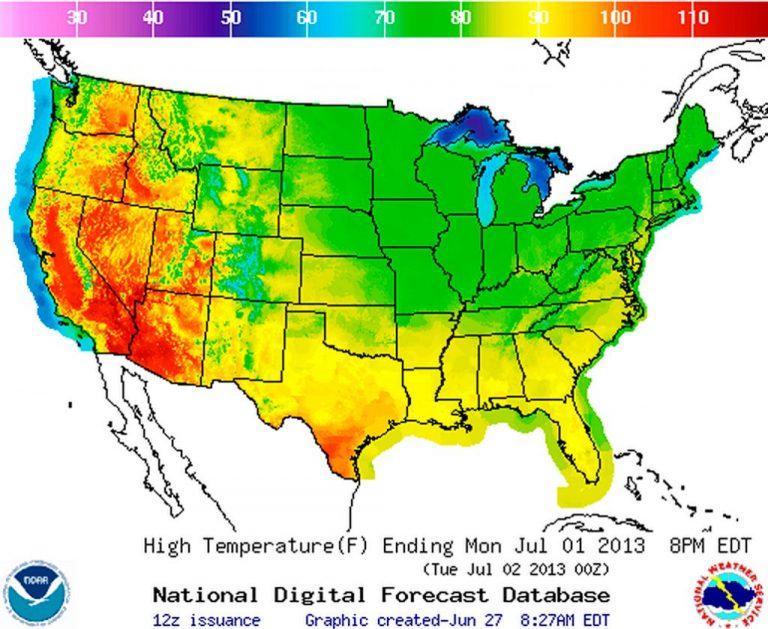
Heat maps, also known as thermal maps, utilize a color gradient to depict temperature variations across a geographical area. Typically, warmer temperatures are represented by red and orange hues, while cooler temperatures are depicted in blue and green. This visual representation allows for quick and intuitive comprehension of temperature patterns, highlighting areas of extreme heat or cold.
The Importance of Heat Maps in California
Heat maps play a pivotal role in understanding and addressing various challenges associated with California’s diverse climate. They provide valuable insights into:
1. Heat Waves and Extreme Temperatures: Heat maps effectively illustrate the spatial distribution of heat waves, enabling authorities to identify areas most vulnerable to extreme temperatures. This information is crucial for implementing early warning systems, providing timely alerts to vulnerable populations, and allocating resources effectively.
2. Public Health and Safety: Heat maps are vital for public health agencies, allowing them to assess the risk of heat-related illnesses and mortality. By identifying areas with high temperatures, public health officials can implement targeted interventions, such as distributing cooling resources and disseminating public health advisories.
3. Agriculture and Water Management: Heat maps are essential for agricultural planning, helping farmers understand the thermal conditions in different regions and optimize crop production. They can also assist in water management by identifying areas prone to water stress due to high temperatures.
4. Infrastructure and Urban Planning: Heat maps are increasingly used in urban planning to assess the impact of urban heat islands, areas within cities that experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas. This information can guide the design of buildings, green spaces, and infrastructure to mitigate the effects of urban heat and improve livability.
5. Climate Change Adaptation: Heat maps are crucial for understanding the potential impacts of climate change on California’s temperature patterns. By analyzing historical data and projecting future scenarios, heat maps can help policymakers develop adaptation strategies to mitigate the risks associated with rising temperatures.
Exploring Different Types of Heat Maps
Heat maps can be categorized based on their data sources, spatial resolution, and temporal scale:
1. Surface Temperature Heat Maps: These maps utilize data from satellites, weather stations, or other sensors to depict surface temperatures. They provide a broad overview of temperature distribution across the state.
2. Air Temperature Heat Maps: These maps focus on air temperature, typically measured at a specific height above ground. They are useful for understanding the thermal environment experienced by humans and other living organisms.
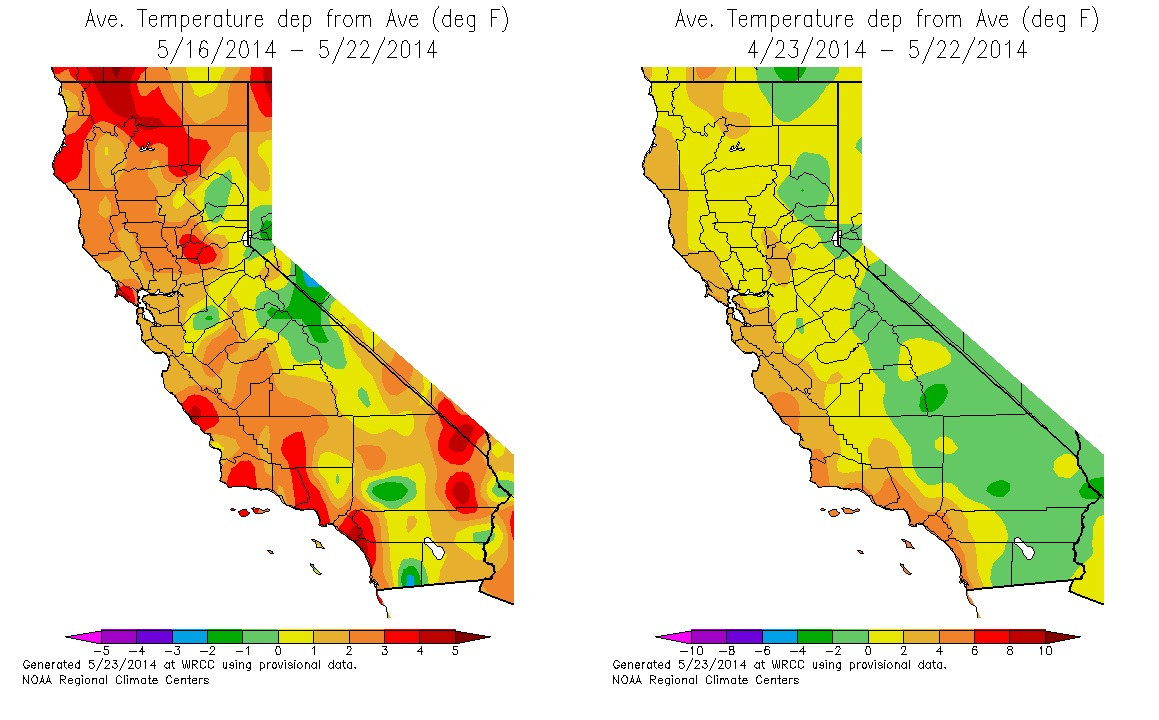
3. Historical Heat Maps: These maps showcase temperature data from previous years, allowing for analysis of long-term trends and identifying potential shifts in temperature patterns over time.
4. Real-Time Heat Maps: These maps provide up-to-date temperature information, allowing for monitoring of current conditions and rapid responses to heat events.
5. Predictive Heat Maps: These maps utilize climate models and historical data to forecast future temperature patterns, providing insights into potential heat waves and extreme temperatures.
Frequently Asked Questions about Heat Maps in California
1. Where can I find heat maps for California?
Several organizations provide access to heat maps for California, including the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the California Department of Public Health, and various academic institutions.
2. What are the limitations of heat maps?
Heat maps provide a valuable overview of temperature patterns, but they have limitations. For instance, they may not capture localized temperature variations within small areas, and their accuracy can be influenced by data availability and sensor limitations.
3. How can I use heat maps to protect myself from heat?
By consulting heat maps, individuals can identify areas with high temperatures and take precautions such as staying hydrated, avoiding strenuous activities during peak heat hours, and seeking shade or air-conditioned spaces.
4. How are heat maps used in climate change research?
Heat maps play a crucial role in climate change research by providing evidence of rising temperatures, identifying areas most vulnerable to heat-related impacts, and informing the development of adaptation strategies.
Tips for Using Heat Maps Effectively
1. Understand the Data Source and Spatial Resolution: Before interpreting a heat map, it is essential to understand the source of the data and the spatial resolution. This information will help determine the reliability and accuracy of the map.
2. Consider the Time Scale: Heat maps can depict temperature data at different time scales, such as daily, monthly, or annual. Selecting the appropriate time scale is crucial for analyzing relevant temperature patterns.
3. Use Multiple Data Sources: Combining data from multiple sources, such as satellites, weather stations, and climate models, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of temperature variations.
4. Integrate Heat Maps with Other Data: Heat maps can be integrated with other relevant data, such as population density, socioeconomic factors, and infrastructure information, to gain deeper insights into the impacts of temperature variations.
Conclusion: The Value of Visualizing California’s Temperature Landscape
Heat maps provide a powerful tool for understanding and addressing the challenges posed by California’s diverse climate. By visually representing temperature patterns, they enable informed decision-making in various sectors, from public health and agriculture to infrastructure planning and climate change adaptation. As California continues to experience the impacts of climate change, the use of heat maps will become increasingly important for ensuring the well-being and resilience of its communities and ecosystems.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling California’s Temperature Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!