Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Physical Map of the United States and Canada
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Physical Map of the United States and Canada
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Physical Map of the United States and Canada. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Physical Map of the United States and Canada
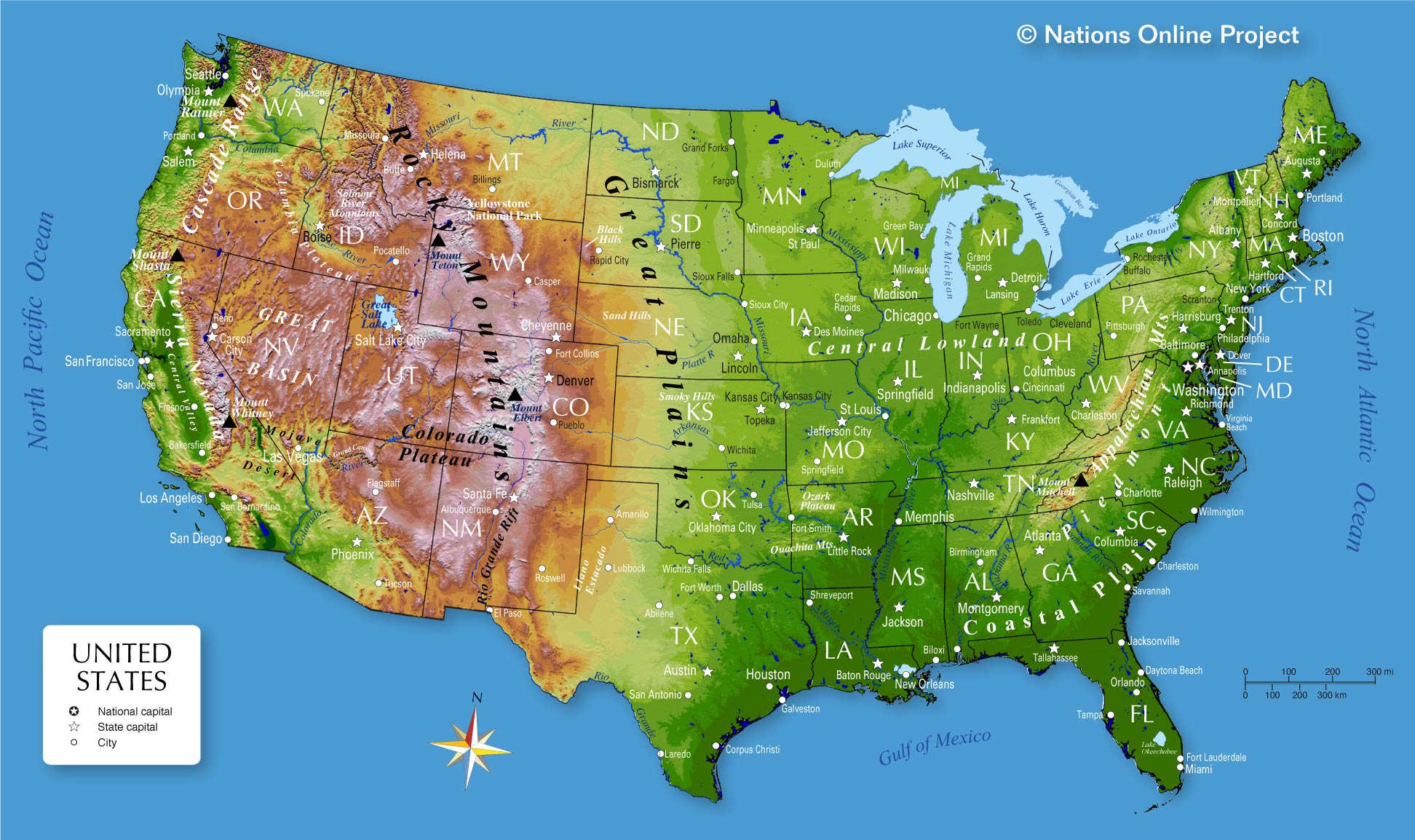
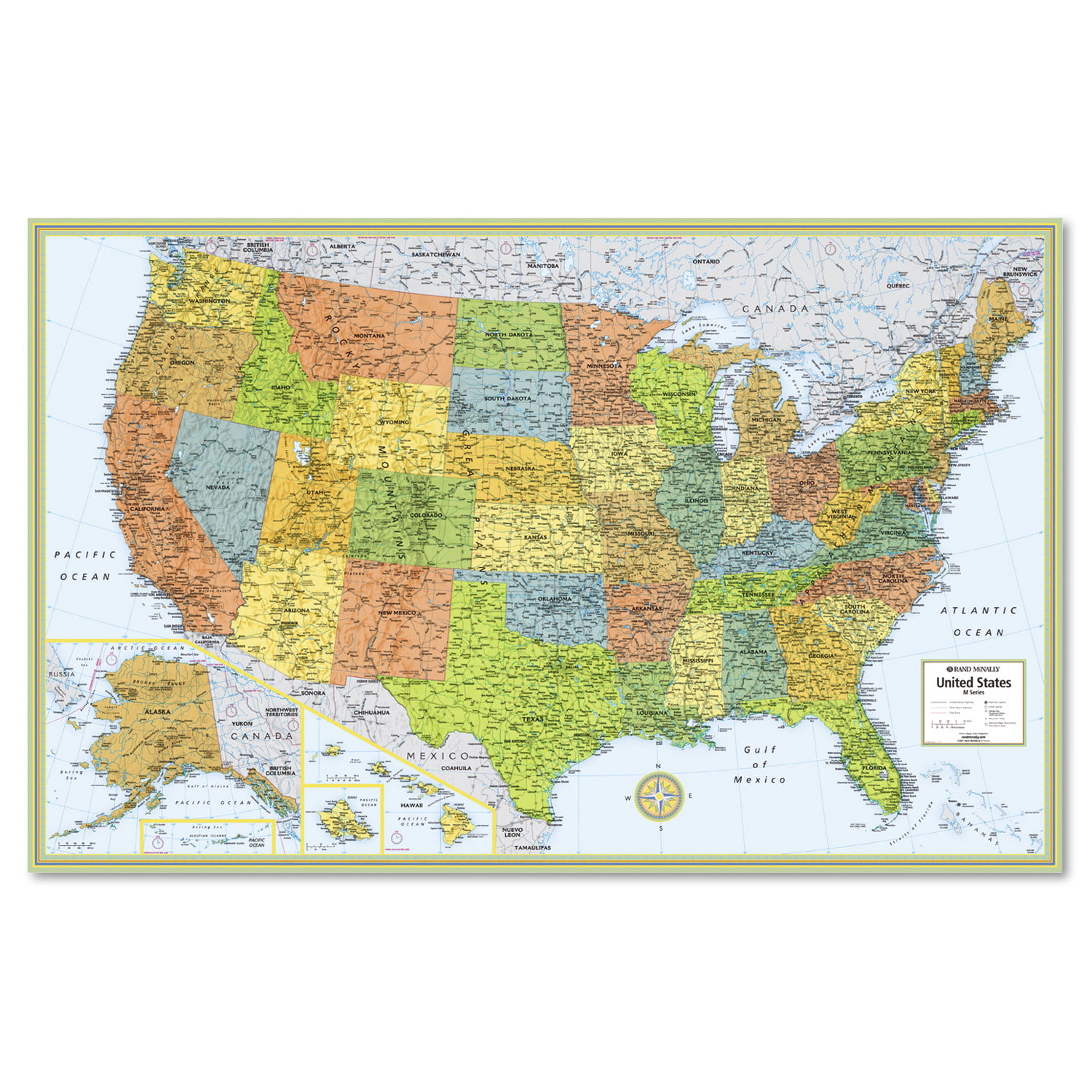
The physical map of the United States and Canada is a visual representation of the intricate tapestry of landforms that define these two North American nations. It goes beyond mere geographical outlines, offering a detailed glimpse into the diverse topography, elevation, and water bodies that shape the landscape and influence the lives of its inhabitants.
Understanding the Terrain: A Visual Journey Through Mountains, Plains, and Coastlines
The physical map reveals the dramatic variations in elevation that characterize the North American continent. Towering mountain ranges, vast plains, and sprawling plateaus are depicted in varying shades of color, providing a clear understanding of the land’s verticality.
-
The Rocky Mountains: This imposing mountain range, stretching from the Canadian Rockies to the southern tip of New Mexico, is a defining feature of the western United States and Canada. Its snow-capped peaks, deep canyons, and rugged terrain showcase the power of tectonic forces.
-
The Appalachian Mountains: While less imposing than the Rockies, the Appalachian Mountains play a significant role in shaping the eastern United States. Their rolling hills, fertile valleys, and forested slopes offer a different kind of beauty, influencing the region’s culture and economy.
-
The Great Plains: Extending from the foothills of the Rockies to the Mississippi River, the Great Plains are a vast expanse of flat, fertile land. This region, historically known for its agriculture, is a testament to the power of erosion and deposition.
-
The Canadian Shield: This ancient geological formation, encompassing a significant portion of central and eastern Canada, is characterized by its rocky, exposed terrain and numerous lakes. Its geology has played a crucial role in shaping the country’s mineral resources and ecosystems.
Waterways: The Lifeblood of the Continent
The physical map highlights the intricate network of rivers, lakes, and coastlines that crisscross the United States and Canada. These waterways are not just geographical features; they are vital arteries that sustain life, facilitate trade, and shape the cultural fabric of these nations.
-
The Mississippi River: The mighty Mississippi River, flowing from its headwaters in Minnesota to the Gulf of Mexico, is a defining feature of the United States. It serves as a transportation route, a source of water, and a habitat for diverse wildlife.
-
The Great Lakes: The five Great Lakes – Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario – are a unique geographical phenomenon, holding a significant portion of the world’s freshwater. They provide recreational opportunities, support a thriving fishing industry, and play a crucial role in the region’s economy.
-
The Pacific and Atlantic Coastlines: The vast Pacific and Atlantic coastlines offer stunning landscapes, diverse ecosystems, and access to important shipping routes. From the rocky shores of Maine to the sandy beaches of California, these coastlines are a source of economic activity and cultural identity.
Beyond Geography: The Importance of the Physical Map
The physical map of the United States and Canada is more than just a static visual representation. It serves as a powerful tool for understanding the intricate relationship between geography and human activity. By revealing the terrain, elevation, and waterways, the map provides insights into:
-
Climate and Weather: The physical map reveals the impact of mountains on rainfall patterns, the influence of coastlines on temperature moderation, and the role of elevation in determining climate zones.
-
Resource Distribution: The map highlights the location of natural resources, including forests, minerals, and water, offering valuable information for economic development and resource management.
-
Infrastructure and Transportation: The physical map helps understand the challenges and opportunities presented by the terrain for transportation infrastructure development, influencing the location of cities, roads, and railways.
-
Human Settlements and Urban Planning: The map reveals the impact of terrain on population distribution, urban development, and the design of infrastructure.
-
Environmental Conservation and Management: The map provides a visual understanding of ecosystems, watersheds, and sensitive areas, guiding conservation efforts and sustainable development practices.
FAQs: Demystifying the Physical Map of the United States and Canada
1. What is the difference between a physical map and a political map?
A physical map focuses on the terrain, elevation, and water bodies of a region, while a political map depicts boundaries, cities, and political divisions.
2. What are the key geographical features of the United States and Canada?
The key geographical features include the Rocky Mountains, the Appalachian Mountains, the Great Plains, the Canadian Shield, the Mississippi River, the Great Lakes, and the Pacific and Atlantic Coastlines.
3. How does the physical map help us understand the climate of the United States and Canada?
The map reveals the influence of mountains on rainfall patterns, the role of coastlines in temperature moderation, and the impact of elevation on climate zones.
4. What are the benefits of studying a physical map?
Studying a physical map helps us understand the relationship between geography and human activity, resource distribution, infrastructure development, and environmental conservation.
5. How can the physical map be used in everyday life?
The physical map can be used for planning trips, understanding weather patterns, researching natural resources, and making informed decisions about environmental issues.
Tips for Using and Interpreting the Physical Map
- Pay attention to the color variations: Different shades of color represent varying elevations, helping visualize the terrain.
- Identify key geographical features: Locate major mountain ranges, rivers, lakes, and coastlines to understand the overall landscape.
- Relate the map to specific locations: Use the map to understand the geographical context of cities, towns, and natural landmarks.
- Consider the scale: The scale of the map influences the level of detail provided. Larger scale maps offer greater precision.
- Use the map in conjunction with other resources: Combine the physical map with political maps, climate maps, and other data sources to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the region.
Conclusion: A Visual Window into the North American Landscape
The physical map of the United States and Canada is an invaluable tool for understanding the complex and diverse landscapes of these two nations. It serves as a visual guide to the terrain, elevation, and waterways that shape the environment, influence human activity, and define the cultural identity of these North American giants. By studying the physical map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the natural world and the intricate relationship between geography and human life.

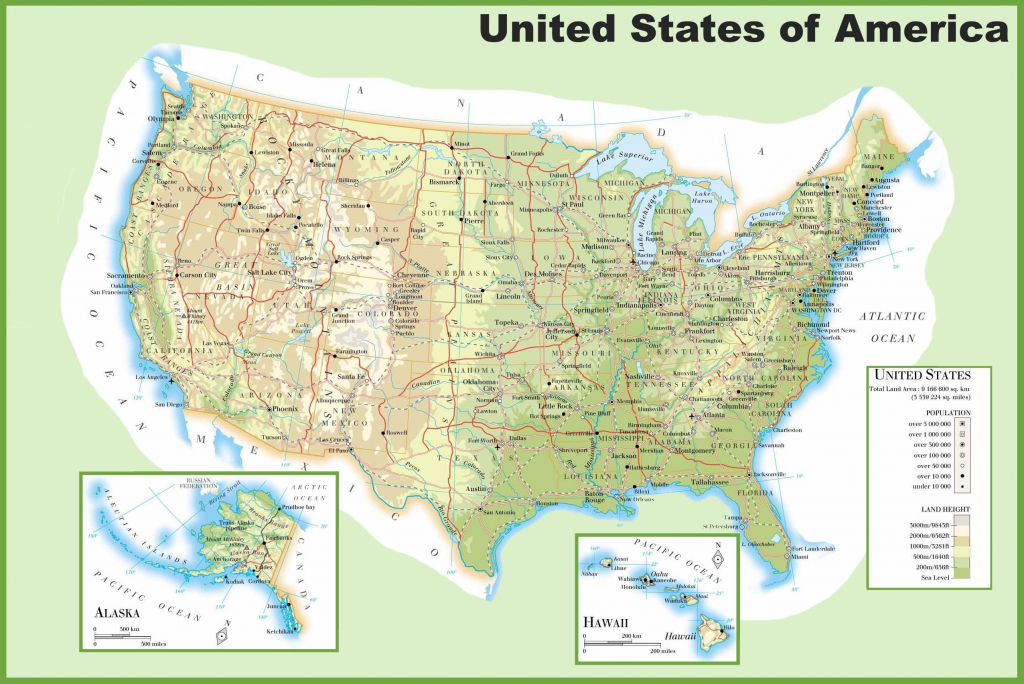
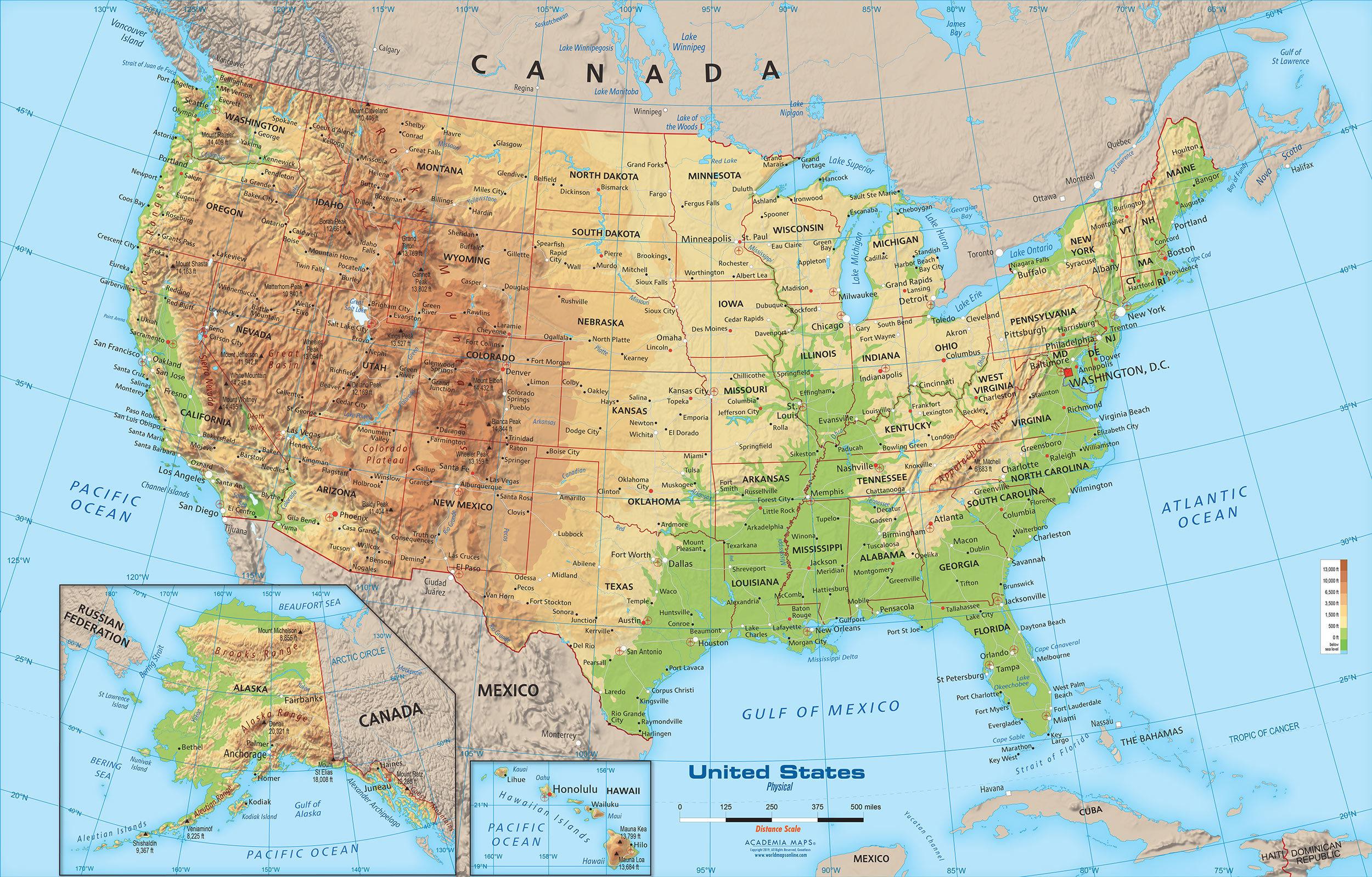

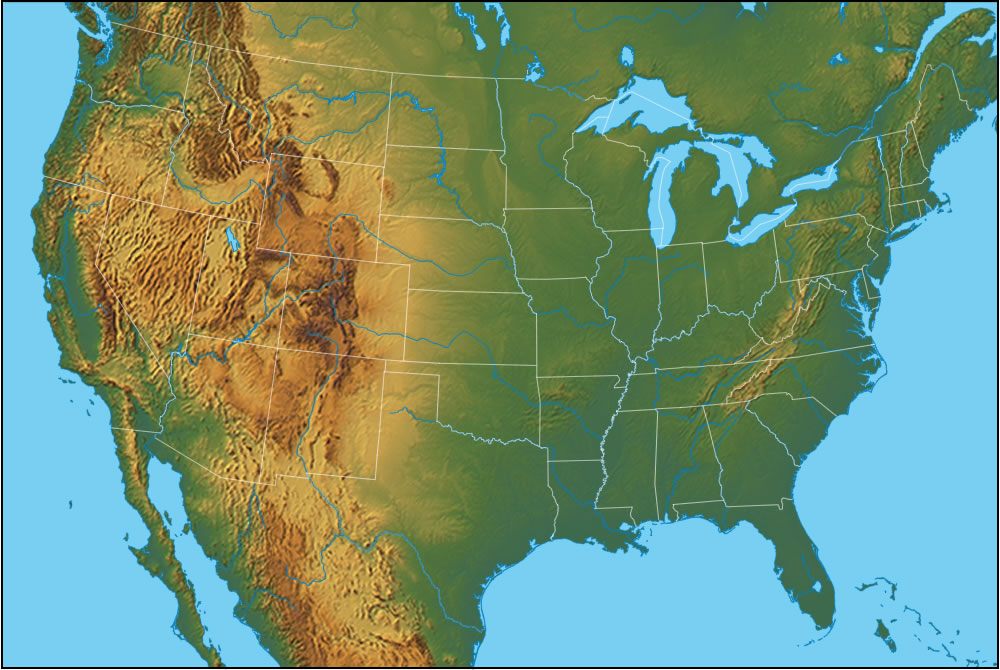


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Physical Map of the United States and Canada. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!