Unveiling the Intricacies of Genetics: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping
Related Articles: Unveiling the Intricacies of Genetics: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Intricacies of Genetics: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Intricacies of Genetics: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping

Genetics, the study of heredity and the variation of inherited traits, is a complex and multifaceted field. Understanding the interconnectedness of its various concepts is crucial for comprehending the intricate mechanisms that govern life. Concept mapping, a visual representation of knowledge, provides a powerful tool for navigating this complex landscape.
Concept Mapping: A Visual Framework for Genetics
A concept map is a diagram that visually depicts the relationships between different concepts. It utilizes nodes, representing individual concepts, and connecting lines, illustrating the connections between them. These connections can represent various relationships, such as:
- Hierarchical relationships: One concept is a subcategory or a more specific example of another.
- Sequential relationships: One concept follows another in a specific order.
- Cause-and-effect relationships: One concept causes or influences another.
- Association relationships: Two concepts are related or occur together.
The Power of Concept Mapping in Genetics
Concept mapping offers numerous advantages for studying and understanding genetics:
1. Organizing Complex Information: Genetics involves a vast array of concepts, from DNA structure and gene expression to inheritance patterns and genetic disorders. Concept mapping helps organize this information into a coherent framework, making it easier to grasp the interconnectedness of different ideas.
2. Visualizing Relationships: By visually representing the relationships between concepts, concept maps provide a clearer understanding of how different aspects of genetics interact and influence each other. This visual representation can enhance comprehension and retention of information.
3. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: When constructing a concept map, individuals may realize they lack understanding of certain connections or concepts. This awareness can stimulate further research and learning.
4. Facilitating Critical Thinking: The process of creating a concept map encourages critical thinking. It requires individuals to analyze concepts, identify relationships, and prioritize information. This active engagement promotes deeper understanding and retention.
5. Enhancing Communication: Concept maps serve as a powerful communication tool. They allow individuals to share their understanding of complex genetic concepts with others in a clear and concise manner, fostering effective collaboration and knowledge exchange.
Concept Mapping in Action: Examples from Genetics
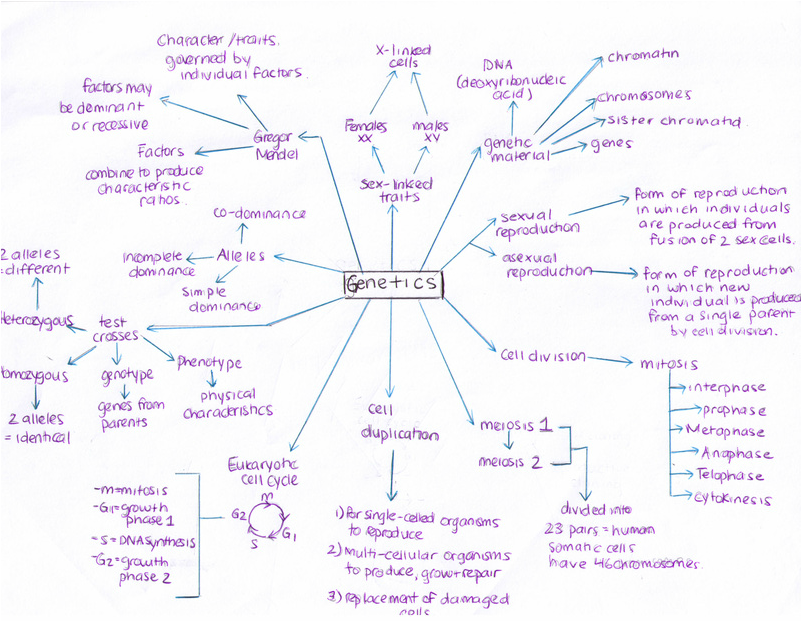
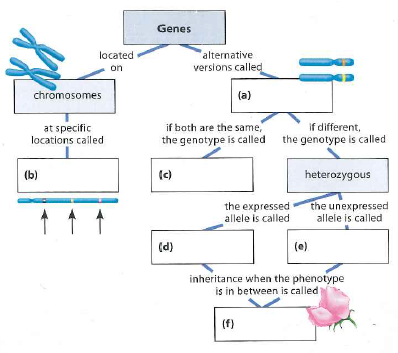
1. Mendelian Inheritance: A concept map for Mendelian inheritance could depict the relationships between key concepts such as genes, alleles, genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, dominant, recessive, and the different inheritance patterns (e.g., autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive).
2. DNA Replication and Transcription: A concept map for these processes could illustrate the steps involved in DNA replication, including the role of enzymes like DNA polymerase and helicase, and the subsequent transcription process, highlighting the role of RNA polymerase and the production of mRNA.
3. Genetic Disorders: A concept map for genetic disorders could depict the different types of mutations (e.g., point mutations, insertions, deletions), their impact on protein function, and the resulting phenotypes associated with various genetic disorders.
4. Genetic Engineering: A concept map for genetic engineering could showcase the various techniques involved, including CRISPR-Cas9, restriction enzymes, and gene cloning, and their applications in areas like gene therapy and agriculture.
FAQs on Concept Mapping in Genetics
Q: What are the essential elements of a concept map for genetics?
A: A concept map for genetics typically includes:
- Concepts: These are the main ideas or terms related to genetics, such as genes, DNA, chromosomes, and inheritance.
- Connections: These are lines or arrows that connect concepts and indicate the relationships between them.
- Linking words: These words describe the nature of the relationship between concepts, such as "causes," "influences," "is a part of," or "is an example of."
Q: How can I create an effective concept map for genetics?
A: To create an effective concept map for genetics, consider these steps:
- Identify the central concept: Determine the main idea or topic you want to explore.
- Brainstorm related concepts: List down all the relevant concepts related to the central concept.
- Group similar concepts: Organize the concepts into clusters based on their similarities or relationships.
- Connect concepts with lines and linking words: Draw lines between the concepts and use linking words to describe the relationships.
- Refine and revise: Review your concept map, ensuring it is clear, concise, and accurately reflects the relationships between concepts.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating a concept map?
A: Common mistakes to avoid when creating a concept map include:
- Overcrowding: Too many concepts or connections can make the map difficult to understand.
- Lack of clarity: Using vague or ambiguous terms can confuse the meaning of the map.
- Inconsistent formatting: Maintaining consistent font size, line thickness, and color schemes improves readability.
- Ignoring hierarchy: Failing to establish a clear hierarchical structure can make the map disorganised.
Tips for Effective Concept Mapping in Genetics
- Start with a clear objective: Define the purpose of your concept map before you begin.
- Use specific and concise language: Avoid using jargon or overly complex terms.
- Focus on key relationships: Highlight the most important connections between concepts.
- Use visual aids: Incorporate images, diagrams, or symbols to enhance understanding.
- Review and refine: Continuously evaluate your concept map and make adjustments as needed.
Conclusion
Concept mapping is a powerful tool for understanding and navigating the complexities of genetics. By visually representing the relationships between concepts, it facilitates comprehension, promotes critical thinking, and enhances communication. Whether used for personal study, collaborative learning, or research, concept mapping empowers individuals to explore the intricate world of genetics with greater clarity and insight.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Intricacies of Genetics: A Comprehensive Guide to Concept Mapping. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!